(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan—Maintaining soil health is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Recently, soil volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have emerged as promising indicators for assessing soil health. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of soil VOC profiles as indicators of soil health in soybean fields.
Soil samples were collected from soybean fields in Fukushima Prefecture, which exhibited diverse soil conditions, over the past three years. These samples were analyzed for VOC content in conjunction with data on soil physical properties, soil metabolome, soil ionome, and soil microbiome as well as rhizosphere chemicals and root microbiome to provide a comprehensive soil health assessment. For the first time globally, the analysis revealed that soil VOC levels increased during the soybean flowering period. Furthermore, the soil VOC profiles exhibited a strong correlation with soil-related omics datasets (soil ionome, soil microbiome, soil metabolome, and soil physical properties) but not with the rhizosphere chemicals and root microbiome datasets obtained from soybean-growing fields.
The findings of this study indicate that soil VOC profiles can function as reliable indicators for evaluating soil health in agricultural environments.
###
This work was supported by Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), "Technologies for Smart Bio-industry and Agriculture" (funding agency: Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution) and by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, Moonshot Research and Development Program for Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (funding agency: Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution, JPJ009237).
Original Paper
Title of original paper:
Soil volatilomics uncovers tight linkage between soybean presence and soil omics profiles in agricultural fields
Journal:
Scientific Reports
DOI:
10.1038/s41598-024-70873-x
Correspondence
Professor KUSANO, Miyako
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba / RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science
Dr. ICHIHASHI, Yasunori
Team Leader of the Plant-Microbe Symbiosis Research and Development Team, RIKEN BioResource Research Center
Professor NIHEI, Naoto
Department of Agriculture, Fukushima University
Professor HAMAMOTO, Shoichiro
Research Faculty of Agriculture, Fundamental AgriScience Research, Bioresource and Environmental Engineering, Hokkaido University
Associate Professor KOBAYASHI, Natsuko I.
Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo
Professor SUGIYAMA, Akifumi
Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University
Related Link
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences
END
Soil volatile organic compound profiles as indicators for soil evaluation in soybean fields
2024-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
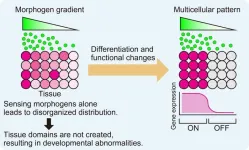
Shedding light on how tissues grow with sharply defined structures
2024-10-08
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, demonstrate how morphogens combined with cell adhesion can generate tissue domains with a sharp boundary in an in vitro model system.
Recent advances that have enabled the growth of tissue cultures into organoids and embryoids have heightened interest as to how tissue growth is controlled during the natural processes of embryo development. It is known that the diffusion of signaling molecules called morphogens directs patterned tissue growth ...
JAMA Network launches JAMA+ AI
2024-10-08
October 8, 2024 (Chicago) — The JAMA Network today announces the launch of JAMA+ AI, an engaging, interactive channel that amplifies the best of the JAMA Network’s content exploring the science of artificial intelligence and digital medicine and its application in health and health care.
JAMA+ AI is a window into the premier scientific content, educational reviews, and commentary on AI and medicine published across JAMA, JAMA Network Open, and the 11 JAMA specialty journals. JAMA+ AI builds on that content with new multimedia materials, including interviews ...
Climate report warns of escalating crisis, urges immediate action as UN summit nears
2024-10-08
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international coalition led by Oregon State University scientists concludes in its annual report published today that the Earth’s worsening vital signs indicate a “critical and unpredictable new phase of the climate crisis” and that “decisive action is needed, and fast.”
The collaboration directed by OSU’s William Ripple and former postdoctoral researcher Christopher Wolf outlines areas where policy change is needed – energy, pollutants, nature, food and economy – in “The 2024 State of the Climate Report: Perilous Times on Planet Earth,” published ...
