(Press-News.org) Public health recommendations generally suggest drinking eight cups of water a day. And many people just assume it’s healthy to drink plenty of water.
Now researchers at UC San Francisco have taken a systematic look at the available evidence. They concluded that drinking enough water can help with weight loss and prevent kidney stones, as well as migraines, urinary tract infections and low blood pressure.
“For such a ubiquitous and simple intervention, the evidence hasn’t been clear and the benefits were not well-established, so we wanted to take a closer look,” said senior and corresponding author Benjamin Breyer, MD, MAS, the Taube Family Distinguished Professor and chair of the UCSF Department of Urology.
“The amount of rigorous research turned out to be limited, but in some specific areas, there was a statistically significant benefit,” Breyer said. “To our knowledge, this is the first study assessing the benefits of water consumption on clinical outcomes broadly.”
The study, which analyzed 18 randomized controlled trials, appears Nov. 25 in JAMA Network Open.
The researchers found the most evidence in favor of drinking water to prevent kidney stones and to help people lose weight.
Drinking eight cups of water a day significantly decreased the likelihood of getting another kidney stone.
Several studies found that drinking about six cups of water a day helped adults lose weight. But a study that included adolescents found that drinking a little more than eight cups of water a day had no effect.
Still, the authors said that encouraging people to drink water before meals would be a simple and cheap intervention that could have huge benefits, given the increased prevalence of obesity.
Other studies indicated that water can help prevent migraines, control diabetes and low blood pressure, and prevent urinary tract infections.
Adults with recurrent headaches felt better after three months of drinking more water.
Drinking about four more cups of water a day helped diabetic patients whose blood glucose levels were elevated.
Drinking an additional six cups a day of water also helped women with recurrent urinary tract infections. It reduced the number of infections and increased the amount of time between them.
And drinking more water helped young adults with low blood pressure.
“We know that dehydration is detrimental, particularly in someone with a history of kidney stones or urinary infections,” said Breyer, who is a member of the UCSF Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics. “On the other hand, someone who suffers from frequent urination at times may benefit from drinking less. There isn’t a one size fits all approach for water consumption.”
Authors: From UCSF, co-authors are Nizar Hakam, MBBS; Jose Luis Guzman Fuentes; Architha Sudhakar; Kevin D. Li; Catherine Nicholas; Jason L. Lui, MD; Peggy Tahir, MLIS; Charles P. Jones, MD; and Stephen Bent, MD. From Weill Cornell Medicine, Behnam Nabavizadeh, MD.
About UCSF Health: UCSF Health is recognized worldwide for its innovative patient care, reflecting the latest medical knowledge, advanced technologies and pioneering research. It includes the flagship UCSF Medical Center, which is a top-ranked hospital, as well as UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals, with campuses in San Francisco and Oakland; Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital; UCSF Benioff Children’s Physicians; and the UCSF Faculty Practice. These hospitals serve as the academic medical center of the University of California, San Francisco, which is world-renowned for its graduate-level health sciences education and biomedical research. UCSF Health has affiliations with hospitals and health organizations throughout the Bay Area. Visit https://www.ucsfhealth.org/. Follow UCSF Health on Facebook or on Twitter
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | Twitter.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Drinking plenty of water may actually be good for you
In the first systematic look, UC San Francisco researchers find it helps with a variety of conditions from obesity to migraine.
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Men at high risk of cardiovascular disease face brain health decline 10 years earlier than women
2024-11-27
Men with cardiovascular disease risk factors, including obesity, face brain health decline a decade earlier—from their mid 50s to mid 70s—than similarly affected women who are most susceptible from their mid 60s to mid 70s, suggest the findings of a long term study, published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The most vulnerable regions of the brain are those involved in processing auditory information, aspects of visual perception, emotional processing and memory, with ...
Irregular sleep-wake cycle linked to heightened risk of major cardiovascular events
2024-11-27
An irregular sleep-wake cycle is associated with a heightened risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, even for those who clock up the recommended nightly hours of shut-eye, finds research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Most studies looking at the impact of sleep on health have focused on sleep length and less is known about the impact of sleep patterns, in particular the impact of irregular sleep—defined as variations in the time a person goes to sleep and wakes up.
To explore this further, the researchers drew on 72,269 people aged 40 to 79, taking part in the UK ...
Depression can cause period pain, new study suggests
2024-11-27
Women are twice as likely as men to suffer from depression and often experience more severe physical symptoms. This gender difference is particularly evident during reproductive years and dramatically impacts the lives of hundreds of millions of people worldwide. However, although links between mental health and reproductive health have been found, the associations have remained underexplored.
