Low-carbon collaborative dual-layer optimization for energy station considering joint electricity and heat demand response
2024-11-14
(Press-News.org)
In a significant step towards achieving the "Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality" goals, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Institute of Technology, in collaboration with Hohai University, have developed a groundbreaking dual-layer optimization strategy for park-level integrated energy systems (PIES). This strategy, which integrates electricity and heat demand response, significantly boosts the economic efficiency and low-carbon operation of energy stations.
The transition to renewable energy sources like wind and solar power has been accelerated by the global push for carbon neutrality. However, the inherent unpredictability and variability of these energy sources present challenges for the stable operation of integrated energy systems. The traditional vertically integrated market trading structure has been inadequate in addressing the complex interactions and collaborative relationships between energy stations and users, leading to suboptimal economic and environmental outcomes.
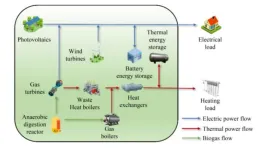
The research team introduced a novel dual-layer optimization framework that involves energy stations and users in a collaborative decision-making process. The upper layer, representing energy stations, determines the selling prices of electricity and heat, output plans for energy supply equipment, and the operational status of battery energy storage. The lower layer, consisting of users, adjusts their electricity and heat demand through demand response. A combination of differential evolution and quadratic programming (DE-QP) was employed to solve the interactive strategies between energy stations and users.
Simulation results demonstrated that the proposed strategy effectively increases the revenue of energy stations by 5.09% and the consumer surplus of users by 2.46% compared to traditional structures. The introduction of biogas as a renewable fuel source in energy stations reduced reliance on non-renewable natural gas, enhancing the stability of natural gas supply and electricity production. The stepped carbon trading strategy further incentivized participants to reduce carbon emissions, leading to a 5.23% reduction in carbon trading costs and a 2.54% decrease in carbon emissions.
This study addresses the critical need for more efficient and sustainable energy systems. By transforming the traditional vertical integrated interaction mode into a thermal-electric collaborative interaction mode, the research enables more flexible adaptation to user energy demands and encourages users to change their energy consumption behavior. The dual-layer optimization strategy not only improves the economic performance of energy stations but also promotes environmental sustainability through reduced carbon emissions.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-14
Hamilton, ON, Nov. 14, 2024, In a groundbreaking study, researchers at McMaster University have identified a potential treatment for Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs diseases—two rare, often fatal lysosomal storage disorders that cause progressive damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
After years of investigating the diseases’ underlying mechanisms, the research team has identified an existing FDA-approved drug that could significantly improve quality of life for affected patients and their families.
“Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs are devastating diseases,” ...
2024-11-14
Since 2018, Sino-US economic and trade relations have become increasingly tense. Between 2018 and 2019, the US imposed seven rounds of tariffs on China, to which China responded with retaliatory measures. The simple average tariff rates on US imports from China rose from 4.07% in January 2018 to 24.43% in December 2019, while the simple average tariff rates on Chinese imports from the US increased from 9.32% in January 2018 to 22.53% in December 2019 (see figure 1).
Consequently, the share of Chinese goods in US imports declined significantly — ...
2024-11-14
We have probably all seen a soybean plant, about 1 meter high with leaves and pods compactly arranged on a main stem with a few short side branches. The wild relative of the domesticated soybean is a long vine with pods widely distributed on many side branches. Plant breeding by farmers thousands of years ago is to thank for this dramatic change.
As human population increases and protein demand doubles, modern plant breeders must further optimize soybean plant architecture and per plant yield for modern farming systems. Conventional ...
2024-11-14
Lancaster University researchers investigating consumer attitudes and behaviours around plastic food packaging have found UK households are ‘wishcycling’ rather than recycling – and say it’s a problem that everyone - government, food producers, waste management and residents – has to solve.
Wishcycling – the act of putting packaging in recycling bins and hoping for the best, rather than knowing it’s recyclable – is something households are doing due to confusing product labels and differing recycling facilities around the country, experts warn.
The academics behind Lancaster ...
2024-11-14
A small clinical trial shows promising results for patients with triple-negative breast cancer who received an investigational vaccine designed to prevent recurrence of tumors. Conducted at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis with a therapy designed by WashU Medicine researchers, the trial is the first to report results for this type of vaccine — known as a neoantigen DNA vaccine — for breast cancer patients.
The study, which found the vaccine to be well-tolerated and to stimulate ...
2024-11-14
Adverse events affect more than a third (38%) of adults undergoing surgery, finds a study of admissions to 11 hospitals in the US state of Massachusetts, published by The BMJ today.
Of the 1009 admissions analysed, nearly half were classified as major (resulting in serious, life threatening or fatal harm) and the majority were considered as potentially preventable.
Although this study may not fully represent hospitals at large, the findings show that “adverse events remain widespread in contemporary ...
2024-11-14
Outsourcing adult social care services in England to the private sector since the 1980s has led to worse care and should be rolled back, argue experts in The BMJ today.
Benjamin Goodair at the Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford and colleagues suggest that removing the profit motive would help improve quality and reduce inequities.
Social care, sometimes referred to as community, residential, or personalised care, for older people and people with physical and mental disabilities is facing record demand but performing worse than any time in recent history, they explain.
One contributor to this, they say, is the outsourcing of care provision from the ...
2024-11-14
**Correction**
A subheading in the press release sent yesterday was incorrect - the line 'Global rates of diabetes doubled over the last two decades' should be ''Global rates of diabetes doubled over the last three decades'.
The subheading and two further occurrences of the same mistake have been corrected in the copy below (in yellow). The rest of the press release remains unchanged.
We sincerely apologise for any inconvenience caused,
The Lancet press office (pressoffice@lancet.com).
The ...
2024-11-14
A new clinical study shows that an inhibitor of Fas ligand (FasL), also called CD95 ligand (CD95L), led to a faster recovery of COVID-19 patients and reduced mortality. On average, it took eight days to recover for patients who received asunercept, a biotherapeutic FasL inhibitor, compared to 13 days in the control group. In addition, mortality was decreased by about 20 per cent. The study ‘Efficacy and safety of asunercept, a CD95L-selective inhibitor, in hospitalised patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19: ASUNCTIS, a multicentre, randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 2 trial’ ...
2024-11-14
Wastewater injection resulting from oil and gas production in Oklahoma caused a dramatic rise in seismic activity in the state between 2009 and 2015. But regulatory efforts to backfill some injection wells with cement and reduce injection volumes have been effective in lowering the state’s induced earthquake rate, according to a new study in The Seismic Record.
The study by Robert Skoumal of the U.S. Geological Survey and colleagues lends further support to the idea that reducing the depth of wastewater injection can decrease seismic activity—a finding that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Low-carbon collaborative dual-layer optimization for energy station considering joint electricity and heat demand response



