(Press-News.org) Mpox in Africa was neglected during the previous outbreak, and requires urgent action and investment by leaders now to prevent global spread, claim experts from The Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response, ex-NZ Prime Minister Helen Clark, former Liberian President and Nobel Peace Prize winner Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, and other global health specialists.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0003714
Article Title: Mpox: Neglect has led to a more dangerous virus now spreading across borders, harming and killing people. Leaders must take action to stop mpox now
Author Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, Columbia, Kenya, Liberia, Mexico, New Zealand, Nigeria, Peru, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States
Funding: The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation is supporting the ongoing work of The Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response under INV-059481. CM, HEM, AN are consultants under this grant. CM led the writing and coordination of this manuscript. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Mpox in Africa was neglected during the previous outbreak, and requires urgent action and investment by leaders now to prevent global spread
2024-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new era of treating neurological diseases at the blood-brain-immune interface
2024-10-17
SAN FRANCISCO—The question of what causes complex neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s or multiple sclerosis continues to confound scientists and doctors, with the unknowns standing in the way of early diagnoses and effective treatments.
Even among identical twins who share the same genetic risk factors, one may develop a particular neurological disease while the other does not.
That’s because unlike diseases such as cystic fibrosis or sickle-cell anemia, which are caused by a single gene, most neurological disorders are associated with many—sometimes hundreds—of rare genetic variants. ...
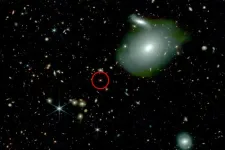
Astronomers detect ancient lonely quasars with murky origins
2024-10-17
A quasar is the extremely bright core of a galaxy that hosts an active supermassive black hole at its center. As the black hole draws in surrounding gas and dust, it blasts out an enormous amount of energy, making quasars some of the brightest objects in the universe. Quasars have been observed as early as a few hundred million years after the Big Bang, and it’s been a mystery as to how these objects could have grown so bright and massive in such a short amount of cosmic time.
Scientists have proposed that the earliest quasars sprang from overly dense ...
New study highlights the dangers of handheld cellphone use among teen drivers
2024-10-17
PHILADELPHIA (October 17, 2024) – A new study, conducted by a group of researchers led by Penn Nursing and Perelman School of Medicine and funded by the Centers for Disease Control, found a strong association between handheld cellphone use and risky driving behaviors among newly licensed teen drivers. The study, published online first in JAMA Open, used a smartphone telematics application to track the driving habits of hundreds of teens and identify potential safety risks.
The investigation found that teens who used their cellphones while driving were significantly more likely to engage in risky driving behaviors, such as hard braking and rapid acceleration. These behaviors can ...
Part of the GBHSH community in Spain uses doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted diseases
2024-10-17
The increasing incidence of sexually transmitted bacterial infections (STIs) is a major public health problem worldwide. Currently, among the therapies being studied is the use of the antibiotic doxycycline as a method of post-exposure prophylaxis after unprotected sex — known as DoxyPEP. Now, the University of Barcelona and the NGO Stop have carried out the first study in Spain on the use of DoxyPEP as a preventive strategy among the gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (GBHSH) community in Spain.
“The results suggest that, although medical and scientific associations rarely endorse the community use of DoxyPEP as a prevention strategy, ...
Researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine receive $4.5 million grant from Department of Defense to study neck injuries
2024-10-17
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Oct. 17, 2024 – Researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine have received a three-year, $4.5 million grant from the Department of Defense to study cervical spine injuries in military personnel.
Musculoskeletal injuries, such as those that occur to the cervical spine (neck), are problematic for military personnel. This is especially true for military personnel who must perform missions in demanding environments with head-supported mass. This head-supported mass includes the baseline protective helmet, communications, specialized night vision technology and other attachments.
“These injuries can lead to a significant number of lost-duty ...
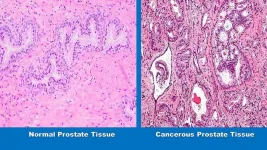
Study suggests a healthy diet may help keep low grade prostate cancer from progressing to more dangerous states during active surveillance
2024-10-17
In a peer-reviewed study believed to be the first of its kind published, a research team led by Johns Hopkins Medicine provides scientific evidence that a healthy diet may reduce the chance of low risk prostate cancer progressing to a more aggressive state in men undergoing active surveillance — a clinical option in which men with lower risk cancer are carefully monitored for progression in lieu of treatments that could have undesired side effects or complications.
The findings are reported today in the journal JAMA Oncology.
“Many men diagnosed with low grade prostate cancer are interested in changes they can ...
Center for Genomic Diagnostics receives first USDA grant
2024-10-17
Foreign animal diseases are a global threat to swine production with the potential for detrimental economic implications. Recently, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign received a three-year grant of $650,000 from the U.S. Department of Agriculture to develop sensitive, rapid, low-cost, and portable point-of-use biosensors to improve on-farm detection and surveillance of African swine fever virus.
ASFV is a large DNA virus that infects swine and can result in a lethal hemorrhagic fever, spread rapidly to neighboring pigs, and cause excessive morbidity ...
The National Tax Journal is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2024 Musgrave Prize and the 2024 Referee Award
2024-10-17
The National Tax Journal is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2024 Musgrave Prize and the 2024 Referee Award.
The Richard A. Musgrave Prize was created in 1999 and is presented each year to the author(s) of the best article published in the National Tax Journal. The award is a tribute to Richard Musgrave, whose work throughout his luminous career was characterized by a powerful blend of analytical clarity, insight drawn from the historical record, and respect for the importance of administrative issues. With this award, the National Tax Association recognizes his many contributions to public policy theory, research, and practice.
This year, ...
Study finds legalization didn’t increase recreational cannabis use among young adults in country of Georgia
2024-10-17
(Boston)—Cannabis is one of the most widely used drugs, with an estimated 219 million users globally in 2021, with the highest number of users in the Americas. It is also the most used drug among young people. In the U.S., cannabis use among young adults (age 19 to 22) reached a historically high level in 2021, with 42.6% reporting use in the past year.
Effects and impact of recreational cannabis legalization and decriminalization on societies is a topic of global relevance and increasing scientific interest. Despite a rapidly growing body of published evidence, findings remain mostly ...
A.J. Drexel Autism Institute study highlights key challenges and opportunities in transitioning autistic individuals into adulthood
2024-10-17
The Autism Transitions Research Project, funded by the Health Resources and Services Administration and led by Drexel University’s A.J. Drexel Autism Institute, has released new findings that underscore critical challenges and opportunities in transitioning autistic youth into adulthood. As approximately 1.2 million autistic individuals are expected to reach adulthood in the coming decade, these insights are vital for shaping future research and services.
The study, “Challenges and Opportunities in Transitioning Autistic Individuals into Adulthood,” led by Anne M. Roux, a research scientist and director at the Policy Impact Project in the ...