In a new study published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, researchers from China and the UK have found that depression can increase the chances of a person experiencing menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea).
Shuhe Liu, lead author of the study and a PhD ...
Wistar Institute scientists identify important factor in neural development
2024-11-26
PHILADELPHIA — (Nov. 26, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s Alessandro Gardini, Ph.D., and lab have shed new light on how certain biological processes determine the development of neural cells. Their findings on a molecular “bridge” complex demonstrate a new level of detail in the understanding of early neural development — which is fundamental for the further understanding of neurodevelopmental syndromes. The new paper, “The enhancer module of integrator controls cell identity and early neural fate commitment” was published in the journal, Nature Cell Biology.
“By achieving a better understanding of how the nervous system develops ...
New imaging platform developed by Rice researchers revolutionizes 3D visualization of cellular structures
2024-11-26
A team of researchers led by Anna-Karin Gustavsson at Rice University has developed an innovative imaging platform that promises to improve our understanding of cellular structures at the nanoscale. This platform, called soTILT3D for single-objective tilted light sheet with 3D point spread functions (PSFs), offers significant advancements in super-resolution microscopy, enabling fast and precise 3D imaging of multiple cellular structures while the extracellular environment can be controlled and flexibly adjusted. The research was recently published in Nature Communications.
Studying ...
To catch financial rats, a better mousetrap
2024-11-26
Enron. Lehman Brothers. More recently, General Electric and Supermicro. During the past quarter century, a variety of high-profile companies have been caught cooking their books.
But they’re often not caught before they’ve cost investors billions of dollars. That’s why analysts have long tried to sniff out businesses that may be using questionable or flat-out illegal accounting tricks to hide poor performance.
New research from Urooj Khan, accounting professor and the Deloitte & Touche Centennial Faculty Fellow at Texas McCombs, proposes a new and more effective way to gauge companies’ “earnings quality.”
In analyses of corporate ...
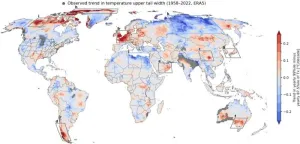
Mapping the world's climate danger zones
2024-11-26
With 2024 on track to be declared the hottest on record, scientists from IIASA and Columbia University have noticed that specific regions are consistently more affected by extreme temperatures. A new study provides the first worldwide map of these regional climate danger zones.
Amid the continued upward march in average temperatures over the past decades, a recent surge of record shattering extreme heat waves raise questions about the degree to which climate models can provide adequate estimates of relations between global mean temperature changes and regional climate risks. The study just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) provides the ...
Emory heart team implants new blood-pumping device for first time in U.S.
2024-11-26
On Nov. 18, the heart failure and transplantation team at Emory University Hospital (EUH) made history, performing the first-ever surgical implantation in the United States of a brand-new type of ventricular assist device (VAD), which provides crucial care to patients with failing hearts.
An expert team led by veteran cardiothoracic surgeon Mani Daneshmand, MD, successfully implanted a novel magnetically levitated pump, a VAD that has been specifically designed for patient ease and long-term health. The BrioVAD System, made by BrioHealth Solutions Inc., was authorized by the FDA to begin clinical trials ...
Congenital heart defects caused by problems with placenta
2024-11-26
Congenital heart defects are the most common form of human birth defect, but we still don’t fully understand what causes them. Previous research had suggested that some heart defects could be triggered by problems with the placenta, the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to the developing embryo. Now, researchers at Nanjing University, China have confirmed this link by focusing on a protein whose levels are reduced in many patients with congenital heart defects, called SLC25A1. SLC25A1 plays a key role in transporting ...
Schlechter named Cancer Moonshot Scholar
2024-11-26
Chelsey Schlechter, MPH, PhD, Huntsman Cancer Institute investigator and assistant professor in the Department of Population Health Sciences at the University of Utah (the U), has been selected as a Cancer Moonshot Scholar.
Schlechter is one of only eleven researchers in the U.S. chosen for the prestigious program this year, which aims to both advance impactful cancer research and broaden the research workforce.
For the project, Schlechter and her team partnered with the Association for Utah Community Health and Utah Community Health Centers—organizations which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Drinking plenty of water may actually be good for youIn the first systematic look, UC San Francisco researchers find it helps with a variety of conditions from obesity to migraine.