Pitchers rejoice? Plasma irradiation might prevent tendon re-tears
Next-generation regenerative treatment shows promise in medicine-engineering collaboration
2024-10-25
(Press-News.org)
The human body, filled with muscles and moving parts, is far from indestructible. Injuries are common, especially where tendons and bones connect. In Japan, rotator cuff tears affect approximately 1 in 4 people over age 50, and reports state that even after surgery, about 20% of cases result in re-tears. To combat this, new healing methods to bolster current clinical practices are needed.
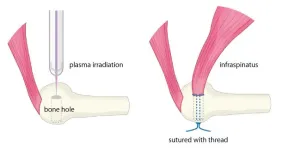
Graduate student Katsumasa Nakazawa, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda, and then Professor Hiroaki Nakamura at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine, along with Graduate School of Engineering Professor Jun-Seok Oh and colleagues have previously reported positive results using non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma for bone and tendon repairs. This time, the team used plasma on rotator cuffs of rabbit models to examine the healing rate and strength of the repair.
The study consisted of two groups, a control and a 5-minute plasma irradiation group where rotator cuffs were detached, irradiated, and then sutured. The histology and mechanical strength differences were compared and examined at intervals of two, four, and eight weeks. The results showed that the plasma irradiation group had a tissue arrangement similar to that of a normal tendon-bone junction after four and eight weeks.
It was also found that more bone tissue was formed than in the control group. In biomechanical testing, the force required to break the plasma irradiated rotator cuff after eight weeks was close to the strength for an undamaged one.
“If the results of this research can be applied to current clinical practices, it may be possible to contribute to more reliable rotator cuff repairs and a reduction in the rate of re-tears,” stated Professor Toyoda. “Furthermore, by introducing this technology to sports medicine, it is expected to speed up athletes’ recovery and improve their performance.”
The findings were published in the Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-25
San Diego, CA (October 24, 2024) — Investigators recently uncovered key insights into newly defined rejection entities in kidney transplantation that may offer improved patient risk categorization post-transplant. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
Kidney transplant rejection continues to threaten the long-term success of kidney transplants, with microvascular inflammation (inflammation within capillaries) playing a pivotal role in graft failure. Due to its complex nature, this inflammation poses a major challenge in clinical practice. In response, the international Banff classification—the ...
2024-10-24
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 06.30pm [US ET] Thursday 24th October 2024**
Peer reviewed / Literature review, systematic review and meta-analysis, opinion / People
Embargoed access to the Commission report and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
The Lancet Public Health: New Commission calls for regulatory reform to tackle the health impacts of the rapid global expansion of commercial gambling
Gambling harms are far more substantial than previously understood, exacerbated by rapid global expansion ...
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown that they can accurately re-create clinical trials of new treatments using ‘digital twins’ of real cancer patients. The technology, called FarrSight®-Twin, which is based on algorithms used by astrophysicists to discover black holes, will be presented today (Friday) at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
The researchers say that this approach could be used by cancer ...
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown for the first time that it is possible for a specially-designed ‘mini-protein’ to deliver a radiation dose directly to tumour cells expressing a protein on their cell surfaces called Nectin-4, which is often found in a number of different cancers.
In a study presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain, Mike Sathekge, Professor and Head of the Nuclear Medicine Department at the University of Pretoria ...
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Patients with advanced bladder cancer that had spread to other parts of the body (metastasised) have responded well in a phase I clinical trial of an investigational drug, TYRA-300. The drug targets changes in the FGFR3 gene that drive tumour growth in about 10%-20% of these patients.
Associate Professor, Ben Tran, a medical oncologist at Peter McCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia, presented the first results as of 15 August 2024 from 41 patients enrolled in the SURF301 study in a late-breaking oral presentation at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics ...
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have discovered key mutations in certain cancer cells that make them resistant to WRN inhibitors, a new class of anti-cancer drugs. The yet-to-be-published findings are presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
Werner helicase (WRN) inhibitors are already being evaluated in phase I clinical trials in patients with tumours that have microsatellite instability (MSI) – a condition in which the genes responsible for monitoring and repairing mistakes in DNA replication stop functioning, and errors are introduced. This is also ...
2024-10-24
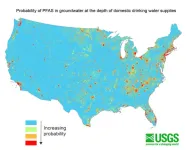
PEMBROKE, N.H. — Approximately 71 to 95 million people in the Lower 48 states – more than 20% of the country’s population – may rely on groundwater that contains detectable concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, also known as PFAS, for their drinking water supplies. These findings are according to a U.S Geological Survey study published Oct. 24.
The predictive model results can help members of the public, water suppliers and regulators understand the potential for PFAS contamination, guide future studies and inform strategic planning for water resources.
USGS scientists are the first to ...
2024-10-24
New Zealand’s native stoneflies have changed colour in response to human-driven environmental changes, new research shows.
Just published in the journal Science, the University of Otago study provides arguably the world’s most clear-cut case of animal evolution in response to change made by humans.
Co-author Professor Jon Waters, of the Department of Zoology, says the stonefly has become a different colour due to recent deforestation.
“In natural forested regions, a native species has evolved ‘warning’ colours that mimic those of a poisonous forest species, to trick predators into ...
2024-10-24
As renewable energy sources such as wind and solar become more widespread, managing the power grid has become increasingly complex. Researchers at the University of Virginia have developed an innovative solution: an artificial intelligence model that can address the uncertainties of renewable energy generation and electric vehicle demand, making power grids more reliable and efficient.
Multi-Fidelity Graph Neural Networks: A New AI Solution
The new model is based on multi-fidelity graph neural networks (GNNs), ...
2024-10-24
One in five children has an identified mental health problem as early as age 3. Early detection is key to earlier intervention, and it also could prevent more severe conditions down the line, such as ADHD, depression and anxiety. Pediatric primary care is an ideal setting to conduct screening for mental health risk, given that pediatricians tend to have close, ongoing relationships with young patients and their families, and broad reach to historically marginalized communities. Since mental health screening of toddlers in primary care is uncommon, it is important to train pediatricians to do so without implicit bias and in a way that prevents unintended ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pitchers rejoice? Plasma irradiation might prevent tendon re-tears
Next-generation regenerative treatment shows promise in medicine-engineering collaboration