(Press-News.org) More time spent sitting, reclining or lying down during the day may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and death, according to a study in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology, and presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2024. More than roughly 10-and-a-half hours of sedentary behavior per day was significantly linked with future heart failure (HF) and cardiovascular (CV) death, even among people meeting recommended levels of exercise.
“Our findings support cutting back on sedentary time to reduce cardiovascular risk, with 10.6 hours a day marking a potentially key threshold tied to higher heart failure and cardiovascular mortality,” said Shaan Khurshid, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at the Massachusetts General Hospital and co-senior author of the study. “Too much sitting or lying down can be harmful for heart health, even for those who are active.”
Insufficient exercise is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Over 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity per week is recommended by current guidelines to promote heart health. However, study experts say exercise is only a small fraction of overall daily activity, and the current guidelines don’t provide specific guidance on sedentary behavior which accounts for a much larger portion of daily activity, despite evidence that it’s directly linked with CVD risk.
This study examined the amount of sedentary time at which CVD risk is greatest and explored how sedentary behavior and physical activity together impact the chances of atrial fibrillation (AF), heart failure (HF), myocardial infarction (MI) and CV mortality.
Among the 89,530 study participants of the UK biobank, the average age was 62 years and 56.4% were women. Participants submitted data from a wrist-worn triaxial accelerometer that captured movement over seven days. The average sedentary time per day was 9.4 hours.
After an average follow-up of eight years, 3,638 individuals (4.9%) developed incident AF, 1,854 (2.1%) developed incident HF, 1,610 (1.84%) developed indecent MI and 846 (0.94%) died of CV causes, respectively.
The effects of sedentary time varied by outcome. For AF and MI, the risk increased steadily over time without major shifts. For HF and CV mortality, increase in risk was minimal until sedentary time exceeded about 10.6 hours a day, at which point risk rose significantly, showing a “threshold” effect for the behavior.
For study participants who met the recommended 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity or more, the effects of sedentary behavior on AF and MI risks were substantially reduced, but effects on higher risk of HF and CV mortality remained prominent.
“Future guidelines and public health efforts should stress the importance of cutting down on sedentary time,” Khurshid said. “Avoiding more than 10.6 hours per day may be a realistic minimal target for better heart health.”
In an accompanying editorial comment, Charles Eaton, MD, MS, Director of the Brown University Department of Family Medicine, said the use of wearable accelerometers has shown that exercise is significantly over-estimated by self-report and sedentary behavior is under-estimated.
Eaton said that replacing just 30 minutes of excessive sitting time each day with any type of physical activity can lower heart health risks. Adding moderate-to-vigorous activity cut the risk of HF by 15% and CV mortality by 10%, and even light activity made a difference by reducing HF risk by 6% and CV mortality by 9%.
“This study adds to the growing evidence of a strong link between sedentary behavior and cardiovascular health,” said Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, SM, Harold H. Hines Jr. Professor at Yale School of Medicine and Editor-in-Chief of JACC. “The findings strongly suggest that we need to get people moving to promote better health.”
There are several limitations of the study, including the inability to know details on where or why people are sitting or lying down for extended periods, such as at the workplace, which could have different impacts on CV risks. Accelerometers worn on the wrist are imperfect at detecting posture and therefore may misclassify standing time as sedentary time. A longer monitoring period may provide more accurate data on activity habits and patterns.
Other limitations include the potential for confounders in study results, selection bias, the inability to measure the actual effects of reallocating sedentary time to other activities, and differences between data from wrist-worn accelerometers versus thigh-worn accelerometers.
For an embargoed copy of the study publishing in JACC, contact JACC Media Relations Manager Olivia Walther at owalther@acc.org.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org or follow @ACCinTouch.
The ACC’s JACC Journals rank among the top cardiovascular journals in the world for scientific impact. The flagship journal, the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) — and specialty journals consisting of JACC: Advances, JACC: Asia, JACC: Basic to Translational Science, JACC: CardioOncology, JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, JACC: Case Reports, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and JACC: Heart Failure — pride themselves on publishing the top peer-reviewed research on all aspects of cardiovascular disease. Learn more at JACC.org.
###
END
XI’AN, CHINA [November 15, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers in the United States—is taking part in the Fourth International Congress of the Asian Oncology Society and the Chinese Congress on Holistic Integrative Oncology (2024 CCHIO) sponsored by the China Anti-Cancer Association (CACA), Chinese Institute of Development Strategy on Holistic Integrative Medicine, and Asian Oncology Society (AOS). The three-day event highlights international collaborations to improve cancer treatment and outcomes across China and beyond.
