(Press-News.org) For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 11 a.m. ET Oct. 4, 2024
Research points to potential new treatment for aggressive prostate cancer subtype
In two separate papers, U-M researchers describe how a gene alteration drives prostate cancer and a potential degrader that stops it
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — When researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center first identified a new subtype of aggressive prostate cancer, they knew they needed to understand how this genetic alteration was driving cancer and how to target it with treatment.
In two new papers, both published in Cell Reports Medicine, they do both, describing the mechanisms of how alterations in the CDK12 gene drive prostate cancer development and reporting on a promising degrader that targets CDK12 and a related gene to destroy tumors.
Researchers previously found loss of the CDK12 gene in about 7% of patients with metastatic prostate cancer, suggesting this alteration may be linked to a more-aggressive form of the disease. This was discovered from DNA and RNA sequencing from patient tumor samples. CDK12 also plays a role in some ovarian cancers.
To understand how CDK12 loss impacts cells on a molecular level, researchers created a mouse model to try to parallel the genetic alterations they were seeing in human prostate cancers.
“What was quite surprising was when we created CDK12 loss in a mouse prostate, this caused precursor lesions to form in the mouse prostate. Then, when we added loss of the p53 oncogene, the mice developed bona fide invasive prostate cancer,” said senior author Arul M. Chinnaiyan, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology and S.P. Hicks Professor of Pathology at Michigan Medicine. “It will be an addition to the field to have a genetically engineered mouse model that parallels what we see in human prostate cancer.”
With the mouse model, researchers then discovered the of mechanism of how CDK12 loss induces DNA damage. The loss of this gene activates other known cancer driver genes, causing them to be overexpressed at a high level while also causing DNA to be replicated very rapidly. The collision of these two processes leads to DNA damage.
“These back-to-back studies taken together are quite impressive. We created an animal model and then deciphered the mechanisms of how CDK12 loss actually drives prostate cancer,” Chinnaiyan said.
The team also found that a partner gene, CDK13, is important in targeting the alteration therapeutically. They developed a potential therapy designed to degrade CDK12 and CDK13. Testing in cell lines and mice showed the degrader specifically binds to CDK12 and CDK13 and stops the growth of cancer cells over normal cells. The degrader can be absorbed orally and would not need to be delivered intravenously. This is notable as most protein degraders are too large to be absorbed orally, which has limited their potential in drug development.
Further, they found that knocking down CDK12/13 activated the AKT pathway, which plays a role in cancer development. Combining the CDK12/13 degrader with existing therapies targeting AKT resulted in a synergistic effect in destroying cancer cells. This suggests the potential to combine a CDK12/13 degrader with other approved therapies.
“It’s well known that single therapies for cancer treatment have been challenging. Oftentimes patients develop resistance. If we can find the right combination, we could prevent resistance mechanisms from occurring. That’s one of the benefits of finding an FDA-approved agent to combine with CDK12/13 degraders,” Chinnaiyan said. “This study also highlights an international collaboration with Ke Ding, Ph.D., a medicinal chemist at the Shanghai Institute of Chemistry, in the development of orally bioavailable CDK12/13 degraders.”
Researchers plan to further develop the CDK12/13 degrader with a goal of moving it to a clinical trial.
Note for patients: This work is preclinical and more research is needed. A CDK12/13 degrader is not currently available in clinical trials. For information on current clinical trials or questions about prostate cancer treatment, call the Michigan Medicine Cancer AnswerLine at 800-865-1125 or visit www.rogelcancercenter.org/clinical-trials.
Additional authors: Jean Ching-Yi Tien, Jie Luo, Yu Chang, Yuping Zhang, Yunhui Cheng, Xiaoju Wang, Jianzhang Yang, Rahul Mannan, Somnath Mahapatra, Palak Shah, Xiao-Ming Wang, Abigail J. Todd, Sanjana Eyunni, Caleb Cheng, Ryan J. Rebernick, Lanbo Xiao, Yi Bao, James Neiswender, Rachel Brough, Stephen J. Pettitt, Xuhong Cao, Stephanie J. Miner, Licheng Zhou, Yi-Mi Wu, Estefania Labanca, Yuzhuo Wang, Abhijit Parolia, Marcin Cieslik, Dan R. Robinson, Zhen Wang, Felix Y. Feng, Jonathan Chou, Christopher J. Lord, Gabriel Cruz, Josh N. Vo, Brian Magnuson, Somnath Mahapatra, Hanbyul Cho, Saravana Mohan Dhanasekaran, Cynthia Wang, Kaijie Zhou, Yang Zhou, Pujuan Zhang, Weixue Huang, Rudana Hamadeh, Fengyun Su, Rui Wang, Stephanie J. Miner, Rohit Mehra, Ke Ding
Funding for this work is from Prostate Cancer Foundation, National Cancer Institute (grants P50-CA186786, U2C-CA271854, R35-CA231996), National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cancer Research UK, Department of Defense, Ministry of Science and Technology of China, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, A. Alfred Taubman Medical Research Institute, American Cancer Society
Disclosure: The University of Michigan and the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry have filed patents on the CDK12/13 degraders and inhibitors mentioned in these papers. Chinnaiyan, Ding, X. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Chang and Tien have been named as co-inventors on these patents.
