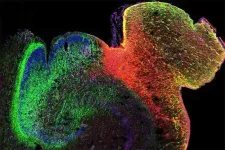
(Press-News.org) A UCLA-led study has provided an unprecedented look at how gene regulation evolves during human brain development, showing how the 3D structure of chromatin — DNA and proteins — plays a critical role. This work offers new insights into how early brain development shapes lifelong mental health.
The study, published in Nature, was led by Dr. Chongyuan Luo at UCLA and Dr. Mercedes Paredes at UC San Francisco, in collaboration with researchers from the Salk Institute, UC San Diego and Seoul National University. It created the first map of DNA modification in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex — two regions of the brain critical to learning, memory and emotional regulation. These areas are also frequently involved in disorders like autism and schizophrenia.
The researchers hope the data resource, which they’ve made publicly available through an online platform, will be a valuable tool scientists can use to connect genetic variants associated with these conditions to the genes, cells and developmental periods that are most sensitive to their effects.
“Neuropsychiatric disorders, even those emerging in adulthood, often stem from genetic factors disrupting early brain development,” said Luo, a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA. “Our map offers a baseline to compare against genetic studies of diseased-affected brains and pinpoint when and where molecular changes occur.”
To produce the map, the research team used a cutting-edge sequencing approach Luo developed and scaled with support from the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center Flow Cytometry Core called single nucleus methyl-seq and chromatin conformation capture, or snm3C-seq.
This technique enables researchers to simultaneously analyze two epigenetic mechanisms that control gene expression on a single-cell basis: chemical changes to DNA known as methylation and chromatin conformation, the 3D structure of how chromosomes are tightly folded to fit into nuclei.
Figuring out how these two regulatory elements act on genes that affect development is a critical step to understanding how errors in this process lead to neuropsychiatric conditions.
“The vast majority of disease-causing variants we’ve identified are located between genes on the chromosome, so it’s challenging to know which genes they regulate,” said Luo, who is also an assistant professor of human genetics at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “By studying how DNA is folded inside of individual cells, we can see where genetic variants connect with certain genes, which can help us pinpoint the cell types and developmental periods most vulnerable to these conditions.”
For example, autism spectrum disorder is commonly diagnosed in children aged 2 and over. However, if researchers can gain a better understanding of the genetic risk of autism and how it impacts development, they can potentially develop intervention strategies to help alleviate the symptoms of autism, like communication challenges, while the brain is developing.
The research team analyzed more than 53,000 brain cells from donors spanning mid-gestation to adulthood, revealing significant changes in gene regulation during critical developmental windows. In capturing such a broad spectrum of developmental phases, the researchers were able to assemble a remarkably comprehensive picture of the massive genetic rewiring that occurs during critical timepoints in human brain development.
One of the most dynamic periods comes around the midpoint of pregnancy. At this time, neural stem cells called radial glia, which have produced billions of neurons during the first and second trimesters, stop producing neurons and begin generating glial cells, which support and protect neurons. At the same time, the newly formed neurons mature, gaining the characteristics they need to fulfill specific functions and forming the synaptic connections that enable them to communicate.
This stage of development has been overlooked in previous studies, the researchers say, due to the limited availability of brain tissue from this period.
“Our study tackles the complex relationship between DNA organization and gene expression in developing human brain at ages typically not interrogated: the third trimester and infancy,” said Paredes, an associate professor of neurology at UCSF. “The connections we’ve identified across different cell types through this work could untangle the current challenges in identifying meaningful genetic risk factors for neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric conditions.”
The findings also have implications for improving stem cell-based models, such as brain organoids, which are used to study brain development and diseases. The new map offers a benchmark for scientists to ensure these models accurately replicate human brain development.
“Growing a healthy human brain is a tremendous feat,” says co-author Dr. Joseph Ecker, professor at the Salk Institute and Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. “Our study establishes an important database that captures key epigenetic changes that occur during brain development, in turn bringing us closer to understanding where and when failures arise in this development that can lead to neurodevelopmental disorders like autism.”
The group’s efforts were supported by the National Institutes of Health’s BRAIN Initiative Cell Atlas Network, or BICAN, which aims to build reference brain cell atlases that will provide a foundational framework for studying brain function and disorders.
Funding was also provided by the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Human Genome Research Institute, the Simons Foundation, the Roberta and Oscar Gregory Endowment in Stroke and Brain Research, the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Shurl and Kay Curci Foundation, National Institute on Drug Abuse and the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Additional authors are: Jingtian Zhou, Yi Zhang, Dong-Sung Lee, Kangcheng Hou, Oier Pastor Alonso, Kevin D Abuhanna, Joseph Galasso, Colin Kern, Chu-Yi Tai, Carlos Garcia Padilla, Mahsa Nafisi, Yi Zhou, Anthony D. Schmitt, Terence Li, Maximilian Haeussler, Brittney Wick, Martin Jinye Zhang, Fangming Xie, Ryan S. Ziffra, Eran A. Mukamel, Eleazar Eskin, Tomasz J. Nowakowski, Jesse R. Dixon, Bogdan Pasaniuc, Joseph R. Ecker, Quan Zhu and Bogdan Bintu.
END
Scientists create first map of DNA modification in the developing human brain
Findings could help pinpoint cell types most vulnerable to conditions like schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Extended Timing: How neurons encode information on timescales that match learning
2024-10-09
New research from the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience published this week in Nature has identified a key step in how neurons encode information on timescales that match learning.
