(Press-News.org) UC Santa Cruz chemists have discovered a new way to produce biodiesel from waste oil that both simplifies the process and requires relatively mild heat. This discovery has the potential to make the alternative fuel source much more appealing to the massive industrial sectors that are the backbone of the nation’s economy.
In 2022, the U.S. transportation sector alone used about 3 million barrels of diesel per day, accounting for about 75% of total consumption of the fuel in this country. That same year, diesel use accounted for about 10% of total energy-related CO2 emissions in the United States, according to the federal Energy Information Administration.
While some companies have turned towards electric vehicles to reduce their carbon footprint, the vast majority of fleets still run on diesel—in part, because biodiesel production is difficult, energy intensive, and so, has slowed adoption. Of all the energy sources used by the U.S. transportation sector in 2022, biofuels accounted for just 6%.
In their study, published on October 3 in the American Chemical Society journal Energy & Fuels, lead author Kevin Lofgren details a new way to turn used vegetable oil into biodiesel that involves sodium tetramethoxyborate (NaB(OMe)4). This chemical, used to make the active ingredient that reacts with oil to make biodiesel, is considered unique because it allows the biofuel to be easily separated from the byproducts of production—by simply pouring them off.
Another benefit is the resulting byproduct can be used to regenerate the most expensive ingredient in the production process. And last but not least, the reaction can be completed in under an hour at temperatures as low as 40°C (104°F)—saving energy and money.
“I always wanted to work on biodiesel,” said Lofgren, a Ph.D. student in chemistry at UC Santa Cruz. “I started exploring this new material that we made to see if it could attack the fats in oil to help catalyze biodiesel, and it all flowed from there.”
While individual consumers increasingly turn to solar and electric energy to power their homes and vehicles, America’s huge industrial sectors still rely on diesel fuel. Lofgren pointed out that the majority of the trucks, trains, and boats that ship goods around the world currently run on diesel engines and won’t be electrified any time soon.
Meanwhile, the researchers point out, biodiesel is a carbon-neutral fuel that is available today and approved to power these vehicles without the need for engine modifications.
Reducing the energy needed to make biofuel
Some of the current methods for making biodiesel produce soap as a byproduct, which makes purifying the fuel difficult and results in less actual product. Other approaches rely on palm oil, which require clearing trees in rainforests to make room for monoculture palm tree plantations. These methods are also energy intensive, requiring extremely high temperatures and pressures. The technique detailed in this study can produce biodiesel at a temperature lower than that required to boil water.
“To make energy takes a lot of energy,” said co-author Scott Oliver, professor of chemistry and biochemistry. “Our method uses waste oil and mild heating, compared to current petroleum refineries that are energy consuming and pollution causing.”
According to the researchers, the method they discovered turns about 85% of used vegetable oil into biodiesel and passes almost all industry standards for use as fuel in heavy machinery and transportation vehicles. The exception was water content, though, it was only slightly higher than the acceptable value. The researchers expect that once this process is scaled up, the water content will be within acceptable levels.
“This new method is special because it is simple and affordable. It has the bonus of being able to regenerate the starting material,” Lofgren said. “It's already low-cost enough to make it competitive. But if you can buy the most expensive ingredient once and then regenerate it, it would be more cost efficient in the long run.”
“Everybody needs energy—every farm, food production plant, and transportation vehicle depend on it,” Oliver said. “This could really impact people. This process can be done at just above room temperature and it's reusable. You don't need to have a refinery; you can potentially use this method on a farm.”
Bakthan Singaram, professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UC Santa Cruz, is co-corresponding author of the paper, “Borate Pathway to FAMEs at Near-Ambient Conditions from Used Oil,” which is funded by an Innovation Catalyst Grant, Climate Action Solutions Program.
END
UC Santa Cruz chemists discover new process to make biodiesel production easier, less energy intensive
2024-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson launches Institute for Cell Therapy Discovery & Innovation to deliver transformational new therapies
2024-11-08
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the launch of its Institute for Cell Therapy Discovery & Innovation, which will build upon longstanding MD Anderson clinical and research expertise to lead the world in developing and advancing impactful cell therapies for patients in need.
The institute will bring together top scientists and clinicians to lead exceptional discovery, translational and clinical research that will deliver new insights in immunology and cell engineering, fueling the creation of transformational new treatments that can be rapidly adapted to address emerging needs in cancer, autoimmune diseases, infections ...
