(Press-News.org) Pioneering research to protect and conserve Arctic whale populations is to begin under a new five-year collaboration between Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions), a world leader in travel exploration.
The partners have signed a five-year Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), beginning in 2024, to research challenges facing marine life in the high Arctic – the most northern part of the Arctic region and one of the world’s most fragile ecosystems.
The agreement will see Heriot-Watt University and HX work together on the Whales & Arctic Vessels Project (WAVE), a collaboration driven by the urgent need to better understand how often and where whales are encountering vessels in the high Arctic, and how whales are responding to these interactions – an area of research that remains largely unexplored.
“We have very little understanding about how frequently Arctic whales are encountering vessels in the high Arctic and how they may be impacted by these interactions,” explained project lead Dr Lauren McWhinnie, an Assistant Professor at Heriot-Watt’s School of Energy, Geoscience, Infrastructure and Society.
“We know in other areas of the world that whales can be affected by vessels in a variety of ways, from exposure to underwater noise to being physically stuck or disturbed. As vessel activity increases in the Arctic, it's important that we work with industry, policy makers and communities to ensure that the maritime sector is operating in a responsible and sustainable manner and is not placing any further pressure on these animals whose habitat is significantly changing due to climate change.”
Heriot-Watt University is the first UK university to partner with HX in a project of this scale. The collaboration will see the two organisations jointly publish findings, delivering impact reports and scientific results that will further the understanding of the pressures on Arctic whale populations and contribute to global conservation efforts.
The partnership will harness HX’s extensive expedition network and will benefit vastly from the company’s ability to engage both guest passengers and the wider public in this important environmental research. Heriot-Watt’s researchers will benefit from access to multiple vessels within the fleet, enabling scientists to conduct multi-year data collection in areas rarely surveyed. Passengers aboard HX ships on planned commercial voyages will also have the opportunity to participate in citizen science programmes, both contributing valuable data and allowing them to see how their contributions can make a difference.
Dr Verena Meraldi, Chief Scientist for HX, said the research would help improve our understanding of the pressures on Arctic whales and enrich the knowledge and experience HX can provide to its guests.
“As Chief Scientist for HX, I have the honour of working alongside various scientists across different disciplines to get a deeper understanding of the processes governing our planet, and the impact we (as humans) are having on it,” Dr Meraldi said. “Conveying this to our guests and getting them involved in projects such as WAVE is exactly the kind of project we look to support. We hope by supporting this project we will support further knowledge and understanding of Arctic whales, and also enrich the journeys and mindset of our guests. This MoU represents a vital collaboration between academia and industry, aiming to advance the scientific understanding of Arctic ecosystems, while making a tangible contribution to whale conservation in the region.”
The collaboration aims to promote global awareness and support the conservation of Arctic whale species, while gathering critical data to inform and support evidence-based management strategies. WAVE also seeks to foster academic growth in marine sciences by supporting and developing the next generation of researchers.
With increasing vessel activity being documented in the Arctic, it is crucial for academia to work alongside industry partners, policymakers, and local communities to ensure that both future and current use of this marine space takes place in a responsible and sustainable manner, the scientists say. This is particularly important given the significant changes to the habitat of Arctic whales, caused by climate driven sea ice reductions, and the need to avoid adding further pressures on these vulnerable species.
Dr McWhinnie said: “When we are working to conserve whales, we are so often on the back foot – reacting to deal with a problem that is already having a documented impact. What’s incredibly exciting about this research is that we are being more proactive, trying to make sure an impact doesn’t occur, and learning from lessons we’ve seen arise elsewhere. As a researcher this is a truly fantastic opportunity to bring about a positive change, and I’m incredibly excited to work with our partners, HX Hurtigruten Expeditions, to ensure that future vessels visiting the Arctic will have a minimal impact on these incredible animals.””
END
Arctic whales research collaboration is signed by Heriot-Watt University and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions)
Project will study where and how often whales encounter vessels in the high Arctic
2024-10-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists develop tool to predict sepsis in apparently healthy newborns
2024-10-29
A genetic signature in newborns can predict neonatal sepsis before symptoms even start to show, according to a new study.
The study, led by UBC and SFU researchers in collaboration with the Medical Research Council (MRC) Unit The Gambia, has the potential to help healthcare workers diagnose babies earlier, including in lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where neonatal sepsis is of particular concern. The research, published today in eBiomedicine, is funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
“Neonatal sepsis is caused by the body’s irregular response ...
AI algorithm accurately detects heart disease in dogs
2024-10-29
Researchers have developed a machine learning algorithm to accurately detect heart murmurs in dogs, one of the main indicators of cardiac disease, which affects a large proportion of some smaller breeds such as King Charles Spaniels.
