(Press-News.org) ATLANTA, Oct. 23, 2024 -- Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes has joined with UL Standards and Engagement to release new guidance for communities at risk for fires in wildland-urban interface (WUI) areas. An estimated 70,000 communities and 45 million residential buildings are at risk of destruction caused by wildfires. Additionally, WUI fires pose significant health risks. The smoke emitted by WUI fires likely contains a mixture of contaminants such as combustion gases, organic and inorganic metal complexes, volatile organic compounds and numerous reaction products. WUI wildfire plumes carry the risks of inhalation of dust and ash, ingestion of contaminated water and absorption of contaminants through dermal contact.
This new guidance “UL 200C Guidance and Practical Strategies for Reducing Public Health Impacts of Wildland-Urban Interface Fires on Community Populations” (the Guide), offers ways for homeowners, building managers, and the public to prepare, respond, and recover from these fire events, while protecting the health of their families and building occupants.
“Wildfires in the United States are becoming larger, more frequent, more destructive, and more toxic,” said Marilyn Black, Ph.D., Vice President and Senior Technical Advisor for CIRI. “In addition to combustion products of forest biomass, synthetic materials from our homes, buildings and cars are adding heavily-polluted air emissions — and residues that contain toxicants, such as carcinogens, and neurotoxins — to our atmosphere. Taking steps to reduce exposure is critical to protecting the current and future health of people, and this Guide is a strong step forward.”
To create the Guide, a unique task force was formed — known as the Protecting Community Health (PCH) Task Force — which convened over several months and arrived at a consensus to formulate this guidance, designed for communities impacted by fire events and conditions.
“The task force felt this Guide was a public health necessity,” said Christopher P. Weis, Ph.D., Principal and Science Director of Weis Toxicology and a member of the task force. “With millions of people being affected by these disasters, including children and populations with limited resources, this timely information will assist public health officials, community planners, and neighborhoods as they help keep homes, buildings, families and citizens safe.”
Topics covered by the Guide include: An overview of WUI fires; Understanding risk before a WUI fire; Protecting indoor air quality; Steps to protecting a home or building; What to do during a WUI fire; Cleaning strategies to mitigate dangerous exposures; and Steps to monitor air and water quality.
The complete Guidance Document can be found at: UL200C_Public-Health-Impacts-of-WUI-Fires.pdf (wildfirehealthrisks.org).
Learn more about CIRI at chemicalinsights.org.
# # #
About Chemical Insights Research Institute
Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes is a nonprofit organization dedicated to scientific research, publication, education, and communication on environmental exposures resulting from technologies and practices, their impact on human health, and processes for reducing health risks. CIRI provides actionable data and resources to help manufacturers, educators, healthcare providers, and consumers make informed environmental health decisions and risk reduction strategies for the protection of human health.
About UL Research Institutes
UL Research Institutes is a nonprofit research organization dedicated to advancing public safety through scientific discovery. Since 1894, our research has advanced our mission toward a safer, more secure and sustainable future. Focused on global risks from fire mitigation and air quality to safe energy storage and digital privacy, we conduct rigorous independent research, analyze safety data and partner with experts to uncover and act on existing and emerging risks to human safety. Discover more at UL.org.
Media Contact
Bert Kelly
Chemical Insights Research Institute
Bert.kelly@ul.org
END
(Boston, MA) — Concussion researchers have recognized a new concussion sign that could identify up to 33% of undiagnosed concussions. After a hit to the head, individuals sometimes quickly shake their head back and forth. Although it has been depicted in movies, television, and even cartoons for decades, this motion has never been studied, named, and does not appear on any medical or sports organization’s list of potential concussion signs. A new study, led by Concussion Legacy Foundation (CLF) CEO and co-founder Chris Nowinski, PhD, says it should.
The study, published today in Diagnostics, reveals that when athletes exhibit this movement, ...
PULLMAN, Wash. – As athletes prepare to dive into Hawaiian waters for the first part of the IRONMAN World Championship on Oct. 26, they may want to pay a little extra attention to the water inside their bodies.
