(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 07 OCTOBER 2024 AT 16:00 (LONDON TIME), 07 OCTOBER 2024 AT 11:00 (US EASTERN TIME).
Global warming could increase the threat posed to whale sharks from large ships, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change.
Researchers from the University of Southampton and Marine Biological Association (MBA) predict that increased ocean temperatures will see this already endangered species driven into new habitats crossed by busy shipping lanes.
The study predicts that the co-occurrence of whale sharks and large ships could be 15,000 times higher by the end of the century compared to the present day.
Lead author Dr Freya Womersley, University of Southampton and MBA Postdoctoral Research Scientist said: “These shifts in the whale sharks’ habitat were most extreme under high emission scenarios. A global reshuffling could lead to core habitat losses in some areas as well as increased co-occurrence with shipping traffic as oceans warm and other variables change.”
Whale sharks, the world’s largest fish, are highly mobile and responsive to changes in temperature. Recent evidence suggests they are also particularly vulnerable to ship strikes - where large marine animals are struck and injured, often fatally, by large vessels in the global fleet.
Researchers used whale shark satellite-tracking data coupled with global climate models to project the distribution of whale sharks under three different future climate scenarios.
The models project core habitat losses of over 50% in some national waters by 2100 under high emissions (where we continue to rely heavily on fossil fuels), with the greatest potential losses in Asia. Under a sustainable development scenario (in line with the target of no more than 2°C of global warming), some areas showed a gain in core habitat, notably in Europe.
“The shifts we predict are likely to be less extreme if we are able to slow warming and mitigate climate change, suggesting that even complex, multi-factor impacts of climate change can be somewhat alleviated by our actions,” says Professor David Sims, co-author and Senior Research Fellow at the University of Southampton and MBA.
The team paired the distribution maps with information on shipping traffic density to determine if these habitat shifts would see whale sharks move into more heavily trafficked areas in future, potentially increasing the likelihood of ship strikes.
They found that some newly suitable habitats overlapped with busy shipping routes. This was the case in the US part of the North Pacific Ocean, the Japanese part of the Eastern China Seas, and the Sierra Leonian part of the North Atlantic Ocean, among many other sites globally.
Some areas, such as the Mexican part of the Gulf of Mexico, saw reductions in co-occurrence, where core habitats shifted into more coastal waters, away from the busy shipping routes in the centre of the Gulf.
Professor Sims says: “Overall ship co-occurrence increased under all future climate scenarios, even if shipping remained at current levels, rather than its anticipated expansion of up to 1,200 per cent by 2050.”
Womersley added: “We show that climate change has the potential to indirectly impact highly mobile marine species through interacting pressures of humans and the environment. This highlights the importance of factoring climate change into discussions around endangered species management.”
Climate-driven global redistribution of an ocean giant predicts increased threat from shipping is published in Nature Climate Change and is available online.
The research was supported by the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and the European Research Council (ERC) under the EU Horizon 2020 Programme.
Ends
Contact
Steve Williams, Media Manager, University of Southampton, press@soton.ac.uk or 023 8059 3212.
Maya Plass, Head of Communications, The Marine Biological Association, comms@mba.ac.uk or +44 (0)1752 426490.
Notes for editors
Climate-driven global redistribution of an ocean giant predicts increased threat from shipping is published in Nature Climate Change. An advanced copy of the paper is available upon request.
For Interviews with Freya Womersley please contact Steve Williams, Media Manager, University of Southampton press@soton.ac.uk or 023 8059 3212.
Images are available here: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1NOKWdPgbCOMj9_rnDMbUideOS9w_-28C For credits see file names.
Additional information
The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world’s challenges. We are among the top 100 institutions globally (QS World University Rankings 2025). Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 22,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni. www.southampton.ac.uk
www.southampton.ac.uk/news/contact-press-team.page
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/UoSMedia
The Marine Biological Association (MBA) is a learned society of scientists and members in 35 countries, across 5 continents. Its in-depth scientific research into the interconnected marine environment is carried out from its prestigious laboratory HQ in Plymouth, UK.
It has royal charter status for its world-leading role in marine biology research. Since 1884, the MBA has worked as a voice for the ocean and in the interests of the global marine biological community.
The MBA’s advanced knowledge has contributed to the work of several Nobel Laureates and over 170 Fellows of the Royal Society.
Discover more: www.mba.ac.uk Twitter: @thembauk
Marine research in the city of Plymouth
Plymouth – Britain’s Ocean City – has been at the forefront of policy relevant marine research for more than a century. It is home to three world-leading scientific institutions (the University of Plymouth, the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, and Plymouth Marine Laboratory) comprising the UK’s largest cluster of marine researchers, recognised globally in terms of publications, impact and influence. Collaborations with colleagues in 98 countries over the last five years place Plymouth at the heart of international scientific and societal advances in fields including climate change, marine pollution, and ecosystem monitoring and prediction.
