(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – Researchers have identified acute effects of cigarette and e-cigarette smoking on vascular function, even without nicotine. The results of the ongoing research are being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
E-cigarettes, also known as vapes, are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled into the lungs. Vapes contain significantly fewer chemicals and toxins than are found in tobacco smoke. As a result, e-cigarettes are believed by many to be less harmful than cigarette smoking. Vapes also come in various flavors, making them popular among young people.
“E-cigarettes have long been marketed as a safer alternative to regular tobacco smoking,” said study lead author Marianne Nabbout, M.D., a radiology resident at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in Little Rock. “Some believe that e-cigarettes don’t contain any of the harmful products, such as free radicals, found in regular tobacco cigarettes, because no combustion is involved.”
While vaping exposes users to fewer toxic chemicals than cigarettes, it can still be detrimental to vascular function and overall health.
In the study conducted at the University of Pennsylvania, Dr. Nabbout and colleagues sought to identify the acute effects on vascular function of cigarette smoking and the immediate effects of e-cigarette vaping, with and without nicotine.
A total of 31 healthy smokers and vapers ranging in age from 21 to 49 years have been included to date. In three separate sessions, study participants underwent two MRI exams, one before and one after each of the following smoking/vaping episodes: tobacco cigarette, e-cigarette aerosol with nicotine and e-cigarette aerosol without nicotine.
A cuff was placed on the upper thigh to restrict blood flow. Once deflated, femoral artery flow velocity (a measure of the speed of blood flow in the femoral artery) and venous oxygen saturation (a measure of the amount of oxygen in the blood that returns to the heart after supplying oxygen to the body’s tissues) were evaluated.
Cerebrovascular (blood flow in the brain) reactivity was measured with a special type of MRI called phase-contrast MRI.
The data of the smokers and vapers was then compared to the baseline scans of 10 non-smokers and non-vapers ranging from 21 to 33 years old.
Following inhalation of each type of vaping or smoking, there was a significant decrease in the resting blood flow velocity in the superficial femoral artery. This artery runs along the thigh and supplies oxygenated blood to the entire lower body.
The decrease in vascular function was most pronounced after inhalation of e-cigarettes containing nicotine, followed by e-cigarettes without nicotine.
Decreased venous oxygen saturation was also present in vapers, whether or not the e-cigarettes contained nicotine. This suggests an immediate decrease in the uptake of oxygen by the lungs after vaping.
“This study serves to highlight the acute effects smoking and vaping can have on a multitude of vascular beds in the human body,” Dr. Nabbout said. “If the acute consumption of an e-cigarette can have an effect that is immediately manifested at the level of the vessels, it is conceivable that the chronic use can cause vascular disease.”
According to Dr. Nabbout, the take-home message for the public is that vaping may not be free of harm. “Ultimately, we are relying on science to help guide the regulation of such products in favor of public health,” she said. “Refraining from smoking and vaping is always recommended.”
This research project is supported by the National Institutes of Health.
Co-authors are Michael C. Langham, Ph.D., Alessandra Caporale, Ph.D., Shampa Chatterjee, Ph.D., Frank T. Leone, M.D., M.S., Andrew Strasser, Ph.D., Christiana Cottrell, B.A., Rasleen Grewal, B.S., and Felix W. Wehrli, Ph.D.
###
Note: Copies of RSNA 2024 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press24.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on vascular imaging, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
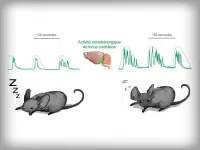
Researchers at the University of Lausanne have identified a novel role for the brain’s ‘locus coeruleus’ in sleep and its disruptions. This brain region facilitates the transition between NREM and REM sleep states while maintaining an unconscious vigilance toward the external world. Stress disrupts its functions and negatively impacts on sleep quality.
Sleep disorders affect an increasing number of people, with potentially serious consequences for their health. Mammalian sleep consists of cycles between two states: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye ...