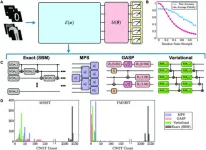
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning
2024-11-08
A recent study by researchers from CSIRO and the University of Melbourne has made progress in quantum machine learning, a field aimed at achieving quantum advantage to outperform classical machine learning. Their work demonstrates that quantum circuits for data encoding in quantum machine learning can be greatly simplified without compromising accuracy or robustness. This research was published Sept.12 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The team’s results, validated through both simulations and experiments on IBM quantum devices, show that their innovative encoding methods reduced circuit ...
New research promises an unprecedented look at how psychosocial stress affects military service members’ heart health
2024-11-08
A University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher will examine the role of cumulative psychosocial stress – as well as race, ethnicity and gender – among U.S. military personnel to gauge their impact on cardiovascular health and healthcare utilization.
The study is funded with a $1 million grant from the Defense Health Agency, part of the Department of Defense (DoD). The findings will help the military develop programs for health promotion and health readiness for active duty and Reserve/National ...
Faster measurement of response to antibiotic treatment in sepsis patients using Dimeric HNL
2024-11-08
The biomarker human neutrophil lipocalin HNL, which was previously shown to be a useful indicator of bacterial infections, may also in the form of Dimeric HNL be used to effectively monitor the success of antibiotic treatment in sepsis. The first promising results in this regard were published in 2019 and now the research group has confirmed these results in a larger study. The study is published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Sepsis, the costliest disease to health care, is a life-threatening condition with high mortality if not diagnosed and ...
Cleveland Clinic announces updated findings in preventive breast cancer vaccine study
2024-11-08
November 8, 2024, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers are presenting updated findings from their novel study of a vaccine aimed at preventing triple-negative breast cancer, the most aggressive and lethal form of the disease.
The study team found that the investigational vaccine was generally well tolerated and produced an immune response in most patients. The team described the side effects of the vaccine, showed the highest tolerated dose to date, and presented the immunologic effects of the vaccine. Findings are being presented at the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Annual Meeting.
Launched in 2021 and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, the ongoing ...
Intergenerational effects of adversity on mind-body health: Pathways through the gut-brain axis
2024-11-08
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “Intergenerational Effects of Adversity on Mind-Body Health: Pathways Through the Gut-Brain Axis” on Tuesday, November 12, 2024, at 2:00 pm ET. The presenter, Bridget Laura Callaghan, Ph.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Psychology at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). At UCLA, Dr. Callaghan directs the Brain & Body Lab in the Department of Psychology and also heads the Mental Disorders and Pain research theme at the Goodman Luskin Microbiome Center. The webinar host, Jeffrey Borenstein, M.D., is the President ...
Watch this elephant turn a hose into a sophisticated showering tool
2024-11-08
Tool use isn’t unique to humans. Chimpanzees use sticks as tools. Dolphins, crows, and elephants are known for their tool-use abilities, too. Now a report in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on November 8, 2024, highlights elephants’ remarkable skill in using a hose as a flexible shower head. As an unexpected bonus, researchers say they also have evidence that a fellow elephant knows how to turn the water off, perhaps as a kind of “prank.”
“Elephants are amazing with hoses,” says Michael Brecht ...
Chimpanzees perform better on challenging computer tasks when they have an audience
2024-11-08
When people have an audience watching them, it can change their performance for better or worse. Now, researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal iScience on November 8 have found that chimpanzees’ performance on computer tasks is influenced by the number of people watching them. The findings suggest that this “audience effect” predates the development of reputation-based human societies, the researchers say.
“It was very surprising to find that chimpanzees are affected in their task performance by ...
New medical AI tool identifies more cases of long COVID from patient health records
2024-11-08
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Researchers from Mass General Brigham are leveraging artificial intelligence to help identify the signs of long COVID, track how different symptoms manifest over time, and eliminate alternative explanations for patients’ symptoms.
The new approach suggests that 22.8% of the population experience the symptoms of long COVID, a figure that may paint a more realistic picture of the pandemic’s long-term toll.
Through analyzing a patient’s history over time, this new AI tool ...
Heat waves and adverse health events among dually eligible individuals 65 years and older
2024-11-08
About The Study: In this time-series study, heat waves were associated with increased adverse health events among dually eligible individuals 65 years and older. Without adaptation strategies to address the health-related impacts of heat, dually eligible individuals are increasingly likely to face adverse outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hyunjee Kim, PhD, email kihy@ohsu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3884)
Editor’s Note: Please ...