(Press-News.org) Many public water systems in the United States use inorganic chloramines to disinfect drinking water, but their decomposition products have long been a mystery. In a new study, researchers report the discovery of chloronitramide anion – a compound whose existence, though not identity, has been known for 30 years. Detected in the tap water of millions of Americans, this compound’s toxicity remains untested, prompting calls for immediate toxicological evaluation and raising questions about the safety of chloramine in public water supplies. For over a century, chemical disinfection of public water supplies has effectively reduced waterborne disease by killing pathogens in drinking water. Inorganic chloramines, like monochloramine (NH22Cl) and dichloramine (NHCl2), have become widely used in the U.S. for this purpose and are used to treat the tap water of nearly one-third Americans. However, for decades, chloramine decomposition has been suspected of producing elusive chemical by-products, including potential nitrogen-containing compounds with unknown toxicity. One such disinfection by-product, referred to simply as an “unidentified product”, remains uncharacterized despite being first identified more than 40 years ago. By combining classic synthesis methods with advanced analytical techniques like high-resolution mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, Julian Fairey and colleagues isolated and identified chloronitramide anion (Cl–N–NO2-) as a previously unidentified product of inorganic chloramine decomposition. Fairey et al. measured chloronitramide anion content in a range of chloraminated water systems in the U.S., detecting levels as high as ~100 micrograms per liter (μg/l), which surpasses the typical regulatory limits for many disinfection by-products (60–80 μg/liter). Notably, this compound was absent in water systems that used alternative disinfectants. Although direct toxicological studies have not yet been conducted, the authors caution that computational analyses suggest that chloronitramide anion may not be benign, emphasizing the need for an immediate toxicological assessment and quantification in source waters, finished drinking waters, and wastewater effluents. “The findings of Fairey et al. may trigger a reevaluation of the wisdom of chloraminating public water supplies,” writes Daniel McCurry in a related Perspective. “Regardless of whether chloronitramide anion is found to be toxic or not, its discovery warrants a moment of reflection for water researchers and engineers.”
***A related embargoed news briefing was held on Tuesday, 19 November, as a Zoom Webinar. Recordings can be found at the following links:
Video: https://aaas.zoom.us/rec/share/9vgXlijMh1GT2RaVczoOs8HNjHQ1KXnZkpXCeBt29jVfTtS0pbSGcYUW3hCUd_Ym._bps7Fb6Rg80Jzff
Audio: https://aaas.zoom.us/rec/share/z30gghwhhhBZNqf3Syz1M19V9v40_lu7U8lD__tenAtWx8fo5ZBDOK4AjfEYsSMN.HpRiuXBzkb0zx0v9
The passcode for both is mD?+Fm9k
END
Chloronitramide anion – a newly characterized contaminant prevalent in chloramine treated tap water
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2024-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Population connectivity shapes cultural complexity in chimpanzees
2024-11-21
Cultural complexity in chimpanzees depends on migration and interaction between groups, echoing early human patterns of cultural evolution, researchers report in a new study. The findings offer insight into the development of cumulative culture in early hominins. Culture, defined as a set of socially learned behaviors, has been increasingly documented across various animal species. However, human culture stands out for its complexity and cumulative nature, where cultural knowledge builds upon previous innovations. While chimpanzees – humans’ closest relatives – demonstrate a variety of cultural ...
Direct hearing tests show that minke whales can hear high-frequency sounds
2024-11-21
For the first time, scientists have directly measured the hearing range of minke whales, discovering that the species can detect high-frequency sounds as high as 90 kilohertz (kHz), according to a new study, demonstrating hearing sensitivity far greater than previously believed. The findings suggest that baleen whales – the planet’s largest mammals – may be even more impacted by anthropogenic ocean noise than currently recognized but have been excluded from regulatory consideration due to underestimated hearing ranges. ...
Whale-ship collision risk mapped across Earth’s oceans
2024-11-21
By mapping global ship traffic and whale habitats, researchers found that 92% of whale habitats overlap with shipping routes, illuminating hotspots for whale-ship collision risk, according to a new study. Although only 7% of high-risk areas currently contain management strategies to reduce ship strikes, the findings show that expanding efforts to just 2.6% of the ocean’s surface could significantly reduce these fatal collisions, aiding whale conservation amid booming global shipping. “Mitigating the negative environmental impacts of marine shipping is essential ...
