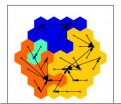
(Press-News.org) The instability of large, complex societies is a predictable phenomenon, according to a new mathematical model that explores the emergence of early human societies via warfare. Capturing hundreds of years of human history, the model reveals the dynamical nature of societies, which can be difficult to uncover in archaeological data.
The research, led Sergey Gavrilets, associate director for scientific activities at the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis and a professor at the University of Tennessee-Knoxville, is published in the first issue of the new journal Cliodynamics: The Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical History, the first academic journal dedicated to research from the emerging science of theoretical history and mathematics.
The numerical model focuses on both size and complexity of emerging "polities" or states as well as their longevity and settlement patterns as a result of warfare. A number of factors were measured, but unexpectedly, the largest effect on the results was due to just two factors – the scaling of a state's power to the probability of winning a conflict and a leader's average time in power. According to the model, the stability of large, complex polities is strongly promoted if the outcomes of conflicts are mostly determined by the polities' wealth or power, if there exist well-defined and accepted means of succession, and if control mechanisms within polities are internally specialized. The results also showed that polities experience what the authors call "chiefly cycles" or rapid cycles of growth and collapse due to warfare.
The wealthiest of polities does not necessarily win a conflict, however. There are many other factors besides wealth that can affect the outcome of a conflict, the authors write. The model also suggests that the rapid collapse of a polity can occur even without environmental disturbances, such as drought or overpopulation.
By using a mathematical model, the researchers were able to capture the dynamical processes that cause chiefdoms, states and empires to emerge, persist and collapse at the scale of decades to centuries.
"In the last several decades, mathematical models have been traditionally important in the physical, life and economic sciences, but now they are also becoming important for explaining historical data," said Gavrilets. "Our model provides theoretical support for the view that cultural, demographic and ecological conditions can predict the emergence and dynamics of complex societies."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are David G. Anderson, professor of anthropology at the University of Tennessee-Knoxville and Peter Turchin, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology and mathematics at the University of Connecticut.
The National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis (NIMBioS) brings together researchers from around the world to collaborate across disciplinary boundaries to investigate solutions to basic and applied problems in the life sciences. NIMBioS is sponsored by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture with additional support from The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Citation: Gavrilets S, Anderson D, Turchin P. 2010. Cycling in the complexity of early societies. Cliodynamics: The Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical History. 1:1 http://escholarship.org/uc/irows_cliodynamics?volume=1;issue=1
Mathematical model explains how complex societies emerge, collapse
2011-01-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Roundworm unlocks pancreatic cancer pathway
2011-01-20
Chapel Hill, NC – The National Cancer Institute estimates that more than 43,000 Americans were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer last year and more than 36,000 died from the disease. Despite advances in genetic science showing that the Ras oncogene is mutated in virtually all pancreatic cancers, scientists have been frustrated by the complexity of the signaling pathways in humans, which make it difficult to pinpoint potential therapeutic targets.
In a study published today in the Cell Press journal Developmental Cell, a team of researchers led by Channing Der, PhD, Distinguished ...
Speeding up Mother Nature's very own CO2 mitigation process
2011-01-20
LIVERMORE, Calif. – Using seawater and calcium to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) in a natural gas power plant's flue stream, and then pumping the resulting calcium bicarbonate in the sea, could be beneficial to the oceans' marine life.
Greg Rau, senior scientist with the Institute of Marine Sciences at UC Santa Cruz and who also works in the Carbon Management Program at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, conducted a series of lab-scale experiments to find out if a seawater/mineral carbonate (limestone) gas scrubber would remove enough CO2 to be effective, and whether ...
Science Translational Medicine: 'Creating Hope Act' incentivizes pediatric drug R&D
2011-01-20
Washington, DC — Recent legislative and regulatory actions make great strides toward establishing much needed incentives for pharmaceutical companies and others to develop and test more medications for pediatric rare diseases, including pediatric cancers, according to commentary by experts from Children's National Medical Center. The commentary appears in the January 19 issue of Science Translational Medicine.
"Pediatricians who treat children with serious and life-threatening diseases often find themselves face to face with the inadequacies of pediatric drug development," ...
Small molecules may prevent ebola infection
2011-01-20
Ebola, a virus that causes deadly hemorrhagic fever in humans, has no known cure or vaccine. But a new study by University of Illinois at Chicago scientists has uncovered a family of small molecules which appear to bind to the virus's outer protein coat and may inhibit its entry into human cells.
The results are to be published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and are now online.
Previous studies have shown that small molecules can interfere with the Ebola infection process, says Duncan Wardrop, associate professor of chemistry at UIC and corresponding author of ...
Like humans, amoebae pack a lunch before they travel
2011-01-20
Some amoebae do what many people do. Before they travel, they pack a lunch.
In results of a study reported today in the journal Nature, evolutionary biologists Joan Strassmann and David Queller of Rice University show that long-studied social amoebae Dictyostellum discoideum (commonly known as slime molds) increase their odds of survival through a rudimentary form of agriculture.
Research by lead author Debra Brock, a graduate student at Rice, found that some amoebae sequester their food--particular strains of bacteria--for later use.
"We now know that primitively ...
University of Illinois study confirms glycerin as a feasible feedstuff for swine
2011-01-20
An increased interest in biofuel production and a growing need to find cost-effective livestock feedstuff alternatives has led University of Illinois researchers to further evaluate the use of glycerin in swine diets.
This study, led by U of I graduate research assistant Omarh Mendoza, was published in the Journal of Animal Science and reports that swine diets may include up to 15 percent glycerin and achieve similar performance to a conventional corn:soybean diet.
"Glycerin is not a new product, but little is known about its role as a feed ingredient for swine," ...
A nanoscale rope, and another step toward complex nanomaterials that assemble themselves
2011-01-20
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have coaxed polymers to braid themselves into wispy nanoscale ropes that approach the structural complexity of biological materials.
Their work is the latest development in the push to develop self-assembling nanoscale materials that mimic the intricacy and functionality of nature's handiwork, but which are rugged enough to withstand harsh conditions such as heat and dryness.
Although still early in the development stage, their research could lead to new applications that ...
US Office of Naval Research achieves milestone
2011-01-20
VIDEO:
This is the Free Electron Laser video.
Click here for more information.
ARLINGTON, Va.-Scientists at Los Alamos National Lab, N.M., have achieved a remarkable breakthrough with the Office of Naval Research's Free Electron Laser (FEL) program, demonstrating an injector capable of producing the electrons needed to generate megawatt-class laser beams for the Navy's next-generation weapon system.
The Dec. 20 milestone, which occurred months ahead of schedule, will be the ...
Investing into Frontier Markets has become easier
2011-01-20
UK-based Veritas Financial Europe announces the official launch of the new information platform for investors - FrontiersInsight.com. This web-based platform is designed for both private as well as institutional investors that have substantial interest in investing into new, previously unexplored Frontier markets with huge upside potential. The unique tools offered by FrontiersInsight will also be useful for brokerage and investment firms, VC and PE companies, research and statistical centers.
The platform covers more than 13,000 public and private companies in developing ...
Office Cleaning Denver Gives You Peace Of Mind
2011-01-20
Milen Peev, owner of Office Cleaning Denver is pleased to announce the expansion of their services to the greater Denver area. In order for a business environment to be optimally functional and productive, staff require a clean work area that is free of clutter and debris.
The team is dedicated to ensuring that all of the needs of an office is met. A representative of the team works closely with business owners to assure that all of the requirements of the office are identified. After meeting and evaluating the building, the representative provides an in depth breakdown ...