(Press-News.org) Along Colombia's Pacific coast, a small shellfish called piangua has been a crucial part of local communities for generations. This humble mollusk is a vital source of income and nutrition for many coastal residents. As a regional resource that can be sustainably utilized, it represents a bioeconomy opportunity and is an example for other regions. But now, scientists are raising the alarm about its future.
A new study reveals that piangua populations are showing concerning signs of decline, largely due to overharvesting. Researchers used cutting-edge DNA analysis to examine these shellfish in two key locations along Colombia's Pacific coast, providing the first detailed genetic profile of these important creatures.
The findings paint a worrying picture. “While piangua populations have been stable for over 100,000 years, recent decades of intensive harvesting have taken their toll,” explained Silvia Restrepo, president of the Boyce Thompson Institute and lead author of the study.
The numbers are striking. Piangua exports from Colombia skyrocketed from just 100 tons per year in 1980 to over 3,000 tons by 2004. In some areas, like Bahía Málaga, the population has plunged by 60%. This dramatic increase in harvesting has forced the piangua onto Colombia's endangered species list.
“We discovered that the piangua are experiencing a significant loss of genetic diversity,” said Restrepo. “This is evidenced by a high level of inbreeding and a reduction in heterozygosity.”
Why is genetic diversity so important? Imagine the gene pool of a species as a deck of cards. Each card represents different genetic traits that help the species survive various challenges – disease resistance, temperature tolerance, or the ability to find food. When overharvesting reduces the population, it's like removing cards from the deck. With fewer "cards" in play, the species becomes less equipped to handle new threats.
The study, recently published in Scientific Reports, also revealed something unexpected. Despite living in connected coastal waters, piangua populations in different areas maintain subtle genetic variations. This suggests that local populations might have special adaptations to their specific environments, making it even more crucial to protect them all.
This research has real-world implications for conservation. Equipped with this new genetic information, scientists, the Colombian government, and local communities can work together to develop better protection strategies. These might include creating protected areas, establishing sustainable harvesting quotas, or implementing restoration programs.
The study marks a significant milestone as the first genetic investigation of piangua in Colombia, complete with the first detailed mapping of its genome. This genetic blueprint will be an invaluable tool for future conservation efforts.
The message is clear for the communities along Colombia's Pacific coast: without immediate action to protect these vital shellfish, they risk losing not just an important food source, but a crucial part of their cultural and economic heritage. The race is on to save the piangua while there is still time.
This research was funded by the Ministerio de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación (MinCiencias) of Colombia.
END
Bioeconomy in Colombia: The race to save Colombia's vital shellfish
2024-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NFL’s Colts bring CPR education to flag football to improve cardiac emergency outcomes
2024-11-19
INDIANAPOLIS, November 18, 2024— The American Heart Association and the Indianapolis Colts this past weekend brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to the Colts Regional Flag Football tournament. At the Kickoff event held at the Indiana Farm Bureau Football Center on Saturday, Nov. 16 more than 100 youth athletes, coaches and league administrators learned lifesaving skills to build their confidence and capabilities to respond in the event of a cardiac emergency. The following day, walk-up style Hands-Only CPR instruction was again available to guests attending the tournament at the Center Grove Bantom ...
Research: Fitness more important than fatness for a lower risk of premature death
2024-11-19
As rates of obesity, as defined by body mass index (BMI), continue to climb in the United States, so have efforts to lose weight, including a new era of weight-loss drugs. Yet a new systematic review and meta-analysis published today in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that cardiorespiratory fitness was a stronger predictor of both cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality than BMI.
The researchers found that fit individuals across all BMI categories had statistically similar risks of death from all causes or cardiovascular disease. By contrast, unfit individuals ...
Researchers use biophysics to design new vaccines against RSV and related respiratory viruses
2024-11-19
LA JOLLA, CA—In most people, the lung-infecting pathogens known as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) trigger mild cold-like symptoms. But in infants and seniors, these viruses can cause severe pneumonia and even death.