Bye-bye microplastics: new plastic is recyclable and fully ocean-degradable
2024-11-21
Researchers led by Takuzo Aida at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) have developed a new durable plastic that won’t pollute our oceans. The new material is as strong as conventional plastics and biodegradable, but what makes it special is that it breaks down in seawater. The new plastic is therefore expected to help reduce harmful microplastic pollution that accumulates in oceans and soil and eventually enters the food chain. The experimental findings were published Nov 22 in Science.
Scientists have been trying to develop safe and sustainable materials that can replace traditional plastics, which are non-sustainable and harm the environment. While ...
Unveiling nature of metal-support interaction: AI-driven breakthrough in catalysis
2024-11-21
How can Artificial Intelligence (AI) help accelerate scientific discovery based on vast amounts of experimental data? A new study by Prof. LI Weixue's team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences shows how this can be achieved in heterogonous catalysis. The results were recently published in Science.
By integrating interpretable AI with experimental data, domain knowledge, and first-principles simulations, the researchers established a general theory of metal-support interaction (MSI), which is one of the most important pillars in catalysis.
Supported metal catalysts ...
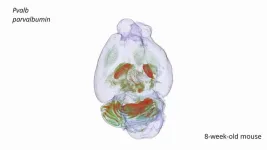
New imaging method enables detailed RNA analysis of the whole brain
2024-11-21
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital have developed a groundbreaking microscopy method that enables detailed three-dimensional (3D) RNA analysis at cellular resolution in whole intact mouse brains. The new method, called TRISCO, has the potential to transform our understanding of brain function, both in normal conditions and in disease, according to the new study published in Science.
Despite great advances in RNA analysis, linking RNA data to its spatial context has long been a challenge, especially in intact 3D tissue volumes. The TRISCO method now makes it possible to perform three-dimensional RNA imaging of whole ...
Stability of perovskite solar cells doubled with protective coating
2024-11-21
Northwestern University scientists have developed a new protective coating that significantly extends the life of perovskite solar cells, making them more practical for applications outside the lab.
Although perovskite solar cells are more efficient and less expensive than traditional silicon solar cells, perovskite has, until now, been limited by its lack of long-term stability. Typically, perovskite solar cells uses an ammonium-based coating layer to enhance efficiency. While effective, ammonium-based layers degrade under environmental stress, such as heat and moisure.
Northwestern ...
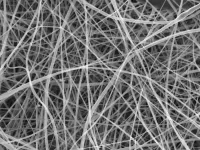
Chemists create world’s thinnest spaghetti
2024-11-21
The world’s thinnest spaghetti, about 200 times thinner than a human hair, has been created by a UCL-led research team.
The spaghetti is not intended to be a new food but was created because of the wide-ranging uses that extremely thin strands of material, called nanofibers, have in medicine and industry.
Nanofibers made of starch – produced by most green plants to store excess glucose – are especially promising and could be used in bandages to aid wound healing (as the nanofiber mats are highly porous, allowing water and moisture in but keeping ...
Empowering neuroscience: Large open brain models released
2024-11-21
The hippocampus is one of the most fascinating brain regions. Associated with the formation of memories, it also helps us to navigate through the world without getting lost. Sensory cortices on the other hand play an important role in how we perceive our environment and make appropriate movements, and how our brains determine what to focus on and what to ignore. While both regions have been extensively studied and many of their secrets revealed, there is still a lot we do not understand about them due to the high complexity of ...
From traditional to technological: Advancements in fresco conservation
2024-11-21
MELVILLE, N.Y., Nov. 21, 2024 – Fresco painting, a technique that dates back to antiquity, involves applying dry pigments to wet plaster, creating stunning artwork that can last for centuries. Over time, however, these masterpieces often face degradation due to delamination, where decorative plaster layers separate from the underlying masonry or structural plaster. This deterioration can compromise the structural integrity of the artwork, necessitating restoration efforts.
Historically, conservators have gently knocked on the plaster with their knuckles or small mallets to assess the condition of the fresco. By listening to the emitted sound, they could identify the delaminated areas ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Chloronitramide anion – a newly characterized contaminant prevalent in chloramine treated tap waterSummary author: Walter Beckwith