(Press-News.org) The Arctic is threatened by strong climate change: the average temperature has risen by about 3°C since 1979 – almost four times faster than the global average. The region around the North Pole is home to some of the world’s most fragile ecosystems, and has experienced low anthropogenic disturbance for decades. Warming has increased the accessibility of land in the Arctic, encouraging industrial and urban development. Understanding where and what kind of human activities take place is key to ensuring sustainable development in the region – for both people and the environment. Until now, a comprehensive assessment of this part of the world has been lacking.
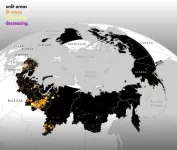
More than 5% of the Arctic show signs of human activity
An international research team led by Gabriela Schaepman-Strub from the Department of Evolutionary Biology and Environmental Studies at the University of Zurich (UZH) has now shed light on this question. Together with US colleagues from NASA and the University of Wisconsin-Madison, the UZH researchers used data of nighttime artificial light observed from satellites to quantify the hotspots and evolution of human activity across the Arctic from 1992 to 2013. “More than 800,000 km2 were affected by light pollution, corresponding to 5.1% of the 16.4 million km2 analyzed, with an annual increase of 4.8%,” says Schaepman-Strub. With the new, standardized approach the researchers were able to spatially assess human industrial activity across the Arctic, independent of economic data.
The European Arctic and the oil and gas extraction regions of Alaska, USA, and Russia were hotspots of human activity, with up to one-third of the land area illuminated. Compared to these regions, the Canadian Arctic was largely dark at night. “We found that, on average, only 15% of the lit area in the Arctic contained human settlements, which means that most of the artificial light is due to industrial activities rather than urban development. And this major source of light pollution is increasing in both area and intensity every year,” says first author Cengiz Akandil, a doctoral student in Schaepman-Strub’s team.
Effects on terrestrial ecosystems and regional sustainability
According to the researchers, these data provide an essential basis for future studies on the impact of industrial development on Arctic ecosystems. “In the vulnerable permafrost landscape and tundra ecosystem, even just repeated trampling by humans, and certainly tracks left by tundra vehicles, can have long-term environmental effects that extend well beyond the illuminated area detected by satellites,” says Akandil.
The negative impacts of industrial activities and light pollution are absolutely critical for the Arctic biodiversity. For example, artificial light at night reduces the ability of Arctic reindeer to adapt their eyes to the extreme blue color of winter twilight, which allows them to find food and escape predators. It also delays leaf coloration and breaking leaf buds, which is critical for the Arctic species where the growing season is limited. Furthermore, human activities foster the expansion of invasive species in the Arctic, and oil and gas extraction frequently lead to environmental pollution – as does the mining industry, which is also expanding.
Documenting industrial activity is crucial for sustainable development
The effects of rapid climate change in the Arctic require local communities to adapt quickly, and the industrial development might further increase the need for adaptation – and enhance the costs on society and the environment. The direct impacts that human activity has on Arctic ecosystems could exceed or at least exacerbate the effects of climate change in the coming decades, the researchers estimate. If the growth rate of industrial development between 1940–1990 is maintained, 50–80% of the Arctic may reach critical levels of anthropogenic disturbance by 2050.
“Our analyses on the spatial variability and hotspots of industrial development are critical to support monitoring and planning of industrial development in the Arctic. This new information may support Indigenous Peoples, governments and stakeholders to align their decision-making with the Sustainable Development Goals in the Arctic,” concludes Gabriela Schaepman-Strub.
END
Rapidly increasing industrial activities in the Arctic
Sustainable development and conservation
2024-10-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scan based on lizard saliva detects rare tumor
2024-10-21
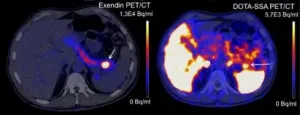
A new PET scan reliably detects benign tumors in the pancreas, according to research led by Radboud university medical center. Current scans often fail to detect these insulinomas, even though they cause symptoms due to low blood sugar levels. Once the tumor is found, surgery is possible.
The pancreas contains cells that produce insulin, known as beta cells. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body absorb sugar from the blood and store it in places like muscle cells. This regulates blood sugar levels. In rare cases, the beta cells malfunction, resulting in a benign tumor called ...
Rare fossils of extinct elephant document the earliest known instance of butchery in India
2024-10-21
During the late middle Pleistocene, between 300 and 400 thousand years ago, at least three ancient elephant relatives died near a river in the Kashmir Valley of South Asia. Not long after, they were covered in sediment and preserved along with 87 stone tools made by the ancestors of modern humans.