END
Whale shark shipping collisions may increase as oceans warm
2024-10-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
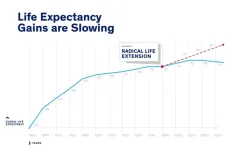
Despite medical advances, life expectancy gains are slowing
2024-10-07
We’ve seen dramatic increases in life expectancy over the 19th and 20th centuries, thanks to healthier diets, medical advances and many other quality-of-life improvements.
But after nearly doubling over the course of the 20th century, the rate of increase has slowed considerably in the last three decades, according to a new study led by the University of Illinois Chicago.
Despite frequent breakthroughs in medicine and public health, life expectancy at birth in the world’s longest-living populations has increased only an ...
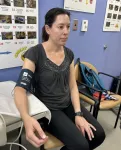
Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds commonly used arm positions can substantially overestimate blood pressure readings
2024-10-07
A study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers concludes that commonly used ways of positioning the patient’s arm during blood pressure (BP) screenings can substantially overestimate test results and may lead to a misdiagnosis of hypertension.
In a report on the study, which will be published Oct. 7 in JAMA Internal Medicine, investigators examined the effects of three different arm positions: an arm supported on a desk, arm supported on a lap, and an unsupported arm hanging at the patient’s side. ...
Arm position and blood pressure readings
2024-10-07
About The Study: This crossover randomized clinical trial showed that commonly used arm positions (lap or side) resulted in substantial overestimation of blood pressure readings and may lead to misdiagnosis and overestimation of hypertension.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tammy M. Brady, MD, PhD, email tbrady8@jh.edu
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.5213)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of ...
Longitudinal changes in epigenetic age acceleration across childhood and adolescence
2024-10-07
About The Study: The transition from childhood to adolescence may represent a sensitive developmental period when racism can have long-term deleterious impacts on healthy human development across the life span. Future research should build on the present study and interrogate which social regularities and policies may be perpetuating discrimination against ethnically and racially minoritized adolescents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Juan Del Toro, PhD, email jdeltoro@umn.edu.
To ...
An early blood test can predict survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer, shows USC study
2024-10-07
A blood test, performed when metastatic prostate cancer is first diagnosed, can predict which patients are likely to respond to treatment and survive the longest. It can help providers decide which patients should receive standard treatment versus who might stand to benefit from riskier, more aggressive new drug trials. The research, part of a phase 3 clinical trial funded in part by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health, was just published in JAMA Network Open.
Before it spreads, prostate cancer can be cured with surgery or ...
Scientists discover that special immune cells stop metastatic cancer
2024-10-07
October 7, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Metastatic disease—when cancer spreads from the primary tumor to other parts of the body—is the cause of most cancer deaths. While researchers understand how cancer cells escape the primary site to seed new tumors, it’s not well understood why some of these wayward cancer cells spawn new tumors— sometimes decades later—while others do not.
Now, a research team at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein ...
Cancer biologists discover a new mechanism for an old drug
2024-10-07
Since the 1950s, a chemotherapy drug known as 5-fluorouracil has been used to treat many types of cancer, including blood cancers and cancers of the digestive tract.
Doctors have long believed that this drug works by damaging the building blocks of DNA. However, a new study from MIT has found that in cancers of the colon and other gastrointestinal cancers, it actually kills cells by interfering with RNA synthesis.
The findings could have a significant effect on how doctors treat many cancer patients. Usually, 5-fluorouracil is given in combination with chemotherapy drugs that damage ...
Food deserts, limited access to transportation linked to more complications among preschool children with SCD
2024-10-07
(WASHINGTON – October 7, 2024) - A new study finds that preschool-aged children with sickle cell disease (SCD) who live in food deserts and have limited access to transportation are at greater risk for acute complications and hospitalizations, despite receiving free evidence-based therapy and social support, according to results published today in Blood Advances.
“Despite the level of care received by the families and patients within our clinic, we still have a gap in terms of being able to address the barriers ...
Space oddity: Most distant rotating disc galaxy found
2024-10-07
Researchers have discovered the most distant Milky-Way-like galaxy yet observed. Dubbed REBELS-25, this disc galaxy seems as orderly as present-day galaxies, but we see it as it was when the Universe was only 700 million years old. This is surprising since, according to our current understanding of galaxy formation, such early galaxies are expected to appear more chaotic. The rotation and structure of REBELS-25 were revealed using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), in which the European ...
How a common economic theory could help save endangered frogs
2024-10-07
A common theory that guides financial investment strategies may be a handy tool to protect an endangered Puerto Rican frog. A new study uses modern portfolio theory to identify future “investments” in natural resource management that may help managers decide which actions to take to protect coquí llanero populations in Puerto Rico.
The 17 species of coquí frogs, and their signature high-pitched chirp, are considered unofficial mascots of Puerto Rico. The entire population of coquí llanero frogs, the smallest and possibly most endangered of the island’s coquís, ...