(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC – As the nation continues to build a diverse, clean-energy workforce, the Department of Energy (DOE) today announced that applications are being accepted for the Summer 2025 term of two undergraduate internship programs.
The Office of Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships (SULI) program and the Community College Internships (CCI) program are unique opportunities open to all current and recent college undergraduates. Interns will learn about science and technology careers, team science, networking, and gain the experience needed to transition from internship to employment.
The application deadline for both programs is January 8, 2025, at 5:00 p.m. EST. A number of workshops, an alumni panel, an online internship fair, and technical support will be available to applicants throughout the process.
Interns chosen will work directly with national laboratory scientists and engineers, assisting them on research or technology projects that support the DOE mission and address critical scientific challenges of importance to the nation, including global warming.
SULI is open to full-time students attending 4-year institutions and community colleges or recent graduates within two years of receiving their bachelor’s degree or associate degree. CCI is for community college students. Both programs are stipend-based and offered three times annually in Fall, Spring, and Summer. Participants residing outside the commuting area are offered round-trip travel to and from the host lab, and financial assistance with lodging.
Workshop Details
Three workshops are planned to provide strategies for submitting a compliant application and learning about the internship experience from the voices of CCI and SULI alumni.
Two additional workshops will introduce the program and application process followed by a final workshop for review of the application process for each program.
In addition, a live alumni panel discussion will showcase the research opportunities and internship experiences of students who have taken part in the programs.
CCI application assistance workshop: October 29, 2024, from 2:00 – 3:00 pm EST (register here)
SULI application assistance workshop: November 6, 2024, from 2:00 – 3:00 pm EST (register here)
CCI/SULI panel workshop: December 3, 2024, from 2:00 – 3:00 pm EST (register here)
Summer Internship Fair
In addition to the workshops, prospective SULI and CCI applicants are invited to engage with representatives from the DOE national laboratories at a virtual Summer Internship Fair scheduled November 14, 2024, from 1:00–5:00 pm EST (register here). During the fair, WDTS staff as well as researchers from the national laboratories will be online and available via chat.
Furthermore, the program office invites applicants and letter of recommendation writers to attend office hours to answer administrative questions such as those pertaining to uploading transcripts, submitting letters of recommendation, and general inquiries. Office hours are scheduled on December 11th and 18th from 2:00 – 3:00 pm EST. Registration (register here) is required for attendance.
The programs offer unique opportunities to gain a glimpse into discovery science research that is at the cutting edge of national priorities.
Sarah Cole of Boise State University, an alumnus of the SULI internship program, was able to learn and contribute to scientific research on energy storage, a key priority for the DOE Office of Science and the nation.
“My SULI internship at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory inspired me to grapple with the question: ‘How can we engineer battery materials to store energy more efficiently?’ My research in the SLAC-Stanford Battery Center focused on elucidating the electrochemical behavior of novel anode compositions based on the Earth-abundant, high storage capacity material: silicon.
“I gained hands-on experience fabricating coin cells, testing the battery prototypes, and conducting experiments at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, teaching me of the importance of engineering high-performance energy storage materials to meet society's growing energy demand,” Cole said.
SULI and CCI are managed by the Office of Workforce Development for Teachers and Scientists (WDTS) in the Office of Science. More information including workshop registration can be found at the WDTS website.
END
Discover science: Applications open for summer 2025 undergraduate internships
An amazing opportunity -- students and recent grads may apply to conduct research and technical projects at national laboratories
2024-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can electricity treat high blood pressure?
2024-10-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Several medications are available to treat high blood pressure, but more than 10 million Americans do not respond to the treatments, according to the American Heart Association. Using a bioelectronic device to deliver pulsed electricity to the body has proven to be a promising strategy to treat drug-resistant hypertension patients, according to Penn State researcher Tao Zhou, although he noted that its practical application in patient care has significant limitations.
Zhou, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics and of biomedical engineering, received ...
Microplastics detected in dolphin breath
2024-10-16
U.S. researchers have detected microplastic particles in air exhaled by wild bottlenose dolphins, suggesting that inhalation may be a relevant route of exposure to these potentially harmful contaminants. Miranda Dziobak of the College of Charleston in South Carolina, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 16, 2024.
Around the world, humans and numerous other animals are exposed to tiny particles of plastic contaminants known as microplastics. In humans and rodents, microplastic exposure has been linked to adverse health impacts, such as oxidative stress and inflammation. Ingestion ...