Papers cited: “Development of an orally bioavailable CDK12/13 degrader and induction of synthetic lethality with AKT pathway inhibition,” Cell Reports Medicine. DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101752
“CDK loss drives prostate cancer progression, transcription-replication conflicts, and synthetic lethality with paralog CDK13,” Cell Reports Medicine. DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101758
Resources:
University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center, www.rogelcancercenter.org
Michigan Medicine Cancer AnswerLine, 800-865-1125
# # #
END
Research points to potential new treatment for aggressive prostate cancer subtype
In two separate papers, U-M researchers describe how a gene alteration drives prostate cancer and a potential degrader that stops it
2024-10-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Studies examine growing US mental health safety net
2024-10-04
A decade after the establishment of the certified community behavioral health clinic (CCBHC) model, more than 60 percent of the US population has access to such facilities and the mental health and substance use disorder treatment services they provide, according to a new study led by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health. Moreover, these clinics are expanding the availability of crisis mental health services, including mobile crisis response teams and stabilization.
“Certified community behavioral health clinics have become a cornerstone of bipartisan strategies to increase access to and improve the ...
Social risk factor domains and preventive care services in US adults
2024-10-04
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of U.S. adults suggests that social risk factor domains were associated with decreased odds of receiving preventive services; this association was cumulative. There is a need to address social risk factors to optimize receipt of recommended preventive services.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Leonard E. Egede, MD, MS, email legede@buffalo.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
Online medication abortion direct-to-patient fulfillment before and after the Dobbs v Jackson decision
2024-10-04
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that online pharmacies play an increasingly critical role in direct-to-patient medication abortion provision, especially with virtual-only platforms. These findings suggest that barriers to accessing online pharmacies for abortion care should be removed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Caila Brander, MSc, email cbrander@ibisreproductivehealth.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34675)
Editor’s ...
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian adolescents likelier than white adolescents to be tested for drugs, alcohol at pediatric trauma centers
2024-10-04
Injured adolescents from marginalized groups treated at pediatric trauma centers are more likely to be tested for drugs and alcohol than white adolescents, even when accounting for injury severity, a study led by researchers at UCLA and Children’s Hospital Los Angeles suggests.
The findings, to be published October 4 in the peer-reviewed JAMA Network Open, suggest that clinician biases could influence the selection of adolescents for biochemical substance use screening at pediatric trauma centers, said Dr. Jordan Rook, a general surgery resident at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and the study’s lead author. ...
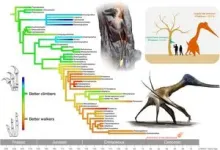
Pterosaurs needed feet on the ground to become giants
2024-10-04
The evolutionary adaptations that allowed ancient pterosaurs to grow to enormous sizes have been pinpointed for the first time by palaeontologists in the Centre for Palaeobiology and Biosphere Evolution at the University of Leicester.
The discovery revealed a surprising twist – the ability to walk efficiently on the ground played a crucial role in determining how large the biggest flying animals could grow, with some reaching wingspans of up to 10 metres.
In a new study published today (4 October) in Current ...
Scientists uncover auditory “sixth sense” in geckos
2024-10-04
University of Maryland biologists identified a hidden sensory talent in geckos that’s shaking up what we thought we knew about animal hearing.
In a new study published in Current Biology on October 4, 2024, the researchers revealed that geckos use the saccule—a part of their inner ear traditionally associated with maintaining balance and body positioning—to detect low-frequency vibrations. According to the researchers, this special “sixth sense” also plays a complementary role to the geckos’ normal hearing and the way they sense ...
Almost half of persons who inject drugs (PWID) with endocarditis will die within five years; women are disproportionately affected
2024-10-04
LONDON, Ont. and REGINA, Sask. – People who inject drugs are dying at an alarming rate from endocarditis, a serious but treatable heart-valve infection.
But their odds of survival improve dramatically, even five years after their first admission to hospital, if they’re treated not just for heart infection but are also provided with addiction support while in hospital, a Canadian study shows.
The study also highlights that women who inject drugs are particularly vulnerable to endocarditis and are affected in disproportionately high numbers.
“Endocarditis is potentially lethal and always costly,” says Dr. Michael Silverman, an infectious ...
Experimental blood test improves early detection of pancreatic cancer
2024-10-04
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Sept. 30, 2024) — An experimental blood test detects early-stage pancreatic cancer more effectively than other available tests, reports a new study published in Cancer Letters.
The findings pave the way for further evaluation of the test in a clinical setting, an important step toward approval as a potential diagnostic method for pancreatic cancer.
“Catching pancreatic cancer early dramatically improves survival, but our current tools for doing so are limited,” said the study’s co-corresponding author Brian Haab, Ph.D., a professor at Van Andel Institute. “Our results reveal that our combination ...
Groundbreaking wastewater treatment research led by Oxford Brookes targets global challenge of toxic ‘forever chemicals’
2024-10-04
Researchers at Oxford Brookes University have pioneered a groundbreaking method to tackle one of the world’s most persistent environmental threats—toxic chemicals in global water supplies.
They have developed a new machine called a hydrodynamic reactor that uses bubbles which form and collapse due to changes in pressure, a process called cavitation. The reactor removes toxic per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), also known as “forever chemicals” from water.
PFAS chemicals were invented in the 1930s and used in convenience products ...
Jefferson Health awarded $2.4 million in PCORI funding
2024-10-04
PHILADELPHIA, Oct. 3, 2024 — Jefferson Health has been awarded $2.4 million by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to implement evidence-based patient education and coaching programs for weight loss across Jefferson Primary Care.
U.S. adult obesity rates have risen to over 40% in the past two decades, increasing risks of diabetes, heart disease and premature death. Led by Baligh Yehia, M.D., MPP, MSHP, President of Jefferson Health, this project will implement sustainable health education programs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Research points to potential new treatment for aggressive prostate cancer subtypeIn two separate papers, U-M researchers describe how a gene alteration drives prostate cancer and a potential degrader that stops it