The remains of these elephants were first discovered in 2000 near the town of Pampore, but the identity of the fossils, cause of death and evidence of human intervention remained unknown until now.
A team ...
Argonne materials scientist Mercouri Kanatzidis wins award from American Chemical Society for Chemistry of Materials
2024-10-21
Mercouri Kanatzidis, a materials scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory and professor at Northwestern University, will receive the 2025 ACS Award in the Chemistry of Materials from the American Chemical Society, the nation’s leading professional organization of chemists.
The award “recognizes and encourages creative work in the chemistry of materials,” according to the citation.
At Argonne, Kanatzidis’s work has focused on the implications of a ...
Lehigh student awarded highly selective DOE grant to conduct research at DIII-D National Fusion Facility
2024-10-21
When it comes to sustainable energy, harnessing nuclear fusion is—for many—a holy grail of sorts. Unlike climate-warming fossil fuels, fusion offers a clean, nearly limitless source of energy by combining light atomic nuclei to form heavier ones, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process.
But it isn’t easy replicating and controlling the process that powers the sun.
“We eventually want to move to producing energy this way,” says Brian Leard ’21 ’25G, a ...
Plant guard cells can count environmental stimuli
2024-10-21
Plants control their water consumption via adjustable pores (stomata), which are formed from pairs of guard cells. They open their stomata when there is a sufficient water supply and enough light for carbon dioxide fixation through photosynthesis. In the dark and in the absence of water, however, they initiate the closing of the pores.
SLAC/SLAH-type anion channels in the guard cells are of central importance for the regulation of the stomata. This has been shown by the group of Professor Rainer Hedrich, biophysicist at Julius-Maximilians-Universität ...
UAMS researchers find ground beef packs bigger muscle-building punch than soy-based alternative
2024-10-21
When it comes to building muscle, not all proteins are created equal.
New research from the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) reveals that 100% ground beef packs a bigger punch for muscle protein synthesis than a soy-based counterpart. In fact, the study suggests that a person would need double the amount of soy-based protein to achieve the same results.
Published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the study examined the anabolic response — how the body builds muscle — after consuming a 4-ounce beef patty versus one or two 4-ounce patties of a soy-based product. The results? Just one serving of beef did the ...
Study: AI could transform how hospitals produce quality reports
2024-10-21
A pilot study led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that advanced artificial intelligence (AI) could potentially lead to easier, faster and more efficient hospital quality reporting while retaining high accuracy, which could lead to enhanced health care delivery.
The study results, published in the October 21, 2024 online edition of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) AI, found an AI system using large language models (LLMs) can accurately process hospital quality measures, ...
Four U-M faculty elected to National Academy of Medicine
2024-10-21
Four University of Michigan faculty have been elected to the National Academy of Medicine, one of the highest honors in medical research.
Kenneth M. Langa, M.D., Ph.D., Erica E. Marsh, M.D., MSCI, FACOG, Santa J. Ono, Ph.D. and Marc A. Zimmerman, Ph.D., are among 100 newly elected health and medical scientists recognized for their outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
They join the 79 other current, former and late U-M faculty who have earned this distinction. NAM members help the Congressionally chartered, private nonprofit organization provide objective advice to the nation on key health ...
FSU College of Medicine research team connects loneliness with heightened risk of dementia in largest study of its kind
2024-10-21
New research led by Florida State University College of Medicine faculty quantified the association between loneliness and dementia by analyzing data from more than 600,000 people around the world — the largest study of its kind.
The meta-analysis of 21 longitudinal studies showed that experiencing feelings of loneliness increased the risk of developing dementia by 31%. The research was published in Nature Mental Health.
“These results are not surprising, given the mounting evidence that link loneliness to poor health,” said Assistant Professor Martina Luchetti, who led the study. “Dementia ...
Berry studying nitrogen vacancy diamond metrology for temperature and pressure sensing
2024-10-21
Tyrus Berry, Assistant Professor, Mathematics, College of Science, received funding for the project: “Nitrogen Vacancy Diamond Metrology for Temperature and Pressure Sensing: Data Assimilation.”
Berry aims to provide the mathematical tools for a robust sensor that can simultaneously measure temperature, pressure, and force over a long range of values in harsh environments.
The sensor readings will be tied to fundamental physics laws, and the mathematical framework will automatically track any drift in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Rapidly increasing industrial activities in the ArcticSustainable development and conservation