Global north’s growing appetite for farmed salmon imperils communities’ access to local fish
2024-10-16
A new paper published today in Science Advances exposes the global aquaculture sector’s growing dependence on wild fish. Despite industry claims to the contrary, these findings highlight how the growing appetite for expensive farmed salmon can leave coastal communities struggling to access affordable local fish like sardines and anchovies. Instead, these small pelagic fish are frequently caught, processed, and “reduced” to fishmeal and fish oil, almost all of which is used to feed farmed fish. These ‘reduction fisheries’ account for 26% of global ocean catch.
“As the aquaculture industry grows, so does its ...
e-Flower records neuronal activity with electronic petals
2024-10-16
Neural spheroids — 3D clusters of brain cells — are emerging as essential tools for understanding neural networks and studying neurological diseases in the lab. EPFL’s e-Flower, a flower-shaped 3D microelectrode array (MEA), allows researchers to monitor the electrical activity of these spheroids in a way that was previously impossible. This breakthrough, published in Science Advances, lays the groundwork for more sophisticated research on brain organoids, which are complex, miniaturized models of brain tissues.
“The ...
Aquaculture uses far more wild fish than previously estimated, study finds
2024-10-16
A study published in the journal Science Advances suggests that global fish farming, or aquaculture, may rely on significantly larger quantities of wild-caught ocean fish than previously calculated. The study is part of a special issue focused on expanding contributions from the aquaculture industry to food systems with an aim towards sustainability.
These findings call into question long-held assumptions about the sustainability of the rapidly growing aquaculture industry and provides a range of plausible estimates for its impact on wild fish populations.
The research, led by an international team of scientists ...
Gene editing approach paves the way to first-in-human clinical trial for rare genetic disease
2024-10-16
A collaborative effort between investigators at the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, demonstrates the potential of precise genome editing technologies, called adenine base editors, to correct disease-causing mutations in stem cells from patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (X-CGD), a rare genetic disorder characterized by high susceptibility to infections. The findings are published in Science Translational Medicine.
Patients with ...
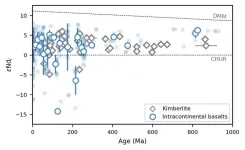
Compositional evolution of the upper mantle driven by plate tectonics
2024-10-16
On present-day Earth, plate subduction continuously modifies the chemical composition of the convecting mantle, and various mantle sources linked to these processes have been widely studied.
However, when did global chemical heterogeneity of the convecting mantle first emerge in Earth's geological history? And how might Earth’s geodynamic evolution have influenced the chemical composition of the convecting mantle over time?
Researchers from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS), along with collaborators from Australia, Switzerland and the USA, have tried to address these questions ...
Virtual reality game used to help students in science classes
2024-10-16
Multilingual students face unique challenges that can hurt their performance in school. New methods of teaching may help close this gap, according to a new study from the University of Georgia.
In the United States, English is the main language used in classrooms. Schools also tend to rely on spoken communication to teach and written exams to assess learning.
That can make it difficult for multilingual students to express themselves. This is especially true in science classes, with their specific terms and complex sentence structures.
So a UGA researcher developed an immersive virtual reality game to communicate scientific ...
Life-saving spongelike “bandage” developed by UCF researchers rapidly stops hemorrhaging and mitigates risk of infection
2024-10-16
Video available here.
Without proper medical invention, injuries sustained from traffic collisions, serious workplace accidents or weapons may result in fatal hemorrhaging.
University of Central Florida researchers aim to prevent such bleeding in potentially deadly situations with a new hemostatic spongelike bandage with antimicrobial efficacy that they recently developed and detailed in a newly published study in the journal Biomaterials Science.
“What happens in the field or during an accident is due to heavy bleeding, patients can die,” says Kausik Mukhopadhyay, assistant professor of materials ...
Model reveals why debunking election misinformation often doesn’t work
2024-10-16
When an election result is disputed, people who are skeptical about the outcome may be swayed by figures of authority who come down on one side or the other. Those figures can be independent monitors, political figures, or news organizations. However, these “debunking” efforts don’t always have the desired effect, and in some cases, they can lead people to cling more tightly to their original position.
Neuroscientists and political scientists at MIT and the University of California at Berkeley have now ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Discover science: Applications open for summer 2025 undergraduate internshipsAn amazing opportunity -- students and recent grads may apply to conduct research and technical projects at national laboratories