Vaccines against both viruses, however, have been difficult to design. Now, Scripps Research scientists have analyzed the structure and stability of a critical RSV and hMPV protein to better design vaccines that target it. Their research, ...
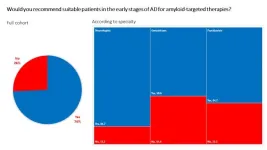
New study highlights physician perspectives on emerging anti-amyloid treatments for Alzheimer’s disease in Israel
2024-11-19
November 19, 2024 - Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel – In a recent study, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center has shed light on physician attitudes toward novel anti-amyloid treatments (ATT) for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), revealing a spectrum of opinions across key specialties. With Israel’s health system structured to provide universal healthcare, the high out-of-pocket costs for new AD therapies have raised questions among medical professionals about the feasibility and practicality of implementing these treatments.
The study, conducted ...
U of M research finds creativity camp improves adolescent mental health, well-being
2024-11-19
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (11/19/2024) — Published in Child Psychiatry and Human Development, a research team led by the University of Minnesota Medical School found that Creativity Camp, a two-week arts intervention delivered as a day camp, had a positive impact on mental health and well-being in adolescents with depression.
The idea behind the study is that engaging in the arts offers a pathway for exploring and expanding new ways of thinking, developing insights and sparking self-discovery.
“As a clinician, I am deeply aware of the urgent need for new treatment options for teens with depression. The findings in this report are promising, and I hope they ...
How human brain functional networks emerge and develop during the birth transition
2024-11-19
Brain-imaging data collected from fetuses and infants has revealed a rapid surge in functional connectivity between brain regions on a global scale at birth, possibly reflecting neural processes that support the brain’s ability to adapt to the external world, according to a study published November 19th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology led by Lanxin Ji and Moriah Thomason from the New York University School of Medicine, USA.
Understanding the sequence and timing of brain functional network ...
Low-dose ketamine shows promise for pain relief in emergency department patients
2024-11-19
Des Plaines, IL — A new study that investigates low-dose ketamine (LDK) as an adjunct to morphine for treating acute pain has been published in the October issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The study, titled Low-dose ketamine as an adjunct to morphine: A randomized controlled trial among patients with and without current opioid use highlights the potential of low-dose ketamine as a valuable tool in pain management, providing a safe and effective option for emergency medicine physicians managing acute pain.
Pain remains one of the most common and challenging complaints ...
Lifestyle & risk factor changes improved AFib symptoms, not burden, over standard care
2024-11-19
Research Highlights:
A clinical trial with adults who have atrial fibrillation (AFib) and an implanted heart device found similar improvements to the amount of time they experienced arrhythmia regardless of whether they received standard care (education pamphlets about healthy diet and exercise), followed a lifestyle/risk factor modification program, or took metformin and followed a lifestyle/risk factor modification program.
AFib burden, a measure of how much time a patient experiences atrial arrhythmia, improved during the treatment period — particularly in the standard of care and lifestyle risk factor modification groups.
Lifestyle and risk factor modification was associated ...
Researchers discover new cognitive blueprint for making and breaking habits
2024-11-19
Cognitive neuroscientists in Trinity College Dublin have published new research describing a brand new approach to making habit change achievable and lasting.
This innovative framework has the potential to significantly improve approaches to personal development, as well as the clinical treatment of compulsive disorders (for example obsessive compulsive disorder, addiction, and eating disorders).
The research was led by Dr Eike Buabang, Postdoctoral Research Fellow in the lab of Professor Claire Gillan in the School of Psychology and has been published as a paper, Leveraging ...
In a small international trial, novel oral medication muvalaplin lowered Lp(a)
2024-11-19
Research Highlights:
The oral medication muvalaplin may safely lower high levels of lipoprotein(a), also known as Lp(a), an independent, inherited risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Muvalaplin is a small molecule inhibitor that prevents the bonding of the two protein components that combine to make Lp(a). There are no currently FDA-approved medications to lower Lp(a) levels, though other medications are currently being evaluated in clinical trials. Muvalaplin is the first oral medication developed to lower Lp(a) levels.
Results ...