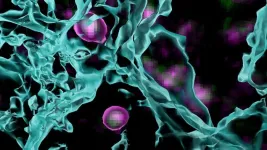
(Press-News.org) Imagine yourself sometime in the far future aboard a routine rocket to Mars. Someone just spilled their drink. Without gravity, it collects in floating blobs that ripple right before your eyes. Now freeze.
What you see might look something like the above image from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory’s (CSHL’s) Cheadle lab. But those purple and green blobs aren’t the floating remains of somebody’s drink. They’re mysterious cells in the brain’s visual cortex called OPCs.
The visual cortex processes everything we see. Incoming visual information is relayed to this outer layer of the brain via synapses—the silver streaks above. When the brain’s neural circuits are first wired up, more connections, or synapses, are created than needed. As the brain accumulates new experiences and information, OPCs shape neural circuitry by pruning unnecessary synapses.
“OPCs are doing all sorts of things in the brain that help it to function in a normal, healthy way,” CSHL Assistant Professor Lucas Cheadle says. OPCs are a specialty of the Cheadle lab. He and his team discovered OPCs’ function as neural landscapers in 2022. Before that, they were thought only to produce oligodendrocytes, cells that sheath and support neurons. Now, Cheadle has developed new ways to zoom in and see OPCs in action.
“We’re able to see what thousands of OPCs, and even smaller groups of 30-50, are doing,” he explains. “From there, we can figure out which synapses are fully engulfed by an OPC, which are in the process of being pruned, and which have maybe just been checked on by an OPC but not processed.”
The new techniques used to produce the image above have become essential tools in Cheadle’s ongoing work. He and his team are now building on their 2022 discovery to help paint a complete picture of OPCs’ role in health and disease. Cheadle explains: “These mysterious cells are one of the primary sources of glioma,” a deadly brain cancer. “They’re potentially involved in Alzheimer’s disease as well.”
It’ll take more research to illustrate these connections in detail. In the meantime, Cheadle is eager to share his lab’s new tools with researchers around the world. “The brain is constantly changing, and the same approaches you’d use to look at one type of cell can’t just be applied across the board,” he says. “We’re adapting and innovating to keep up with it—to better understand how the brain works.”
END
One experiment: The brain’s landscapers
2024-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI-supported dermatology: Now for darker skin tones too, thanks to a new data set
2024-10-10
In many countries in Africa, up to nine out of ten children suffer from a skin problem, and there are far too few local dermatologists. Artificial intelligence could help with diagnosis, but needs to be trained with the relevant images, so researchers have created a new data set for dark skin tones.
Demand is high, the lack of dermatologists acute: in many countries in Africa, there is less than one dermatology specialist per one million people – compared to the World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation of ...
Understanding how smiling influences relationship building during real-life conversations
2024-10-10
Smiling during conversations creates warmth, making people feel more comfortable and connected. For example, a friendly smile when meeting someone new can ease nervousness. A smile can soften tension in a debate, showing respect among the participants despite disagreement. In fact, extensive studies have been conducted in the past in an attempt to understand smiling interactions in a natural conversation. Despite these studies, however, little is known about the extent to which one’s smile influences or gets affected by the other person’s smile during a conversation.
A new study sought to investigate this by quantifying ...
British Heart Foundation Data Science Centre launches first open challenge to explore AI ECG potential
2024-10-10
The British Heart Foundation (BHF) Data Science Centre, led by Health Data Research UK, is hosting an open challenge which invites competitors to explore the potential of Artificial Intelligence to improve the use of electrocardiogram (ECG) for cardiovascular disease patient care. The challenge has been co-designed with members of public and patients affected by cardiovascular disease.
The BHF Data Science Centre is collaborating with experts from the University of Edinburgh to use a synthetic imaging dataset made up of approximately 20,000 simulated electrocardiogram (ECG) images. Competitors will be invited to develop algorithms which can make ...
