Development of a simple, revolutionary printing technique for periodic nano/microstructures
2024-10-31
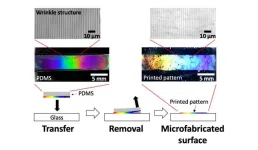
(Press-News.org) 1. A team of researchers from NIMS and the University of Connecticut has developed a printing technique capable of forming a periodic nano/microstructure on the surface of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) slab and easily transferring it onto the surface of a glass substrate. This technique enables us to create materials with useful functions—including water-repellency and the ability to generate structural colors—without expensive equipment and complex processes. In addition, the technique may be used to fabricate materials capable of realizing anti-fogging and/or generating structural colors on their surfaces—functions potentially useful in the development of innovative gas sensors.
2. Due to their diverse functional capabilities, periodic nano/microstructures have long been a focus of research and development in materials science. Fabricating them using conventional techniques is, however, a lengthy process requiring the use of large, expensive equipment. In addition, these techniques are unsuitable for creating periodic nano/microstructures over large surface areas. Although this could be achieved using existing printing technologies, inks suitable for forming periodic nano/microstructures and methods of refilling them are still being explored. A simple technique for fabricating periodic nano/microstructures was therefore highly demanded.
3. This research team recently developed an easy, repeatable technique for printing a periodic nano/microstructure on a glass substrate surface using a PDMS slab. A PDMS slab contains liquid PDMS which functions as an ink when it is exuded from the slab’s surface. The slab is able to form a periodic wrinkled structure on its surface. This can then be transferred to a glass surface by bringing the PDMS slab into contact with the glass surface and then removing it, leaving the periodic nano/microstructure behind. Other types of periodic nano/microstructures can be printed on the surface of a glass substrate in addition to winkle structure, such as columnar and wavy structures. Moreover, other substances (e.g., silicone oils and silica nanoparticles) can be dispersed in liquid PDMS, allowing the resulting periodic nano/microstructures to have properties desirable for a variety of intended purposes.
4. Using this newly developed printing technique, the team hopes to create periodic nano/microstructures that can be used to satisfy social demands by realizing anti-fogging or generating structural colors on their surfaces—functions potentially useful in the development of innovative gas sensors. The technique could also be used to fabricate superhydrophobic and superoleophobic surfaces and materials useful in atmospheric water harvesting. To achieve these goals, the team first plans to optimize the experimental conditions under which it can produce various forms of printable periodic nano/microstructures.
***
5. This project was carried out by a research team led by Kota Shiba (Principal Researcher, Research Center for Macromolecules and Biomaterials, NIMS) and Luyi Sun (Professor, University of Connecticut).
6. This research was published in Advanced Science, an open access journal, on August 29, 2024.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-31
Reports of drug-related supply-chain issues were 40% less likely to result in drug shortages in Canada versus the United States, according to a new study from University of Pittsburgh researchers and published today in JAMA.
The analysis looked at drugs that had reports of supply-chain disruptions between 2017 and 2021 in both countries and found that within 12 months of an initial U.S. report, nearly half resulted in drug shortages in the U.S. versus about one-third in Canada. There was also a consistently lower ...
2024-10-31
About The Study: Drug-related reports of supply chain issues were 40% less likely to result in meaningful drug shortages in Canada compared with the U.S. These findings highlight the need for international cooperation between countries to curb the effects of drug shortages and improve resiliency of the supply chain for drugs.
Quote from corresponding author Katie J. Suda, PharmD, MS:
“Our U.S. drug supply chain is linked globally – shortages in one country can happen in another country – presenting an opportunity to compare and ...
2024-10-31
About The Study: The results of this prospective cohort study suggest that evidence-based smoking cessation treatment within 6 months following a cancer diagnosis maximizes survival benefit. This study supports smoking cessation as an important early clinical intervention for patients after being diagnosed with cancer.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul M. Cinciripini, PhD, email pcinciri@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
2024-10-31
HOUSTON ― Smokers who are diagnosed with cancer now have more incentive to quit, as researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have found survival outcomes were optimized when patients quit smoking within six months of their diagnosis.
Study results, published today in JAMA Oncology, found a 22%-26% reduction in cancer-related mortality among those who had quit smoking within three months after tobacco treatment began. The best outcomes were observed in patients who started tobacco treatment within six months of a cancer diagnosis and were abstinent from smoking three months later. Survival for these patients increased from 2.1 years for ...
2024-10-31
CONTACT: Heide Aungst
HAungst@som.umaryland.edu
(216) 970-5773 (cell)
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11 am on OCT. 31
Genomic Databases Need More Diversity
University of Maryland School of Medicine Researchers Create Large Database of Latin American Populations to Tackle Health Disparities
BALTIMORE, Oct. 31, 2024: It is commonly known that most genomic databases are biased toward people with European ancestry. Scientists have warned that leaving out other populations could skew results in areas such as drug development, ...
2024-10-31
Recent rules that require all new building and road projects in England to address and offset their impact on nature are excellent in principle but flawed in their implementation, leading environmental economists argue.
Under Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG), which became law this year, new building or infrastructure developments must achieve a 10% net gain in biodiversity or habitat.
In a new study published in One Earth, experts criticise the implementation of the policy which forces the majority of off-setting to occur within or near development sites rather than where it might most ...
2024-10-31
INDIANAPOLIS – Although much rarer than either breast or prostate cancers, testicular cancer is the most common solid tumor in males between the ages of 15 and 35, with approximately 10,000 young men diagnosed annually in the United States.
With the goals of informing surgical management, improving long-term outcomes and lowering death rates of patients with testicular cancer, a study led by urologist and health services researcher Clint Cary, M.D., MPH, MBA, of the Indiana University School of Medicine and the Regenstrief ...
2024-10-31
Dr. Chani Traube, the Gerald M. Loughlin, MD Professor of Pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been awarded a $3.4 million grant, with the possibility of extending to a total of $17 million over five years, from the National Institutes of Health, for a large-scale clinical trial called Optimizing Pain Treatment in Children on Mechanical ventilation (OPTICOM).
OPTICOM, funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, is part of the NIH’s HEAL KIDS PAIN initiative. The OPTICOM study will enroll 644 children in 14 pediatric intensive care units across the United States that are part of the institute’s ...
2024-10-31
The Chan Zuckerberg Biohub San Francisco (CZ Biohub SF) and The 15 White Coats, Inc., have launched two initiatives that will provide travel grants as well as coursework in metagenomic sequencing and genomic epidemiology to aspiring physicians from underrepresented groups. CZ Biohub SF is one of a group of research institutes created and supported by the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI).
The new initiatives are driven by CZ Biohub SF’s Rapid Response Team, which offers training, tools, and technologies to help build sustainable scientific relationships—with a special emphasis on the use of genomic sequencing platforms for pathogen discovery and detection—in laboratories ...
2024-10-31
The next step for fully integrated textile-based electronics to make their way from the lab to the wardrobe is figuring out how to power the garment gizmos without unfashionably toting around a solid battery. Researchers from Drexel University, the University of Pennsylvania, and Accenture Labs in California have taken a new approach to the challenge by building a full textile energy grid that can be wirelessly charged. In their recent study, the team reported that it can power textile devices, including a warming element and environmental sensors that transmit ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Development of a simple, revolutionary printing technique for periodic nano/microstructures