The research team, led by the University of Cambridge, adapted an algorithm originally designed for humans and found it could automatically detect and grade heart murmurs in dogs, based on audio recordings from digital stethoscopes. In tests, the algorithm detected heart murmurs with a sensitivity ...
What animal societies can teach us about ageing
2024-10-29
Red deer may become less sociable as they grow old to reduce the risk of picking up diseases, while older house sparrows seem to have fewer social interactions as their peers die off, according to new research which shows humans are not the only animals to change our social behaviour as we age.
A collection of 16 studies, including six from the University of Leeds, have been published today as part of a special issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, investigating ageing and society across the natural world.
One study into red deer shows that ...
Enhancing the accuracy of wearables that measure blood glucose levels
2024-10-28
Diabetes is an increasingly pervasive disease, currently affecting over 500 million adults worldwide. Since there is as yet no cure for type 1 or type 2 diabetes, patients must regularly monitor their BGLs to keep them in check. Though BGL-measuring devices relying on painful finger pricks have been the gold standard for decades, modern technology is slowly opening doors to better alternatives.
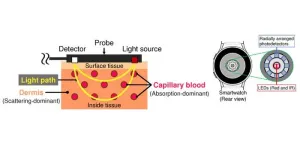
Many researchers have proposed noninvasive methods to monitor BGLs using widely available wearable devices, such as smartwatches. For example, by placing the LEDs ...
Increasing social supports for new mothers with opioid use disorder
2024-10-28
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a growing public health problem among pregnant and parenting people in the U.S. Between 1999 and 2014, the number of pregnant women with OUD increased by more than four times. This trend also coincides with a rise in pregnancy-associated maternal overdose mortality.
Researchers at Thomas Jefferson University, led by Meghan Gannon, PhD, MSPH, investigated how community-based supports, like doulas, can be integrated into health care for mothers who use opioids. Using a social network analysis, ...
Mitigating the neurotoxic effects of lead exposure
2024-10-28
Lead exposure is a risk to any human, but children are most vulnerable to the element’s neurotoxicity, which can lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties and mood changes among other symptoms. There has been some progress in reducing exposure and preventing neurotoxicity, but hundreds of thousands of American children are still affected.
A new study by Thomas Jefferson University neuroscientist Jay Schneider, PhD, suggests that the toxic effects of lead can be mitigated by attentive maternal care and an enriched environment ...
Developing kidneys from scratch
2024-10-28
To Alex Hughes, Assistant Professor in Bioengineering within Penn Engineering and in Cell and Developmental Biology within Penn Medicine, the kidney is a work of art. “I find the development of the kidney to be a really beautiful process,” says Hughes.
Most people only ever see the organ in cross-section, through textbooks or by dissecting animal kidneys in high school biology class: a bean-shaped slice with lots of tiny tubes. “I think that really undersells how amazing the structure is,” says ...
Airbnbs associated with more crime in London, new study shows
2024-10-28
Since its founding in 2008, the short-term homestay platform Airbnb has expanded to 100,000 cities in more than 220 countries, and, according to data from the company, 1.5 billion guests had stayed in Airbnb-listed properties through 2023.
Much of the academic research on Airbnb activity comes from economics and business literature and focuses on housing-supply impacts, says David Kirk, professor of criminology at the University of Pennsylvania. Yet research on neighborhood impacts is limited, and that research neglects the impacts of Airbnb activity on measures of community cohesion and safety.
Kirk teamed with University of Cambridge criminologist ...
New study finds invasive plants drive homogenization of soil microbial communities across U.S.
2024-10-28
Invasive plants are doing more than just taking over landscapes — they’re also changing the soil beneath them. A new study co-authored by Matthew McCary, assistant professor of biosciences at Rice University, reveals that these species are reshaping soil microbial communities across the U.S., making them more uniform and altering how ecosystems function. The findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Oct. 24, shed light on the far-reaching impacts of invasive plants, which extend beyond what we see above ground.
The ...
Researchers’ new outreach strategy succeeds, sets blueprint for detecting invasive species in Florida
2024-10-28
Invasive species in Florida like Nile monitors and Argentine black-and-white tegus pose a growing threat to the Sunshine State’s environment, economy and public safety. South Florida’s warm climate, disturbed habitats and bustling pet trade have made it a hotspot for these non-native, cryptic reptiles. However, finding these elusive creatures has always been a challenge – until now.
University of Florida researchers are showcasing how a focused outreach initiative in Palm Beach County has led to a successful increase in reports of invasive reptiles in Florida. The findings are documented in the latest study published in Scientific Reports and authored by researchers at UF/IFAS ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] Arctic whales research collaboration is signed by Heriot-Watt University and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions)Project will study where and how often whales encounter vessels in the high Arctic