Scientists issue urgent warning on climate emergency
2024-10-08
A new report published in BioScience warns that the world is facing a climate emergency of unprecedented magnitude. The "2024 State of the Climate Report," by an international team of scientists led by Oregon State University's William Ripple and Christopher Wolf, presents alarming evidence that climate change is worsening at a dangerous pace.
In the report, the authors update 35 annually reported "planetary vital signs," which provide ongoing timeseries of human climate-related activities ...
First successful demonstration of a dual-media NV diamond laser system
2024-10-08
Measuring tiny magnetic fields, such as those generated by brain waves, enables many new novel opportunities for medical diagnostics and treatment. The research team led by Dr. Jan Jeske at Fraunhofer IAF is working on a globally innovative approach to precise magnetic field measurements: Laser Threshold Magnetometry. The researchers have now combined an NV diamond and a laser diode in a resonator, successfully demonstrating the sensor system with two active media for the first time. This outstanding paper has been published in Science Advances and represents a significant progress in the BMBF-funded research project NeuroQ.
Quantum ...
A call to bridge the gap in cancer clinical trial funding
2024-10-08
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina — A growing reliance on industry-sponsored cancer clinical trials in the United States is a reason for concern, say researchers from the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center.
In a Journal of Clinical Oncology editorial, Yara Abdou, MD, and Norman E. Sharpless, MD, responded to a new study by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle that found enrollment in industry-sponsored cancer clinical trials doubled between 2008 and 2022 while federally supported trial enrollment remained flat. From 2018 to 2022, cancer clinical trial enrollment was eight times greater in industry-sponsored studies compared to federal studies.
Abdou and Sharpless called ...
Despite heavy marketing, most Americans reject the new weight-loss drugs
2024-10-08
Washington, D.C. — A new national survey shows that, despite intense marketing, most Americans do not want the new weight-loss injectables, such as Wegovy and Ozempic. The survey was conducted by Morning Consult for the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, a non-profit organization with more than 17,000 physician members, on Sept. 5, 2024, and included 2,205 adults.
Asked to respond to the statement, “If I wanted to lose weight, I would rather take an injectable weight-loss drug, rather than make a diet change,” only 23% agreed or strongly agreed, while 62% disagreed or strongly disagreed and another 14% said they were not ...
Ochsner Children’s Hospital named No.1 hospital for kids in Louisiana for fourth consecutive year
2024-10-08
NEW ORLEANS – For the fourth year running, Ochsner Children’s Hospital upholds its position as the No. 1 hospital for kids in Louisiana according to the 2024-2025 Best Children’s Hospital rankings by U.S. News & World Report. Ochsner Children’s Hospital continues to shine nationally with Top 50 rankings in three specialties: pediatric cardiology and heart surgery, pediatric gastroenterology and gastrointestinal surgery and pediatric orthopedics. This prestigious recognition marks eight consecutive years on the ranking list, a unique achievement ...
Rates of a tick-borne parasitic disease are on the rise
2024-10-08
HERSHEY, Pa. — Rates of babesiosis, a tick-borne parasitic disease, increased an average of 9% per year in the United States between 2015 and 2022 and four in 10 patients were found to be co-infected with another tick-borne illness such as Lyme disease, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and Penn State College of Medicine.
“These findings suggest that clinicians should have a heightened vigilance of co-infection of other tick-borne illness among patients admitted with babesiosis,” said Paddy Ssentongo, infectious disease fellow, Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and lead author of the study. ...
Crohn's & Colitis Foundation survey reveals more than 40% of IBD patients made significant financial sacrifices to pay for their healthcare
2024-10-08
NEW YORK, NY – October 8, 2024 - The Crohn's & Colitis Foundation released findings from its latest healthcare access survey, revealing that more than 40% of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients have made significant financial trade-offs to afford their healthcare. The survey highlighted that among all respondents, 30% reported giving up vacations or major household purchases, 22% increased their credit card debt, and 21% cut back on essential items such as food, clothing, or basic household items.
The survey, published today in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, included responses ...