Contrary to previous research, a Washington State University-led study of three decades of the IRONMAN’s top competition found a connection between dehydration and exercise-induced muscle cramps.
Based on medical data of more than 10,500 triathletes, the study, published in the Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, found a strong link between dehydration and participants seeking treatment for muscle cramps during the competition. ...
Images of coastal houses being carried off into the sea due to eroding coastlines and powerful storm surges are becoming more commonplace as climate change brings a rising sea level coupled with more powerful storms. In the U.S. alone, coastal storms caused $165 billion in losses in 2022.
Now, a study from MIT shows that protecting and enhancing salt marshes in front of protective seawalls can significantly help protect some coastlines, at a cost that makes this approach reasonable to implement.
The new findings are being reported in the journal Communications ...
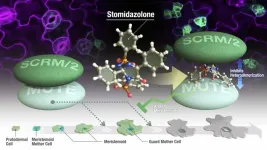
Researchers from Nagoya University Institute of Transformative Biomolecules (WPI-ITbM) in Japan and their colleagues have identified and derivatized a chemical compound that effectively regulates the density of stomata in model plants. Stomata are crucial for water regulation. As the environment grows increasingly unpredictable, managing water consumption for crops during droughts through chemical methods will become increasingly important. The results of their study were published in Nature Communications.
Manipulating protein interactions using chemical compounds is revolutionizing ...
“While exposure to persecution, war and displacement is associated with high rates of psychological disorders, such as PTSD and depression, remarkably the majority of refugees, despite having gone through very difficult experiences, don’t go on to develop a psychological disorder,” says Prof. Nickerson, Director of the Refugee Trauma and Recovery Program at UNSW’s School of Psychology.
Despite this, previous research has focused on trying to understand factors that predict psychopathology or psychological distress, rather than factors that ...
Tea is a significant global commodity, with an industry worth tens of billions of dollars and growing. However, its production—both in terms of quantity and quality—is highly sensitive to climate variations, particularly in the context of long-term human-induced global warming and its associated shorter-term impacts such as extreme weather events.
To tackle this challenge, a collaborative initiative between UK and Chinese scientists and tea industry stakeholders has been launched. This project, known as “Tea-CUP” ...
Women are more likely to receive good care during pregnancy where AI and other clinical software tools are used, a large review of research has found.
In a paper published in eClinicalMedicine researchers have conducted a review of over 12,000 papers and 87 articles for different AI and related software tools, investigating the impact of their use in maternity settings. A meta-analysis of 35 included studies found the odds of improved outcomes was 1.69 times higher in women cared for using CDSS, with data from over 5.2 million pregnancies in both High-Income and ...
The British Sleep Society has released a position statement in the Journal of Sleep Research advocating for the abolition of the twice-yearly clock changes in the UK and the restoration of permanent Standard Time (Greenwich Mean Time). This recommendation is based on scientific evidence highlighting the adverse effects of the clock change and Daylight Saving Time (DST) on sleep and circadian health.
The British Sleep Society emphasizes that sleep is central to health and well-being and the enforced changes of clock time to DST can interfere negatively with sleep regulation. “What we often don’t realize is that DST changes our schedules, moving them ...
Animal tracking studies for ecology and conservation all face technological limitations such as high costs or the need for tags to remain in close proximity to detectors. In research published in Methods in Ecology and Evolution, investigators describe a solution that can overcome many current limitations by employing the massive global network of personal mobile phones as gateways for tracking animals using Bluetooth low energy beacons.
In areas with medium to high density of people, these simple, lightweight, and inexpensive beacons can provide regular updates of position with a battery life of 1–3 years. Through field testing ...
In research published in the British Journal of Social Psychology, investigators examined the relationship between countries’ parental leave policies and young adults’ perceptions of social norms for the division of childcare duties between mothers and fathers.
In the study of 19,259 university students (11,924 women) from 48 countries, the degree to which participants believed childcare is equally divided among mothers and fathers and the degree to which they believed childcare should be equally divided were both stronger when parental leave was available in their particular country.
Analyses of time since policy change suggested ...