(Press-News.org) Black holes continue to captivate scientists: they are purely gravitational objects, remarkably simple, yet capable of hiding mysteries that challenge our understanding of natural laws. Most observations thus far have focused on their external characteristics and surrounding environment, leaving their internal nature largely unexplored. A new study, conducted through a collaboration between the University of Southern Denmark, Charles University in Prague, Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati (SISSA) in Trieste, and Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand, and published in Physical Review Letters, examines a common aspect of the innermost region of various spacetime models describing black holes, suggesting that our understanding of these enigmatic objects may require further investigation.
According to the corresponding author, postdoc Raúl Carballo-Rubio from the research center CP3-Origins at the University of Southern Denmark, the key insight from this study is that “the internal dynamics of black holes, which remain largely uncharted, could radically transform our understanding of these objects, even from an external perspective.”
The Kerr solution to the equations of General Relativity is the most accurate representation of rotating black holes observed in gravitational astrophysics. It depicts a black hole as a maelstrom in spacetime, characterized by two horizons: an outer one, beyond which nothing can escape its gravitational pull, and an inner one that encloses a ring singularity, a region where spacetime as we know it ceases to exist. This model aligns well with observations, as deviations from Einstein's theory outside the black hole are regulated by new physics parameters, which govern the core's size and are expected to be quite small.
However, a recent study conducted by the international team mentioned above has highlighted a critical issue concerning the interior of these objects: while it was known that a static inner horizon is characterised by an infinite accumulation of energy, the study demonstrates that even more realistic dynamic black holes are subject to significant instability over relatively short timescales. This instability is due to an accumulation of energy that grows exponentially over time until it reaches a finite, but extremely large, value, capable of significantly influencing the overall geometry of the black hole and thus altering it.
The ultimate outcome of this dynamic process is still unclear, but the study implies that a black hole cannot stabilise in Kerr geometry, at least over long timescales, although the speed and magnitude of deviations from Kerr spacetime remain under investigation. As Stefano Liberati, professor at SISSA and one of the study's authors, explains: “This result suggests that the Kerr solution—contrary to previous assumptions—cannot accurately describe observed black holes, at least on the typical timescales of their existence.”
Understanding the role of this instability is therefore essential for refining theoretical models of the interior of black holes and their relationship to the overall structure of these objects. In this sense, it could provide a missing link between theoretical models and potential observations of physics beyond General Relativity. Ultimately, these results open new perspectives for studying black holes, offering an opportunity to deepen our understanding of their internal nature and dynamic behaviour.
END
The dynamic core of black holes
A new study investigates the internal dynamics of black holes and their implications for future astrophysical observations
2024-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving energy production by boosting singlet fission process
2024-11-01
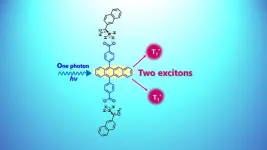
Fukuoka, Japan—In organic molecules an exciton is a particle bound pair of an electron (negative charge) and its hole (positive charge). They are held together by Coulombic attraction and can move within molecular assemblies. Singlet fission (SF) is a process where an exciton is amplified, and two triplet excitons are generated from a singlet exciton. This is caused by the absorption of a single particle of light, or photon, in molecules called chromophores (molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light). Controlling the molecular orientation and arrangement of chromophores is crucial for achieving high SF efficiency in materials with strong potential for optical ...
Smoking cessation and incident cardiovascular disease
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this cohort study, smoking and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk exhibited a dose-dependent association, with light ex-smokers having a CVD risk similar to that of never-smokers relatively soon after smoking cessation. For heavy ex-smokers, greater than 25 years might be required for the residual CVD risk to align with that of never-smokers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Seung Yong Shin, MD, PhD, email theshin04@korea.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Cannabis use during early pregnancy following recreational cannabis legalization
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this time-series study, recreational cannabis legalization implementation in California was associated with an increase in rates of cannabis use during early pregnancy, defined by both self-report and toxicology testing, driven by individuals living in jurisdictions that allowed adult-use retailers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelly C. Young-Wolff, PhD, MPH, email kelly.c.young-wolff@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3656)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Research shows Cleveland Clinic’s therapeutic virtual yoga program can be effective for chronic low back pain
2024-11-01
Research Shows Cleveland Clinic’s Therapeutic Virtual Yoga Program Can Be Effective for Chronic Low Back Pain
Participants also reported better sleep quality and reduced use of pain medications
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, November 01, 2024, 11:00 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers found that a 12-week therapeutic virtual yoga program for chronic low back pain can be a feasible, safe and effective treatment option. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
Chronic low back pain is very common — up to 20% of adults worldwide have long-lasting or recurrent lower back pain. In severe cases, ...
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
2024-11-01
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
Precision diagnostics for diseases that affect the brain and other organs brought closer by new ability to exclusively access contents of organ-derived extracellular vesicles in blood
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Brain disorders like Parkinson’s (PD) or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) start to develop in patients much earlier than when their first clinical symptoms appear. Treating patients at these early stages could slow or even stop their ...
Regional and global experts convene in Accra, Ghana to update cancer treatment guidelines for Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-11-01
Accra, GHANA [October 29, 2024] — International oncology experts are gathering in Accra, Ghana for a series of meetings beginning today, to update cancer treatment recommendations in the NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa. This is the latest event from a longstanding collaboration between the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), American Cancer Society (ACS), and National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI) that collectively ...
China University of Geosciences (Beijing) unveils clues to an enigmatic geological process
2024-11-01
Cratons are fascinating yet enigmatic geological formations. Known to be relatively stable portions of the Earth’s continental crust, cratons have remained largely unchanged for billions of years. Although cratons have survived many geological events, some are undergoing decratonization—a process characterized by their deformation and eventual destruction. For example, the North China Craton (NCC), an ancient continental crust block, is known to have begun extensive decratonization during the Mesozoic era, largely due to tectonic and geochemical modifications and destabilization of its base (or ‘keel’). However, explaining the mechanisms ...
Fueling greener aviation with hydrogen
2024-11-01
Despite ongoing efforts to curb CO2 emissions with electric and hybrid vehicles, other forms of transportation remain significant contributors of greenhouse gases. To address this issue, old technologies are being revamped to make them greener, such as the reintroduction of sailing vessels in shipping and new uses for hydrogen in aviation. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have used computer modeling to study the feasibility and challenges of hydrogen-powered aviation.
“While there is a long way to go for hydrogen aviation to be realized at scale, we hope that our ...
Education, occupation, and wealth affect the risk of cognitive impairment
2024-11-01
Socioeconomic factors such as education, occupation, and wealth influence the likelihood of developing cognitive impairment or dementia in later life and whether a person is likely to recover, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Scientific Reports, followed 8,442 adults aged 50 and above in England over 10 years from 2008/09 to 2018/19, to examine how socioeconomic factors at the start of the study were associated with changes in cognitive status.
The researchers tracked how these people moved between various states: healthy, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia. They also considered the possibility ...
Revealing causal links in complex systems
2024-11-01
Getting to the heart of causality is central to understanding the world around us. What causes one variable — be it a biological species, a voting region, a company stock, or a local climate — to shift from one state to another can inform how we might shape that variable in the future.
But tracing an effect to its root cause can quickly become intractable in real-world systems, where many variables can converge, confound, and cloud over any causal links.
Now, a team of MIT engineers hopes to provide some clarity in the pursuit of causality. They developed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
[Press-News.org] The dynamic core of black holesA new study investigates the internal dynamics of black holes and their implications for future astrophysical observations