A timing mismatch
Learning takes seconds to minutes. However, the best-understood mechanisms of how the brain encodes information happen at speeds closer to neural activity—around 1000 times faster. These mechanisms, known as Hebbian plasticity, suggest that if two connected neurons are both active within a hundredth of a second, then the connection between the two neurons is strengthened. In this ...
Dual immunotherapy plus chemotherapy benefits specific subset of patients with lung cancer
2024-10-09
HOUSTON ―Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have demonstrated that patients with metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring specific mutations in the STK11 and/or KEAP1 tumor suppressor genes were more likely to benefit from adding the immunotherapy tremelimumab to a combination of durvalumab plus chemotherapy to overcome treatment resistance typically seen in this patient population.
Study results, published today in Nature, identify ...
Scientists discover viral trapdoor blocking HIV and herpes
2024-10-09
Scientists discover viral trapdoor blocking HIV and herpes
Ghent, 10 October 2024 – A group of researchers led by Xavier Saelens and Sven Eyckerman at the VIB-UGent Center for Medical Biotechnology discovered how a protein linked to the human immune system wards off HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus-1 by assembling structures in the cell that lure in these viruses and then trap them or even take them apart. The research was spearheaded by first author George Moschonas, published in Cell Host and Microbe, and could be used to devise new strategies to combat these viruses.
The innate immune system of the human body can sense and respond to viruses by ...
Study uncovers mutations and DNA structures driving bladder cancer
2024-10-09
How bladder cancer originates and progresses has been illuminated as never before in a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the New York Genome Center. The researchers found that antiviral enzymes that mutate the DNA of normal and cancer cells are key promoters of early bladder cancer development, and that standard chemotherapy is also a potent source of mutations. The researchers also discovered that overactive genes within abnormal circular DNA structures in tumor cells genes drive bladder cancer resistance to therapy. These findings are novel insights into bladder cancer biology and point to new therapeutic strategies for this ...
A matter of taste: Electronic tongue reveals AI inner thoughts
2024-10-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A recently developed electronic tongue is capable of identifying differences in similar liquids, such as milk with varying water content; diverse products, including soda types and coffee blends; signs of spoilage in fruit juices; and instances of food safety concerns. The team, led by researchers at Penn State, also found that results were even more accurate when artificial intelligence (AI) used its own assessment parameters to interpret the data generated by the electronic tongue.
The researchers published their results today (Oct. 9) in Nature.
According to the researchers, ...
Another step towards decoding smell
2024-10-09
We often only realize how important our sense of smell is when it is no longer there: food hardly tastes good, or we no longer react to dangers such as the smell of smoke. Researchers at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB), the University of Bonn and the University of Aachen have investigated the neuronal mechanisms of human odor perception for the first time. Individual nerve cells in the brain recognize odors and react specifically to the smell, the image and the written word of an object, for example a banana. The results of this study close a long-standing knowledge gap between animal and human odor research and have now been published in the renowned ...
Plant Science Research collaboration will explore key mosses critical to storing carbon
2024-10-09
ST. LOUIS, MO, October 9, 2024 - Plant scientists at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology have been awarded a four-year National Science Foundation (NSF) Enabling Discovery through GEnomics (EDGE) grant to advance their understanding of sphagnum moss, a crucial component of peatlands and a vital player in global ecosystems. The collaborative research team will develop genetic and genomic resources to study sphagnum's life cycle, growth, and adaptation to various environmental conditions.
Sphagnum ...
Researchers examine the persistence of invisible plastic pollution
2024-10-09
Plastic pollution – tiny bits of plastic, smaller than a grain of sand – is everywhere, a fact of life that applies even to newborn rodents, according to a Rutgers Health study published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
Researchers have long understood that micro- and nanoplastic particles (MNPs), which enter the environment through oxidation and natural degradation of consumer products, are easily deposited in the human body through inhalation, absorption and diet.
Experts also understand that these pollutants can cross the placental barrier and deposit ...
Coffee during pregnancy safe for baby’s brain development
2024-10-09
A University of Queensland-led study has failed to find any strong links between drinking coffee during pregnancy and neurodevelopmental difficulties in children, but researchers are advising expectant mothers to continue following medical guidelines on caffeine consumption.
Dr Gunn-Helen Moen and PhD student Shannon D’Urso from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience (IMB) led an in-depth genetic analysis of data from tens of thousands of families in Norway.
“Scandinavians are some of the biggest coffee consumers in the world, drinking at least 4 cups a day, with little stigma about drinking coffee during pregnancy,” ...
SwRI-led instrument aboard Jupiter-bound spacecraft nails in-flight test
2024-10-09
SAN ANTONIO — October 9, 2024 —As European Space Agency (ESA)’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) spacecraft hurtled past the Moon and Earth in mid-August to provide its first gravity assist maneuver to the Jovian system, the Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) instrument imaged the UV emissions radiating from the Earth and Moon.
It was a successful test of one of three science instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to ESA’s Juice mission. The UVS data collected were then analyzed and found to be consistent with expectations for the Moon and the Earth. This confirmation that the instrument works ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Scientists create first map of DNA modification in the developing human brainFindings could help pinpoint cell types most vulnerable to conditions like schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder