(Press-News.org)
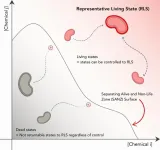
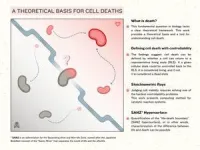
Cellular death is a fundamental concept in the biological sciences. Given its significance though, its definition depends on the context in which it takes place, and lacks a general mathematical definition. Researchers from the University of Tokyo propose a new mathematical definition of death based on whether a potentially dead cell can return to a predefined “representative state of living,” which are the states of being that we can confidently call “alive.” The researchers’ work could be useful for biological researchers and future medical research.
While it’s not something we like to think about, death comes for us all eventually, whether you’re an animal, a plant, or even a cell. And even though we can all differentiate between what is alive and dead, it might be surprising to know that death at a cellular level lacks a widely recognized mathematical definition. Given that cell death plays such an important role in various biological processes and can have important health implications, it’s of critical importance to understand what we really mean by cellular death, especially in research.
“My long-term scientific goal is to understand the inherent difference between life and nonlife, mathematically; why the transition from nonlife to life is so difficult, while the other way around is so easy,” said Assistant Professor Yusuke Himeoka from the Universal Biology Institute. “Our aim in this project was to develop a mathematical definition and computational method to quantify the life-death boundary. We were able to do this by exploiting an important feature of biological reaction systems, specifically enzymatic reactions within cells.”
Himeoka and his team proposed a mathematical definition of cell death. It’s based on the way cellular states including metabolism can be controlled by modulating the activities of enzymes. They define dead states as those states from which cells cannot return to an apparent “living” state, regardless of the modulation of any biochemical processes. This led them to develop a computational method for quantifying the life-death boundary, which they call “stoichiometric rays.” The method was developed by focusing on enzymatic reactions and the second law of thermodynamics, which states that systems naturally move from ordered to disordered states. Researchers could use these methods to better understand, control, and possibly even reverse, cellular death in controlled lab experiments.
“This method of computation is not applicable to autonomic systems, however, the systems which make the machinery for control, such as proteins. Autonomy is one of the hallmarks of living systems. I would like to extend our method so that it can also be applied to these,” said Himeoka. “We naively believe that death is irreversible, but it is not so trivial and does not have to be the case. I believe that should death come more under our control, human beings, our understanding of life, and society will change completely. In this sense, to understand death is crucial in terms of science and also in terms of social implications.”
###
Journal article:
Yusuke Himeoka, Shuhei A. Horiguchi, and Tetsuya J. Kobayashi. “A theoretical basis for cell deaths”, Physical Review Research, DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.02169
Funding:
This work is supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers JP22K15069, JP22H05403, JP24H01118 to Y.H.; 24K00542, 19H05799 to T.J.K.), JST (Grant Numbers JPMJCR2011, JPMJCR1927 to T.J.K.), and GteX Program Japan Grant Number JPMJGX23B4. S.A.H. is financially supported by the JSPS Research Fellowship Grant No. JP21J21415.
Useful links:
Universal Biology Institute
https://park.itc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/UBI/index_e.html
Graduate School of Science
https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Research contact:
Assistant Professor Yusuke Himeoka
Universal Biology Institute, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
yhimeoka@g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About The University of Tokyo:
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on X (formerly Twitter) at @UTokyo_News_en.
END
On November 27, the prestigious journal Nature will publish the results of an innovative breast cancer research project from the Netherlands. This study, the SONIA trial, showed that delaying and shortening the duration of a specific anti-cancer therapy (CDK4/6 inhibitors) in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer leads to similar survival outcomes, while reducing toxicity and achieving substantial cost reductions: over 45 million euros per year in the Netherlands and over 5 billion dollars in the United States. This is the first time an efficiency study like this has been conducted in collaboration with Dutch health ...
A fungus discovered in the mouse stomach may hold a key to fungal evolution within the gastrointestinal tract, according to new research led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The finding suggests that preclinical studies until now have overlooked a major influencer of mouse physiology.
Scientists recently have come to appreciate the importance, for human health and disease, of microbes—often called “commensals”—that naturally dwell in the gut. Bacterial commensals, for example, are known to have ...
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is proud to be recognized for the impact on the future of drug discovery and development, as a distinguished honoree of the Showcase AI and Biotech Innovation Award on November 13, 2024, at the Fifth Endeavor Venture Group & Mount Sinai Health System Healthcare AI and Technology Investor Summit. Michelle Chen, Ph.D., Chief Business Officer of Insilico Medicine, received the award on behalf of the company.
Delivered ...
Lugano, Switzerland, 27 November 2024 – The ESMO Asia Congress 2024 is the annual event dedicated to multidisciplinary oncology in the Asian region. It will feature a broad spectrum of topics in cancer research, including novel treatment modalities, in-depth discussions on the management of specific cancer types, pan-Asian trials and subgroup analyses of cutting-edge studies relevant for the patients in the area. Data will be presented and discussed by leading experts from across Asia and beyond. The congress will be held onsite in Singapore from 6-8 December, with no virtual option available.
Programme highlights
Subgroup ...
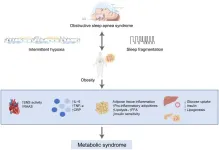
Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of mortality globally, particularly among individuals with both obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and metabolic syndrome (MetS). These two conditions exacerbate each other, creating a vicious cycle that increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the pathophysiological relationship between OSA and MetS is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. This review explores current knowledge on the connection between OSA and MetS and discusses the progress in treatment ...
Chimpanzees are known for their remarkable intelligence and use of tools, but could their cultures also evolve over time like human cultures? A new, multidisciplinary study led by the University of Zurich suggests that some of their most advanced behaviors may have been passed down and refined through generations.
In recent decades, scientists have clearly demonstrated that chimpanzees, like humans, pass on complex cultures such as tool use from generation to generation. But human culture has become vastly more sophisticated, ...
By providing flexibility services to renewable energy systems, consumers can both help in balancing power grids and receive financial benefits. Hosna Khajeh’s doctoral dissertation from the University of Vaasa, Finland, introduces new methods that enable the efficient utilisation of energy users’ flexibility resources in distribution and transmission networks.
As the use of weather-dependent renewable energy sources increases, power systems need to become more flexible to guarantee energy supply at all times. One of the necessary steps for the future is making it possible for consumers to support both national and local power grids with ...
Factors beyond carbohydrates have a substantial influence on blood glucose levels meaning current automated insulin delivery systems miss vital information required for glucose regulation, a new study has found.
A team of researchers from the University of Bristol analysing automated insulin delivery data from people with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) discovered that unexpected patterns in insulin needs are just as common as well-established ones.
The study, published today in JMIRx Med aimed to identify patterns in changes of insulin needs and to analyse how frequently these occur in people with T1D who use the OpenAPS, a state-of-the-art, ...
Solid oxide cells (SOCs), including solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs), are among the most promising energy conversion technologies due to their high efficiency and fuel flexibility. However, the high-temperature sintering required for their manufacture often leads to undesirable reactions at the electrolyte and electrode interface, degrading cell performance. A thin, dense ceria-based barrier layer, typically composed of gadolinium-doped ceria (GDC), is widely used to prevent these reactions. Achieving sufficient densification ...
The Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), headed by Minister Yoo Sang-im, held the launch ceremony for the "AI Safety Institute" (AISI) on Wednesday, November 27, at the Pangyo Global R&D Center.
At the "AI Seoul Summit"last May, leaders from 10 countries recognized safety as a key component of responsible AI innovation and emphasized the importance of establishing AI safety institutes and fostering global collaboration for safe AI. President Yoon Suk Yeol also expressed his commitment, stating, "We will work towards establishing an AI safety institute in Korea and actively participate ...