Heart failure, atrial fibrillation & coronary heart disease linked to cognitive impairment
2024-10-10
Statement Highlights:
Previous studies have found that 14-81% of patients with heart failure experience some degree of cognitive impairment affecting language, memory or executive function.
Evidence also indicates that people with atrial fibrillation have a 39% increased risk of memory or thinking problems; adults with heart disease have a 27% higher risk of developing dementia; and up to 50% of individuals experience cognitive decline after a heart attack.
Managing heart health from an early age is important, not only for preventing heart disease but also for protecting brain health and reducing the risk of cognitive impairment in later life.
Embargoed until 4:00 a.m. CT/5:00 ...
To make children better fact-checkers, expose them to more misinformation — with oversight
2024-10-10
In an era when online misinformation is seemingly everywhere and objective facts are often in dispute, UC Berkeley psychologists in a new study have presented a somewhat paradoxical partial solution: Expose young children to more misinformation online — not less.
Doing so in limited circumstances, and with careful oversight and education, can help children gain the tools they'll need to sort fact from fiction online, said Evan Orticio, a Ph.D. student in UC Berkeley’s Department of Psychology and lead author of a paper published today ...
Renowned psychiatrist professor Celso Arango advocates for primary prevention in mental health
2024-10-10
In a revealing Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on October 10, 2024, Professor Celso Arango, a prominent psychiatrist and researcher, outlines his vision for the future of mental health care. Professor Arango, who serves as Director of the Institute of Psychiatry and Mental Health at Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón and Professor of Psychiatry at the Universidad Complutense de Madrid, advocates for a paradigm shift towards primary prevention in psychiatry.
Professor Arango's career trajectory, from his early exposure to ...
Ketamine pioneer Dr. Carlos A. Zarate Jr. reshapes depression treatment landscape
2024-10-10
Bethesda, Maryland - 10 October 2024. In a revealing Genomic Press Interview published on 10 October 2024, Dr. Carlos A. Zarate Jr., NIH Distinguished Investigator and pioneer in rapid-acting antidepressant research, offers a glimpse into the personal motivations and scientific breakthroughs that have defined his career. The interview, part of the journal's Innovators and Ideas series, showcases Dr. Zarate's journey from a young tennis instructor in Argentina to a leading figure in psychiatric research at the National Institute ...
Glowing approach could aid carpal tunnel-related surgery
2024-10-10
In modern office life, avoiding the onset of carpal tunnel syndrome might be a daily struggle. The worst case could mean needing surgery to alleviate compression of the nerves or to repair damaged nerves. Helping surgeons visually check the areas where neural blood flow has decreased due to chronic nerve compression can lead to improvements in diagnostic accuracy, severity assessments, and outcome predictions.
With this in mind, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team involving Graduate School of Medicine student Kosuke Saito and Associate Professor Mitsuhiro Okada investigated the use of fluorescein angiography, a method employed in neurosurgery and ophthalmology ...
The hidden costs of free apps – more than personal data
2024-10-10
Procrastination, sleep deprivation and reduced focus are part of the price we pay for free mobile apps. This is according to researchers at Linköping University and RISE, who have investigated the costs hidden behind the free apps. Based on their results, they also have some advice for decision-makers.
Most of us are becoming aware that our digital attention is hard currency for companies like Google and Facebook. By analysing our digital behaviour patterns, they can target tailored advertising directly to our feeds. Our attention becomes the product that is sold to advertisers. For example, YouTube’s three billion monthly users generated ...
Hot dragonfly summer: species with darker wings have evolved to withstand heat and attract partners
2024-10-10
Temperature determines where species can live and if they are threatened by a warming climate. So, for a long time, biologists studied how heat tolerance affects survival. Yet, less is known about how thermal traits influence reproduction, which is directly linked to extinction risk.
Now, researchers in the US have examined if males of dragonfly species that produce sexual signals in the form of dark coloration on their wings are more resistant to heat. They published their results in Frontiers in Ethology.
“We show that dragonfly species that have evolved dark breeding coloration on ...