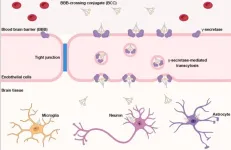
New York, NY [November 25, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed an innovative approach—demonstrated in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue—to safely and effectively deliver therapeutics into the brain, providing new possibilities for treating a wide range of neurological and psychiatric diseases.
Published in the November 25 online issue of Nature Biotechnology [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02487-7], the study introduces a first-of-its-kind blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugate (BCC) system, designed to overcome the protective barrier that typically blocks large biomolecules from ...
The ancient Vikings certainly had the travel bug. Between the late eighth century and approximately 1050 CE, they roamed the Atlantic in their longships all the way to Newfoundland, Labrador, and Greenland, as well as exploring the Mediterranean and continental Eurasia.
Among the places the Vikings are known to have settled were the Faroe Islands, an archipelago of 18 islands in the North Atlantic. They probably weren’t the first to do so: archaeologists have found evidence that these islands had been inhabited since approximately 300 CE, possibly ...
Affordability in Canada affects not just groceries but also medications, with 1 in 20 people unable to take their medications as prescribed because of cost, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241024.
Prescription medications are not universally covered under Canada’s 13 provincial and territorial health insurance systems. In 2021, Canadian households paid more than $7.4 billion out of pocket for prescription medications.
The study, which included a nationally representative ...
Remotely operated camera traps, sound recorders and drones are increasingly being used in conservation science to monitor wildlife and natural habitats, and to keep watch on protected natural areas.
But Cambridge researchers studying a forest in northern India have found that the technologies are being deliberately misused by local government and male villagers to keep watch on women without their consent.
Cambridge researcher Dr Trishant Simlai spent 14 months interviewing 270 locals living around the Corbett Tiger Reserve, a national park in northern India, including many women from nearby villages.
His report, published today in the journal Environment and Planning ...
Around 450,000 children are being failed by the UK education system because they have a special educational need and disability (SEND) that is effectively unrecognised by most schools and local education authorities, an author has warned.
Supporting Colour Blindness in Education and Beyond, by author Marie Difolco, shines a spotlight on a commonly-overlooked SEND in modern classrooms: colour blindness (also known as colour vision deficiency, or CVD). She also warns that many myths surround this condition, with many people believing it just means not being able to tell the ...
Osaka, Japan – Smartphone-based augmented reality, in which visual elements are overlaid on the image of a smartphone camera, are extremely popular apps. These apps allow users to see how furniture would look in their house, or navigate maps better, or to play interactive games. The global phenomenon Pokémon GO, which encourages players to catch digital creatures through their phone, is a well-known example.
However, if you want to use augmented reality apps inside a building, prepare to lower your expectations. ...
Study sought to better understand how humans evolved to become skilled at thinking about others
Newer parts of the brain that support social interactions are connected to and in constant communication with the ancient amygdala
First study to map with fMRI never-before-seen details of the brain’s social cognitive network
CHICAGO --- We’ve all been there. Moments after leaving a party, your brain is suddenly filled with intrusive thoughts about what others were thinking. “Did they think I talked too much?” “Did my joke offend them?” “Were ...
Black men on buses and trains — whether as passengers or transit workers — face hostile encounters that threaten their sense of safety and well-being, according to a new study by a Keough School of Global Affairs sociologist. By reinforcing racist tropes that they are dangerous or invisible, these encounters can also erode Black men’s sense of dignity and self-worth.
“Black men who want to go to work, school, appointments, visit others, or do any of the other things that people use public transport for, find the experience to be degrading rather than liberating,” said Gwendolyn Purifoye, assistant professor of racial justice and conflict transformation in ...
Increase in annual rates of obesity were largest by far: 7.8% in 2016 to 22.3% in 2023
Vaginal birth complications increased 22.4%; cesarean birth complications increased 48.9%
Non-Hispanic Black mothers faced more than double the rate of severe complications compared to non-Hispanic white mothers
Illinois data reflects national increases in obesity, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and gestational diabetes in pregnant people of all ages
CHICAGO --- A new study from Northwestern Medicine reveals a troubling ...