(Press-News.org) Cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia (CBTI) delivered during pregnancy significantly reduces postpartum depressive symptoms in mothers, new research from UBC shows.
Researchers from the Vancouver and Okanagan campuses investigated whether treating insomnia during pregnancy could alleviate symptoms of postpartum depression, which affects many new mothers.
“Early intervention is crucial for infant and maternal mental health,” says Dr. Elizabeth Keys, an Assistant Professor in UBCO’s School of Nursing and study co-author. “Our research explores how addressing sleep problems, like insomnia, can lead to better mental health outcomes for families, helping parents and their children thrive.”
The randomized controlled trial involved 62 women experiencing insomnia and evaluated the effects of a five-week CBTI intervention adapted for pregnancy. Participants were assessed for insomnia and depression symptoms before the intervention, immediately after and six months postpartum.
Results indicate that effective insomnia treatment during pregnancy may serve as a protective factor against postpartum depression.
While poor sleep during and after pregnancy is common, it is often dismissed as inevitable. Dr. Keys says many parents may not realize that evidence-based treatments, like CBTI, are available.
“Our study adds to the growing evidence that treating insomnia during pregnancy is beneficial for various outcomes,” Dr. Keys says. “It’s time to explore how we can make this treatment more accessible to pregnant women across the country, with the goal of improving sleep health equity.”
This study highlights the interdisciplinary collaborations happening between UBC’s Vancouver and Okanagan campuses, along with researchers from across Canada. Dr. Tavis Campbell and Dr. Elizabeth Keys are from UBCO’s School of Nursing, while Dr. Lianne M. Tomfohr-Madsen, a Canada Research Chair in Mental Health and Intersectionality, is based at UBC Vancouver.
Dr. Keys and Dr. Tomfohr-Madsen are lead investigators on the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Sleep Equity Reimagined team and members of the Canadian Sleep Research Consortium.
The study appears in the October issue of Journal of Affective Disorders.
END
Sleeping for 2: CBT for insomnia combats postpartum depression
UBC Okanagan researchers say early interventions help moms sleep better
2024-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Financial incentive encourages healthiness: why isn't it used more often?
2024-10-17
Move more, quit smoking, lose weight: great resolutions, hard to keep. But does it get easier if there is a financial incentive in return? According to research by Radboud University and others, it can be an effective tool, although there are still some obstacles. They presented their findings this week in Economisch Statistische Berichten (ESB).
Some lifestyle interventions are more effective than others, but in general, financial incentives are a ‘powerful tool to help reduce health inequalities in the Netherlands’, says Koen van der Swaluw of Radboud University. Despite knowing more and more about the effectiveness of financial incentives to promote ...
People sympathize with bullied AI bots
2024-10-17
In an Imperial College London study, humans displayed sympathy towards and protected AI bots who were excluded from playtime.
The researchers say the study, which used a virtual ball game, highlights humans' tendency to treat AI agents as social beings – an inclination that should be considered when designing AI bots.
The study is published in Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies.
Lead author Jianan Zhou, from Imperial’s Dyson School of Design Engineering, said: “This is a unique insight into how humans interact ...
Providencia rustigianii has virulence gene akin to Salmonella’s
2024-10-17
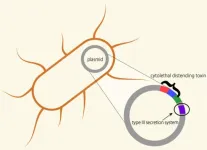
Salmonella and E. coli are well-known bacteria that cause food poisoning, but less understood are species of Providencia, another causative agent of serious symptoms. Providencia rustigianii, isolated from pediatric gastroenteritis patients, has now undergone whole genome sequencing by a research team led by Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Shinji Yamasaki of the Graduate School of Veterinary Science and the Osaka International Research Center for Infectious Diseases.
Members of the team had previously reported that P. rustigianii carries a cytolethal distending toxin virulence gene on its plasmid. Elimination of this gene did not ...
Ozempic (and similar medications) may be the new treatment for opioid and alcohol use disorder
2024-10-17
A new study published in the scientific journal Addiction has found that people with opioid or alcohol use disorder (OUD, AUD) who take Ozempic or similar medications to treat diabetic/weight-related conditions appear to have a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose and a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication than people with OUD and AUD who do not take Ozempic or similar medications.
Ozempic is one of several medications, called glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists or GLP-1 RAs, that are prescribed to treat diabetes, obesity, and other weight-related medical conditions. The medications interact with ...
Artificial nests boost penguin breeding success, but there’s no one-size-fits-all design
2024-10-17
Artificial nests can boost the breeding success of endangered African penguins, but different designs are more effective at different colonies according to a new study by an international team of researchers from South Africa and the UK. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society journal, Ecological Solutions and Evidence.
A new study, led by researchers at Nelson Mandela University, which monitored the breeding success of African penguins for 12 years across South Africa has found that artificial ...
Study: Pediatric healthcare facilities need more staff dedicated to infection prevention
2024-10-17
Arlington, Va. — October 17, 2024 — A new paper published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) describes efforts at a major children’s hospital to assess and fulfill its staffing needs for infection prevention and control, highlighting the challenges of allocating sufficient resources to this important role. Infection preventionists (IPs) at Boston Children’s Hospital found that conventional methods for calculating the number of staff for these roles do not accurately reflect the current needs of healthcare systems or the specific needs of a pediatric ...
Marine experts challenge reliability of vessel strike prediction models
2024-10-17
A new study has raised questions about current approaches to predicting the risk of vessel strikes on whales.
Led by researchers at Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland, an international team of scientists compared eight models currently in place to assess and forecast the risk of ships colliding with whales. The study reveals notable inconsistencies in the results across the different models.
Most reports of vessel collisions involve large whales but all species can be affected. Globally, strikes are under-reported and can often go undetected, particularly when they involve large vessels. Collisions can result in animals being injured or killed, and vessels ...
USC study finds link between PFAS, kidney function and gut health
2024-10-17
New research has revealed that the connection between per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, and kidney damage may be tied to dysregulation of the gut microbiome, which is made up of bacteria and other microorganisms that live in the digestive tract.
PFAS are manufactured chemicals used in a wide range of products, including everything from furniture to food packaging. They are often called “forever chemicals” because once they accumulate in the environment or the human body, they take a very long ...
Compound drought-heatwave events underrecognized in global soils
2024-10-17
Soil is essential for life and plays a crucial role in Earth's ecosystem, providing support for plant roots and hosting countless microorganisms. In a warming world, it is important to understand how soil hydrothermal conditions, particularly dry-hot extremes, have changed already and how they will respond to further warming.
In a study published in PNAS, researchers led by Prof. ZHANG Yunlin from the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) and Bangor University, have quantified global soil compound drought-heatwave (SCDHW) ...
Pursuing the biological mechanisms and diversity of marine life through international collaboration
2024-10-17
The Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and France’s National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) have signed an agreement to establish the International Research Laboratory “Eco-Evo-Devo of Coral Reef Fish Life Cycle” (IRL EARLY). The ceremony took place on October 7 at the STS Forum in Kyoto, Japan.
Since life began in our oceans, it has diversified into a wide variety of different organisms. However, the true extent of marine diversity remains unknown, as do many species and their ecologies. Investigating the biological mechanisms of marine life can not only provide a deeper understanding of the life cycles and evolution of these organisms, it ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Sleeping for 2: CBT for insomnia combats postpartum depressionUBC Okanagan researchers say early interventions help moms sleep better