(Press-News.org) In a new study evaluating meditation for chronic lower back pain, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have discovered that men and women utilize different biological systems to relieve pain. While men relieve pain by releasing endogenous opioids, the body’s natural painkillers, women rely instead on other, non-opioid based pathways.
Synthetic opioid drugs, such as morphine and fentanyl, are the most powerful class of painkilling drugs available. Women are known to respond poorly to opioid therapies, which use synthetic opioid molecules to bind to the same receptors as naturally-occurring endogenous opioids. This aspect of opioid drugs helps explain why they are so powerful as painkillers, but also why they carry a significant risk of dependence and addiction.
“Dependence develops because people start taking more opioids when their original dosage stops working,” said Fadel Zeidan, Ph.D., professor of anesthesiology and Endowed Professor in Empathy and Compassion Research at UC San Diego Sanford Institute for Empathy and Compassion. “Although speculative, our findings suggest that maybe one reason that females are more likely to become addicted to opioids is that they’re biologically less responsive to them and need to take more to experience any pain relief.”
The study combined data from two clinical trials involving a total of 98 participants, including both healthy individuals and those diagnosed with chronic lower back pain. Participants underwent a meditation training program, then practiced meditation while receiving either placebo or a high-dose of naloxone, a drug that stops both synthetic and endogenous opioids from working. At the same time, they experienced a very painful but harmless heat stimulus to the back of the leg. The researchers measured and compared how much pain relief was experienced from meditation when the opioid system was blocked versus when it was intact.
The study found:
Blocking the opioid system with naloxone inhibited meditation-based pain relief in men, suggesting that men rely on endogenous opioids to reduce pain.
Naloxone increased meditation-based pain relief in women, suggesting that women rely on non-opioid mechanisms to reduce pain.
In both men and women, people with chronic pain experienced more pain relief from meditation than healthy participants.
"These results underscore the need for more sex-specific pain therapies, because many of the treatments we use don’t work nearly as well for women as they do for men,” said Zeidan.
The researchers conclude that by tailoring pain treatment to an individual’s sex, it may be possible to improve patient outcomes and reduce the reliance on and misuse of opioids.
"There are clear disparities in how pain is managed between men and women, but we haven’t seen a clear biological difference in the use of their endogenous systems before now,” said Zeidan. “This study provides the first clear evidence that sex-based differences in pain processing are real and need to be taken more seriously when developing and prescribing treatment for pain.”
Link to study: https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae453
Co-authors on the study include Jon Dean, Mikaila Reyes, Lora Khatib, Gabriel Riegner, Nailea Gonzalez, Julia Birenbaum and Krishan Chakravarthy at UC San Diego, Valeria Oliva at Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Grace Posey at Tulane University School of Medicine, Jason Collier and Rebecca Wells at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Burel Goodin at Washington University in St Louis and Roger Fillingim at University of Florida.
This study was funded, in part, by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (grants R21-AT010352, R01-AT009693, R01AT011502) and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (UL1TR001442).
# # #
END
Men and women process pain differently, study finds
Men and women experience pain relief differently; new study may help explain why women have more chronic pain and are less responsive to opioid treatments
2024-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Korean research team proposes optimal utilization strategy for hydrogen energy, the key to carbon neutrality
2024-10-16
A joint research team, led by Dr. Sang Yong Park from the National Climate Technology Center at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) and Professor Dong Gu Choi from the Department of Industrial and Management Engineering at POSTECH, has developed an energy system model optimized for Korea's environment and proposed an optimal strategy for utilizing hydrogen energy.
Hydrogen is being highlighted as a key resource for achieving the government's "2050 Carbon Neutrality Scenario." It is not only a clean energy source in itself but can also be produced using surplus power from renewable ...
NFL Player Ambassadors urge fans to learn lifesaving CPR in 90 seconds
2024-10-16
DALLAS, October 16, 2024 — More than half of all people who experiencing sudden cardiac arrest outside of hospital don’t receive immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). As a result, 9 out of 10 times they die[1]. Yet it takes just 90 seconds to learn the fundamentals of Hands-Only CPR to save a life. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. To save more lives, the American Heart Association and the National Football League (NFL) are actively putting boots on the ground - cleats on the field - to educate ...
Most older adults don’t trust AI-generated health information — but many aren’t sure what to trust
2024-10-16
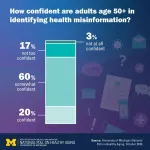
While the vast majority of people over 50 look for health information on the internet, a new poll shows 74% would have very little or no trust in such information if it were generated by artificial intelligence.
