(Press-News.org) Australians under 50 are experiencing stagnating life expectancy while older cohorts, especially men, are living longer, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU).
The study examined longevity trends and patterns in six English-speaking countries (Australia, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States) and compared them with other high-income countries.
The results show striking similarities between English-speaking countries in terms of adverse health outcomes for young and middle-aged adults under fifty.
Lead author and ANU demographer, Dr Sergey Timonin, said the study reveals that Australia is performing worse in life expectancy for younger cohorts when compared to non-Anglophone high-income countries but is ahead of the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada.
“For the under fifties in Australia, we found that life expectancy is behind the majority of high-income countries, which was quite surprising. We already knew that the US and UK suffer from this problem, but we didn’t expect to see Australia (as well as Canada and New Zealand) in this group,” Dr Timonin said.
“However, compared to English-speaking countries, Australians still enjoy a higher life expectancy, including at younger ages. It also has one of the world’s highest life expectancies at older ages.”
The research challenges the findings of a previous study in The Economist that found Australians ‘are healthier than their peers’.
Stagnating life expectancy trends were reported in some high-income countries before the COVID-19 pandemic, but according to the researchers, there’s been a lack of comparative studies that provide a broader and more detailed perspective on the phenomenon.
“In the pre-pandemic period in 2010-19, the increase in life expectancy slowed in all Anglophone countries, except Ireland, mainly due to stagnating or rising mortality at young adults and middle-aged adults under fifty,” Dr Timonin said.
“Each of the English-speaking countries has experienced a marked mortality disadvantage for cohorts born since the early 1970s relative to the average of the other high-income countries.”
The study found that life expectancy in younger cohorts in Australia was negatively impacted by suicide, drug and alcohol-related behaviours, and traffic accidents.
“External causes of death and substance use disorders were found to be the largest contributors to the observed disadvantage at these ages,” Dr Timonin said.
“Recreational drug use and risky behaviours are mostly related to mentally driven disorders.”
The researchers believe that although future gains in life expectancy in wealthy societies like Australia will increasingly depend on reducing mortality at older ages, adverse health trends among younger people are a cause for concern.
“This emerging and avoidable threat to health equity in English-speaking countries should be the focus of further research and policy action,” Dr Timonin said.
“There is scope for English-speaking countries to improve the health of their younger populations and to halt the widening gap in mortality compared with other high-income countries.”
The research is published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
END
Aussies above 50 are living longer, while younger people are suffering
2024-10-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
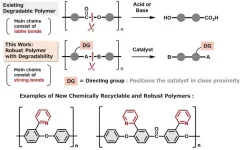
New polymer design breaks the tradeoff between toughness and recyclability
2024-10-07
Osaka, Japan – Plastics underpin much of modern life—areas like medicine, technology, and food safety would be unrecognizable without plastics and their useful properties. However, the toughness of plastics, which is often desirable, also makes them a dangerous pollutant and difficult to recycle. The solution to this serious and growing problem is making plastics easier to recycle.
In a study recently published in Chemical Science, researchers at Osaka University have found a way to make tough, high-performance polymers, the main component of plastics, that can be broken down easily and precisely into their component parts and ...
Tax, smoke-free legislation, and anti-smoking campaigns linked to smoking reduction
2024-10-07
Tobacco use remains a significant global health challenge, despite extensive control measures at both national and international levels. Smoking continues to be a leading cause of premature death, with exposure to tobacco—whether through active smoking or secondhand smoke—significantly increasing the risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory conditions, and diabetes. These NCDs account for nearly 75% of annual global deaths.
A wide range of strategies has been developed to combat smoking and promote public health, including taxation, mass media campaigns, health warnings on packaging, marketing ...
Targeting failure with new polymer technology to enhance sustainability
2024-10-07
Targeting failure with new polymer technology to enhance sustainability
Sustainability is a complex problem with many different players and influenced by policies, society, and technical perspective.
We are reminded every day in the media of the unnecessary amount of waste that we are generating with pervasive pictures of plastic garbage patches floating in the oceans or stranded on our beaches.
Scientists within ASU’s School of Molecular Sciences (SMS) and the Biodesign Institute’s Center ...
Stigma has a profound impact on health outcomes must be addressed
2024-10-07
A new article published in Nature Reviews Disease Primers underscores the profound role that stigma can play in health care -- and how addressing stigma-related barriers can significantly improve health outcomes for individuals and communities around the world.
“Stigma has harmful effects on health, equity and justice,” says lead author Carmen Logie, a professor at the University of Toronto’s Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work (FIFSW). "And while we need more rigorous evaluation of interventions ...
Has the affordable care act’s dependent coverage expansion benefited young adults diagnosed with cancer?
2024-10-07
The federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed in 2010 includes a Dependent Coverage Expansion (DCE) provision that permits dependents to remain on their parents’ health insurance plans from age 19 to 25 years, the age group that has historically had the highest uninsured rate in the United States. A recent analysis reveals that during the ACA’s first decade, survival rates of DCE-eligible young adults with cancer have improved. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
To examine whether young adults with cancer diagnoses have ...
A new study reveals a key mechanism driving atherosclerosis in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
2024-10-07
A team of researchers from the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC), the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas Margarita Salas (CIB-CSIC), and the Instituto de Ciencias de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM-CSIC) has made a significant breakthrough in understanding the underlying causes of cardiovascular disease in patients with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS), an ultra-rare genetic disorder that accelerates the aging process. The most serious consequence of HGPS is the early onset of cardiovascular disease, leading to premature death at an average age of 14.5 years.
The study was led by Dr. Vicente Andrés, ...
HPV vaccination switch to 1-dose gender-neutral approach
2024-10-07
Canadian vaccination programs could switch to a 1-dose gender-neutral human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination approach and eliminate cervical cancer, suggests new modelling in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240787.
“Our results have important policy implications in Canada, and in other similar high-income countries evaluating whether to switch to 1-dose HPV vaccination,” writes Dr. Marc Brisson, a full professor at Laval University, Québec, and director of the Mathematical Modeling and Health Economics of Infectious Diseases Lab at the ...
Scurvy: Not just an 18th-century sailors’ disease
2024-10-07
Scurvy, or vitamin C deficiency, is not just an 18th-century seafarers’ disease, as a case study of a 65-year-old woman with mobility issues and social isolation shows. In an article published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240769, clinicians describe how scurvy should be considered in patients with abnormal bleeding and nonspecific symptoms.
The patient visited the emergency department at a downtown Toronto hospital for leg pain and weakness, skin lesions, and discoloration. She also had several chronic health ...
Scientists discover a secret to regulating our body clock, offering new approach to end jet lag
2024-10-07
Singapore, 7 October 2024—Scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School and the University of California, Santa Cruz, have discovered the secret to regulating our internal clock. They identified that this regulator sits right at the tail end of Casein Kinase 1 delta (CK1δ), a protein which acts as a pace setter for our internal biological clock or the natural 24-hour cycles that control sleep-wake patterns and other daily functions, known as circadian rhythm.
Published in the journal PNAS, their findings could ...
Impact of pollutants on pollinators, and how neural circuits adapt to temperature changes
2024-10-04
The Kavli Foundation and the U.S. National Science Foundation are collaborating to accelerate research in the emerging field of neurobiology in changing ecosystems, stemming from the foundation’s efforts in this area first announced in 2023. A joint Kavli-NSF grantmaking program was launched in December of 2023.
Building on early success of this program, Kavli and NSF announce its continuation with a second call for proposals, open through February 10, 2025, for projects tackling hard problems in this understudied field.
Research ...