The results of numerous high-impact phase 3 clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23–27.
Hyponatremia, or a chronically low blood salt level, is the most common electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients, and is associated with higher risks of death and re-hospitalization. In a recent trial, 2,173 hospitalized patients with hyponatremia from 9 centers across Europe were assigned to undergo either targeted correction of blood salt levels according to guidelines or to receive routine care for hyponatremia. The primary outcome was the combined risk of death or rehospitalization within 30 days of study inclusion. During the trial, 60.4% patients in the targeted group reached normal blood salt levels, compared with 46.2% patients in the control group. Within 30 days, 8.6% and 13.0% of patients in the intervention group died or were re-hospitalized, respectively, compared with 8.5% and 14.0% of patients in the control group, leading to a combined event rate of 21.0% in the intervention group and 22.2% in the control group. “Better correction of hyponatremia did not lead to an improvement in mortality and hospitalization rates,” said corresponding author Julie Refardt, MD, PhD, of Erasmus MC, in The Netherlands. “Therefore, in hospitalized patients, hyponatremia seems to be rather a marker of worse outcome instead of its cause.”
Impact of Targeted Hyponatremia Correction on 30-Day Mortality and Rehospitalization Rate
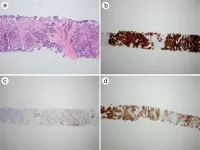
The randomized VALIANT trial investigated the efficacy and safety of pegcetacoplan, a complement inhibitor, in adolescents and adults with native (before transplant) or post-transplant recurrent complement 3 glomerulopathy or primary immune complex–mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. In the trial, 63 patients received pegcetacoplan and 61 received placebo for 6 months. Pegcetacoplan reduced proteinuria (elevated protein in the urine, which is a sign of kidney dysfunction) by 68.3% compared with placebo. “The results were consistent across patients with different characteristics,” said corresponding author Carla M. Nester, MD, of the University of Iowa. “In addition, pegcetacoplan demonstrated favorable safety across native and post-transplant populations.”
VALIANT: A Randomized, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo (PBO)-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial of Pegcetacoplan for Patients with Native or Post-transplant Recurrent Glomerulopathy (C3G) or Primary Immune Complex Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (IC-MPGN)
Compared with placebo, semaglutide (a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist) significantly reduced the risks of major kidney outcomes, cardiovascular events, and death from any cause in adults with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the FLOW trial. In a recent analysis of data on 3,533 participants, investigators assessed whether kidney outcomes differed based on individuals’ kidney function at the start of the trial. “We found that the benefit on kidney outcomes was consistent regardless of CKD severity at study entry,” said corresponding author Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle. “Ongoing studies are investigating the mechanisms of kidney protection by semaglutide, and whether semaglutide is also safe and efficacious for CKD in persons with type 1 diabetes or those without diabetes.”
Semaglutide Reduced Risks of Major Kidney Outcomes Irrespective of CKD Severity in the FLOW Trial
Chronic pain is common among people receiving maintenance hemodialysis for kidney failure, but treatment options are limited due to unacceptable toxicities of many pain medications. The “HOPE Consortium Trial to Reduce Pain and Opioid Use in Hemodialysis”, funded by the NIH Helping to End Addiction Long-term® Initiative (NIH HEAL Initiative®) and administered by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, was a multicenter, randomized clinical trial of Pain Coping Skills Training, a non-pharmacologic cognitive behavioral therapy intervention designed to increase self-efficacy for managing pain. The trial, which enrolled 643 participants at 16 centers and 103 outpatient dialysis facilities, showed that the intervention had benefits on the primary outcome of pain interference (a measure of the effects of pain on activities, mood, and relationships) and on several secondary outcomes including depression, anxiety, and quality of life. “Future work will focus on how to best broadly implement this intervention in the dialysis setting,” said corresponding author Laura M. Dember, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine.
Pain Coping Skills Training for Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: The HOPE Consortium Randomized Clinical Trial
Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are a preferred method for initial vascular access in patients requiring hemodialysis, but failure of AVF maturation can occur in some patients. In a trial of 242 patients with hemodialysis undergoing surgical vascular access creation, half of the patients were randomized to Humacyte's acellular tissue engineered vessel (ATEV), a bioengineered human tissue that can be used for repairing and replacing blood vessels and for hemodialysis access. The ATEV group had higher success rates in maintaining 6-month functional patency (81% versus 68%) and 12-month secondary patency (68% versus 62%) compared with traditional AVFs, especially in female, diabetic, and obese patients. “These findings suggest that ATEV could be a reliable option for vascular access for these subgroups with high risk of AVF failure, without compromising safety,” said corresponding author Mohamad A. Hussain, MD, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital. “Next steps include the sponsor discussing the potential pathway to pursuing approval with the US Food and Drug Administration, and an ongoing trial, CLN-PRO-V012, where use of ATEV versus AVF is being studied in female dialysis patients, a high unmet need population.”
Prospective Randomized Trial of Humacyte's Acellular Tissue Engineered Vessel vs. Autologous ArteriovenousFistula for Hemodialysis Access
Dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, improves kidney health in patients with CKD, but there is uncertainty about the extent of its effects when started after CKD has progressed to later stages. In the Dapagliflozin and Renal Surrogate Outcomes in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease (DAPA advKD) trial, 180 patients with stages 4 and 5 CKD were randomized 2:1 to dapagliflozin plus integrated CKD care or integrated CKD care alone. Over a median of 1.62 years, average estimated glomerular filtration rate slopes were -2.24 and -3.67 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the dapagliflozin and control groups, respectively, indicating a slower reduction in kidney function in the dapagliflozin group. The dapagliflozin group also had lower rates of kidney and cardiovascular outcomes such as acute kidney injury and heart failure. “Our study focused on patients with advanced chronic kidney disease to test whether dapagliflozin can still benefit those with severely reduced kidney function. We found that this medication helped slow the decline in kidney function and reduced the need for dialysis or other advanced treatments,” said corresponding author Yi-Wen Chiu, MD, of Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, in Taiwan. “Our next steps are to continue studying its long-term safety and effectiveness in this group.”
Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with CKD Stages 4-5
Join ASN and approximately 12,000 other kidney professionals from across the globe at Kidney Week 2024 in San Diego, CA. The world's premier nephrology meeting, Kidney Week, provides participants with exciting and challenging opportunities to exchange knowledge, learn the latest scientific and medical advances, and listen to engaging and provocative discussions with leading experts in the field. Early programs begin on October 23, followed by the Annual Meeting from October 24-27. Follow the conversation at #KidneyWk.
About ASN
Since 1966, ASN has been leading the fight to prevent, treat, and cure kidney diseases throughout the world by educating health professionals and scientists, advancing research and innovation, communicating new knowledge and advocating for the highest quality care for patients. ASN has nearly 21,000 members corresponding 140 countries. For more information, visit www.asn-online.org and follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn, and Instagram.
# # #
END