Meanwhile, 20% of older adults have little or no confidence that they could spot misinformation about a health topic if they came across it.
That percentage was even higher among older adults who say their mental health, physical health or memory is fair or poor, and among those who report having a disability that limits their activities. In other words, those who might ...
Invention quickly detects earliest sign of heart attack
2024-10-16
With heart attacks, every second counts. A new blood test diagnoses them in minutes rather than hours and could be adapted as a tool for first responders and people at home.
“Heart attacks require immediate medical intervention in order to improve patient outcomes, but while early diagnosis is critical, it can also be very challenging—and near impossible outside of a clinical setting,” said lead author Peng Zheng, an assistant research scientist at Johns Hopkins University. “We were able to invent a new technology that can quickly and accurately establish if someone is having a heart attack.”
The proof-of-concept work, which can be modified to detect infectious ...
New research confirms that young adults can also have large vessel occlusion strokes thought to happen in older adults, given the rise of stroke risk factors in younger adults
2024-10-16
New research published in the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases confirms that strokes thought to happen in older adults are possible in the younger (defined as 18-50 years old) population. Large Vessel Occlusion Acute ischemic Strokes (LVO-AIS) are considered to be the most debilitating strokes which occur due to blockage of large cerebral arteries usually from blood clots or plaque build up. LVO-AIS is typically thought to occur in older adults given that older individuals are known to have risk factors for large vessel occlusions. However, new research confirms that the younger population can have risk factors ...
Grasslands live in the climate change fast lane
2024-10-16
Although all ecosystems are affected by a changing climate, the impacts can take a while to appear. Changes in forest biodiversity, for example, are known to lag behind changes in a habitat's temperature and precipitation.
Grasslands, on the other hand, are responding to climate change almost in real time, according to new research by the University of Michigan. Put another way, forests accumulate climate debt while grasslands are paying as they go, said the study's lead authors, Kai Zhu and Yiluan Song.
"Climate change does have consequences for our ecosystems. It's going to come sooner or later," said Song, a postdoctoral fellow at the ...
Mount Sinai Doctors to present at ID Week 2024
2024-10-16
Experts in infection prevention and control at the Mount Sinai Health will present new research and insights at ID Week, the joint annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists in Los Angeles from October 16-19.
Mount Sinai doctors and researchers are also available for comment on breaking health news including the flu, COVID variants, HIV/AIDS, mpox, West Nile virus, measles, and fall vaccinations.
PRESENTATIONS and POSTER SESSIONS
*All abstracts and presentations ...
Rewriting the future: New molecules reversibly change with light and heat
2024-10-16
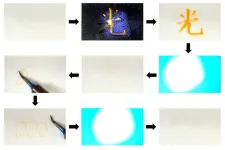
In this age of cloud storage, few people are backing up data on CD-RWs. The technology to rewrite data on compact discs was made possible by phase-change materials altered by the light and heat of lasers, though this had a limit of 1,000 rewrites. Today, scientists investigating photoswitching molecules, which change their properties when irradiated, have been finding possible applications for these materials, ranging from photopharmacology to data storage.
Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering student Shota Hamatani, Dr. Daichi Kitagawa, a lecturer, and Professor Seiya Kobatake synthesized aza-diarylethenes, which have nitrogen in place of carbon in a molecular structure ...
New breakthrough in quantum computing development, hybrid quantum error correction technology
2024-10-16
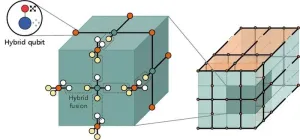
A major challenge in realizing quantum computers is the development of 'quantum error correction' technology. This technology offers a solution for addressing errors that occur in the qubit, the basic unit of quantum computation, and prevents them from being amplified during the computation. Without quantum error correction, it would be impossible for quantum computers to outperform classical counterparts, and thus efforts to advance this technology are ongoing worldwide.
Dr. Seung-Woo Lee's research team at the Korea ...
Unlocking the future: Information processing at the speed of light
2024-10-16
The integration of photonics into quantum computing has profound implications across various domains. As the demand for faster and more secure computational capabilities intensifies, photonic quantum computing emerges as a pivotal force, with the photonics market projected to reach USD 837.8 billion by 2025.
Harnessing the unique properties of light, photonic quantum computing revolutionizes data processing by encoding information in photons, offering unprecedented speed and efficiency for solving complex problems that traditional methods struggle to address. Photonic quantum computers can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
[Press-News.org] Men and women process pain differently, study findsMen and women experience pain relief differently; new study may help explain why women have more chronic pain and are less responsive to opioid treatments