Recovery of testing for heart disease risk factors post-COVID remains patchy
Analysis of 49 million patients finds that the number of blood pressure readings taken in England may still be below expected levels in 2024
2024-11-26
(Press-News.org) Routine screening to detect risk factors for heart disease dropped sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic in England, and some key measurements, such as blood pressure readings, may still lag behind pre-pandemic levels. These findings are reported in a new study by Frederick Ho and Naveed Sattar of the University of Glasgow, Scotland, UK, and colleagues published November 26th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, patients went without routine face-to-face health checks, which are important for detecting common cardiometabolic conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. Previously, it was unknown whether these health checks had recovered to pre-pandemic levels.
Researchers looked at how often clinicians took measurements of 12 risk factors for cardiometabolic disease between November 2018 and March 2024, using records from more than 49 million adults in England. They saw a sharp drop in the numbers of measurements being performed from March 2020 to February 2022, but most of the risk factor measurements returned to normal by 2022 to 2023. Blood pressure measurements were an exception, and as of March 2024 were still not back to normal, especially in patients belonging to lower socioeconomic levels.
The findings from the new research confirm previous studies showing that patients missed important routine health checks during the pandemic lockdowns. This lack of screening for cardiometabolic conditions likely explains previous observations that fewer patients received preventive prescriptions, like drugs to lower blood pressure, during the pandemic. The long-term disruption of blood pressure screening identified by the study could lead to missed opportunities for treatment, increasing the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, or even death. This could also exacerbate existing health disparities for lower-income patients.
The authors add, “These data alert us to potential missed opportunities to measure key risk factors for chronic diseases, which are on the rise in the UK in an alarming way. Health care workers need better ways to more efficiently capture and then act upon changes in risks to prevent important diseases. The use of new technologies to capture data and better empower patients to make important lifestyle changes are needed.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004485
Citation: Ho FK, Dale C, Mizani MA, Bolton T, Pearson ER, Valabhji J, et al. (2024) Routine measurement of cardiometabolic disease risk factors in primary care in England before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med 21(11): e1004485. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1004485
Author Countries: United Kingdom
Funding: see manuscript
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-26
While NASA’s NEOWISE telescope ended its journey through space on Nov. 1, 2024, the team at IPAC, a science center at Caltech, was working on one further gift from the prolific mission.
The final data release from NEOWISE was released to the astronomy community just two weeks later, on Nov. 14, encompassing over 26 million images and nearly 200 billion sources detected by the telescope. And today, IPAC is releasing six new images from the mission’s archival data as a tribute to this landmark project, available here: https://www.astropix.org/link/3b2x
NEOWISE ...
2024-11-26
"Research in the last several decades has established endothelial cells (ECs) as a dynamic interface critical for vascular protection.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 26, 2024 – This editorial was published by Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) in Volume 16, Issue 17, titled, “The silent protector: Nucleoporin93’s role in vascular health.”
Written by Julia Michalkiewicz, Tung D. Nguyen, and Monica Y. Lee from The University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, ...
2024-11-26
WASHINGTON, Nov. 26, 2024 – Human activities are causing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels to rise, which increases the global average surface temperature—and poses a threat to crop growth. Escalating concerns about climate change’s impact on global food security inspired researchers from Banaras Hindu University in India to create a way to explore how these factors influence crop yields.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, the researchers share a mathematical model created to capture the nonlinear relationships between CO2, temperature, human population, ...
2024-11-26
About The Study: This cohort study among individuals participating in a weight loss program found that nearly half of those consuming alcohol at baseline decreased their alcohol use after anti-obesity medication initiation. There may be properties of anti-obesity medications that lead to reduced use. For example, naltrexone decreases cravings for alcohol and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) may attenuate the rewarding effects of alcohol, similar to food.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lisa R. Miller-Matero, PhD, email lmatero1@hfhs.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
2024-11-26
A multinational collaboration co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has uncovered a potential explanation for why some cancer patients receiving a type of immunotherapy called checkpoint inhibitors experience increased susceptibility to common infections.
The findings, published in the journal Immunity, provide new insights into immune responses and reveal a potential approach to preventing the common cancer therapy side effect.
“Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies have revolutionised cancer treatment ...
2024-11-26
Amphibians hold a significant place in evolution, representing the transition from aquatic to terrestrial lifestyles. They are crucial for understanding the brain and spinal cord of tetrapods—animals with four limbs, including humans. A group of scientists led by a team at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now shows how harmless viruses can be used to illuminate the development of the frog nervous system. The results have now been published in Developmental Cell.
Virus. When you hear the word, you probably shudder. But not all viruses are bad or cause disease. Some are even used for therapeutic ...
2024-11-26
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications and VAST Data are giving supercomputing system Delta and the newly launched DeltaAI a boost in their storage and application performance.
NCSA launched Harbor, a service that provides very fast storage for global home and software directories across all NCSA open-science resources. Its deployment has led to a 400% increase in application launch performance for the Delta system, among many other gains.
Over the last two years, we’ve seen a significant increase in ...
2024-11-26
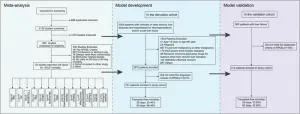
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking advancement in liver failure care: the CATCH-LIFE-MELD score (Chinese Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Consortium (CATCH-LIFE)-MELD score). This innovative tool, developed by an international team led by Xia Yu and colleagues, enhances the accuracy of predicting short-term survival outcomes for patients suffering from acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). The study, published in eGastroenterology, promises to revolutionize patient management and treatment planning for this life-threatening condition.
“ACLF presents unique challenges due to its rapid progression and high mortality rates,” said Dr. Yu Shi, senior researcher at Zhejiang University ...
2024-11-26
A recent special issue of the journal Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters has brought together some of China's top scientists to provide a picture of the latest progress in understanding and controlling air pollution.
Fine particulate matter, referred to as PM2.5, and ground-level ozone (O3) are the main pollutants degrading the air quality of China’s cities and wider urban regions. Both have serious human health effects, such as heart disease, asthma, and lung damage.
The World Health Organization (WHO) provides clear guidelines regarding acceptable concentrations ...
2024-11-26
SAN FRANCISCO—November 26, 2024—Subtle signs of Alzheimer’s disease can emerge decades before a diagnosis—often in the form of irregular behaviors that reflect very early stages of brain dysfunction.
But until now, identifying and measuring these slight behavioral changes in a scientific way hasn’t been feasible, not even when studying Alzheimer’s in mice.
In a study published in Cell Reports, a team of scientists at Gladstone Institutes used a new video-based machine learning tool to pinpoint ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Recovery of testing for heart disease risk factors post-COVID remains patchy
Analysis of 49 million patients finds that the number of blood pressure readings taken in England may still be below expected levels in 2024