“NCCN ...
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
Hunted nearly to extinction during 20th century whaling, the Antarctic blue whale, the world’s largest animal, went from a population size of roughly 200,000 to little more than 300. The most recent estimate in 2004 put Antarctic blue whales at less than 1% of their pre-whaling levels.
But is this population recovering? Is there just one population of Antarctic blue whales, or multiple? Do these questions matter for conservation?
A team led by Zoe Rand, a University of Washington doctoral student, tackles these questions ...
A group of South Korean researchers has decided to utilize AI technology to support customer counseling services. Through this, it will provide a significant boost to the performance and efficiency of counselors in various industries, while improving the overall quality of customer counseling services, ultimately making it easier to meet the customers’ needs and expectations while opening up the possibility for realizing new values.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that ...
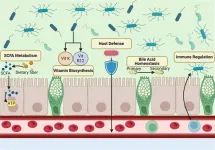
The gut microbiome, an ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms in the human digestive tract, has been increasingly linked to chronic diseases. Research led by Dr. Connor Prosty and his team at McGill University consolidates recent findings that demonstrate a causal role for the gut microbiome in the progression of multiple diseases, ranging from gastrointestinal conditions to immune-related and psychiatric disorders. Published in eGastroenterology, this narrative review examines how manipulating the gut microbiome ...
Family Heart Foundation Appoints Dr. Seth Baum as Chairman of the Board of Directors
Dr. Seth Baum, Florida Atlantic University, Named Chairman of the Family Heart Foundation’s Board of Directors
The Family Heart Foundation® is proud to announce the appointment of Dr. Seth Baum as the Board of Directors Chairman. An esteemed expert in preventive cardiology and lipidology, Dr. Baum has insights and extensive experience that will contribute to the Foundation’s strategic mission to increase awareness for lay public, expand screening for high-risk populations, improve understanding and education for healthcare teams, and promote ...
A new route to materials with complex ‘disordered’ magnetic properties at the quantum level has been produced by scientists for the first time.
The material, based on a framework of ruthenium, fulfils the requirements of the ‘Kitaev quantum spin liquid state’ - an elusive phenomenon that scientists have been trying to understand for decades.
Published in Nature Communications the study, by scientists at the University of Birmingham, offers an important step towards achieving and controlling quantum materials with sought-after new properties that do not follow ...
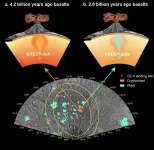
Basalt samples returned by the Chang’e-6 mission have revealed volcanic events on the lunar farside at 2.8 billion years ago (Ga) and 4.2 Ga, according to research conducted by Prof. LI Qiuli’s lab at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This work was recently published in Nature.
“Unraveling the volcanic history of the lunar farside is crucial for understanding the hemispheric dichotomy of the Moon,” said Prof. LI.
The asymmetry between the Moon’s nearside and farside—encompassing differences in basalt distribution, topography, crustal thickness, and thorium ...
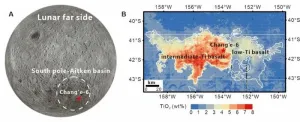
The Moon has a global dichotomy, with its near and far sides having different geomorphology, topography, chemical composition, crustal thickness, and evidence of volcanism.
To better understand this dichotomy, Professor XU Yigang’s team from the Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated lunar soil samples from the far side South Pole-Aitken (SPA) Basin of the Moon returned by the Chang’e-6 mission.
Their work was published in Science on Nov. 15.
“The samples returned by Chang’e-6 provide a best opportunity to investigate the lunar global dichotomy,” said Professor ...
Dietary zinc deficiency promotes lung infection by Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria — a leading cause of ventilator-associated pneumonia, according to a new study published Nov. 15 in the journal Nature Microbiology.
A Vanderbilt University Medical Center-led team of researchers discovered an unexpected link between the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-13 (IL-13) and A. baumannii lung infection, and they demonstrated that blocking IL-13 prevented infection-associated death in an animal model.
The findings suggest that anti-IL-13 antibodies, which are FDA-approved for use in humans, may protect against bacterial pneumonia in patients with zinc deficiency.
“To ...
In what could one day become a new treatment for epilepsy, researchers at UC San Francisco, UC Santa Cruz and UC Berkeley have used pulses of light to prevent seizure-like activity in neurons.
The researchers used brain tissue that had been removed from epilepsy patients as part of their treatment.
Eventually, they hope the technique will replace surgery to remove the brain tissue where seizures originate, providing a less invasive option for patients whose symptoms cannot be controlled with medication.
The ...