Eife studying legal surveillance as social determinant of health
2024-11-11
(Press-News.org)
Erin Eife, Assistant Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Surveillance as a Social Determinant of Health: Understanding the Impact of Pending Charges on Health Outcomes.”
Eife will conduct this research under the advisement of Evan Lowder, Associate Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), and Lauren Brinkley-Rubinstein, Associate Professor in the Department of Population Health Sciences at Duke University.
Eife aims to produce knowledge about the relationships among pending charges, one’s likelihood to feel anxious, and one’s likelihood of using illicit substances.
In the age of major bond reform, this study is timely. Specifically, there has been a decrease in pretrial incarceration but a suspected increase in other forms of pretrial surveillance, and this study seeks to demonstrate that alternatives to pretrial incarceration, such as electronic monitoring and drug testing, are similarly harmful to people with criminal legal (CL) contact. Documenting the relationships among pending charges, anxiety, and substance use may help to expose some of the ways that the community surveillance perpetuated by well-intentioned bond reform can actually reproduce the outcomes that it seeks to eradicate.
Eife will serve as Principal Investigator of the proposed study.
The scope of work for George Mason will include: (1) serving as the prime institution for the study; (2) leading the development of the study’s two aims; (3) coordinating data cleaning and analysis; and (4) leading dissemination of scientific findings of the study.
Eife received $16,200 from The Miriam Hospital on a subaward from the National Institutes of Health for this project. Funding began in Oct. 2024 and will end in late Dec. 2024.
###
ABOUT GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
George Mason University is Virginia’s largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls more than 40,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the past half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity, and commitment to accessibility. In 2023, the university launched Mason Now: Power the Possible, a one-billion-dollar comprehensive campaign to support student success, research, innovation, community, and stewardship.Learn more at gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-11
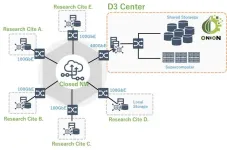
Tokyo & Osaka, Japan – Osaka University and NEC Corporation (NEC; TSE: 6701) are moving forward with efforts to realize a data infrastructure supporting Open Science. In 2021, The Joint Research Laboratory for Integrated Infrastructure of High Performance Computing and Data Analysis was established within the D3 Center, Osaka University (Director: Professor Susumu Date*1) by Osaka University and NEC. The result of the Joint Research Laboratory will be showcased at the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC24) scheduled ...
2024-11-11
“As we eagerly adopt Al models, we need to take a moment to think about the potential biases that they may contain.”
BUFFALO, NY - November 11, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on November 7, 2024, titled “ Beyond the hype: Navigating bias in AI-driven cancer detection.”
In this editorial, researchers from the Mayo Clinic emphasize the need to address potential biases in Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools used for cancer detection to ensure fair and equitable healthcare. Authors Yashbir Singh, Heenaben Patel, Diana V. Vera-Garcia, Quincy A. Hathaway, ...
2024-11-11
New research from Colorado State University shows that workplace leaders who are financially stressed are more likely to be abusive toward their subordinates – particularly if the leader is a man.
The findings, published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, provide insight into leader behavior due to a common source of stress. The research was led by Assistant Professor Keaton Fletcher in the Department of Psychology in partnership with Associate Professor Trevor Spoelma in the Anderson School of Management at the University ...
2024-11-11
In recent years, there has been a rising interest in combining traditional natural medicines with essential nutrients to foster a holistic approach to human health. The focus on integrating both elements reflects an understanding of health that transcends the simple absence of disease, encompassing physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. This review highlights how traditional medicine systems, such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and other indigenous practices worldwide, can be harmonized with nutritional science to form a comprehensive healthcare approach. Such a combination has the potential to improve disease prevention and enhance overall ...
2024-11-11
Online e-cigarette retailers are not consistently adhering to laws aimed at preventing the sale of vaping products to minors, including regulations on age verification, shipping methods and flavor restrictions, report researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego.
In a study published online on Nov. 11, 2024 in JAMA, researchers asked 16 people to purchase flavored vape products online and have them delivered to their homes in the County of San Diego, ...
2024-11-11
About The Study: In this study, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), which include abuse, neglect, and family dysfunction, were prevalent among children with notable disparities across participant demographic characteristics and contexts. As principal antecedent threats to child and adolescent well-being that can affect later life prospects, ACEs represent a pressing global social issue. Effective early identification and prevention strategies, including targeted co-designed community interventions, can reduce the prevalence of ACEs and mitigate their severe effects, thereby minimizing the harmful health consequences of childhood adversity in future generations.
Corresponding ...
2024-11-11
About The Study: In this cohort study, asthma was associated with memory difficulties in children, which may be more severe if asthma onset is earlier in childhood and may extend to executive function abilities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicholas J. Christopher-Hayes, MA, email nchristopherhayes@ucdavis.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.42803)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of ...
2024-11-11
Asthma is associated with memory difficulties in children, and early onset of asthma may exacerbate memory deficits, according to a new study from the University of California, Davis. The study, the first of its kind to connect asthma to memory deficits in children, was published in Nov. 5 in JAMA Network Open.
“This study underscores the importance of looking at asthma as a potential source of cognitive difficulty in children. We are becoming increasingly aware that chronic diseases, not only asthma but also diabetes, heart disease and others may place children at increased risk of cognitive difficulties,” said lead author Simona Ghetti, a professor of psychology ...
2024-11-11
An international study led by a University of Queensland researcher has found frailty increases a person’s risk of dementia, but early intervention may be the key to prevention.
Dr David Ward from the Centre for Health Services Research tracked the data of nearly 30,000 participants of 4 longitudinal studies in the United Kingdom and the United States, enabling researchers to detect changes in people’s health and function 20 years before they were diagnosed with dementia.
“The accumulation of age-related conditions is indicative of increasing frailty, which we found accelerates up to 9 years prior to a dementia diagnosis,” Dr Ward said.
“Our ...
2024-11-11
Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA) is potentially life-threatening condition that can cause severe anemia and other abnormalities. It’s a rare genetic blood disorder that occurs when the bone marrow fails to make red blood cells. Currently the only cure is a stem cell transplant, but this is only a viable option for select patients. Otherwise, children with DBA require lifelong follow-up care to manage symptoms, such as steroids and blood transfusions.
New data publishing 11/11 in Cell Stem Cell provides strong support for the first-in-human universal gene therapy trial for DBA through regulated GATA1 expression. Notably, it’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Eife studying legal surveillance as social determinant of health