(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Alcohol’s ability to increase people’s pain threshold is one reason that drinking also leads to more aggressive behavior, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that the less pain that study participants felt after drinking an alcoholic beverage, the more pain they were willing to inflict on someone else.
“We’ve all heard the idiom ‘I feel your pain,’” said study co-author Brad Bushman, professor of communication at The Ohio State University.
“But if intoxicated people can’t feel their own pain, they might be less likely to feel empathy when others feel pain, and that could lead them to be more aggressive.”
The study was published recently in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
This study used an experimental design that has been used in research studies since 1967 and has been approved for use in humans in this study and others.
This new research involved two independent laboratory experiments, one with 543 participants and the other with 327 participants, all of whom reported consuming 3-4 alcoholic beverages per occasion at least once a month. They were recruited by newspaper advertisements and paid $75. The methods for the two experiments were identical.
After giving informed consent, participants were given 20 minutes to drink an alcohol or placebo beverage. The orange juice beverages looked identical so participants wouldn’t know which one they got. For the placebo drinks, the researchers put a small amount of alcohol on the top of the orange juice and sprayed the rim of the glass with alcohol so that it tasted like an alcoholic beverage.
After drinking the beverage, each participant received one-second electrical shocks to two fingers on one hand. The researchers increased shocks in intensity until the participant described the shock as “painful.” That was labeled the participant’s pain threshold.
They then participated in an online competitive reaction time task in which the winner could deliver a shock to the loser. The shocks ranged from 1 (low) to 10, which was the level the participant rated as “painful.” Participants could also choose how long the shocks lasted.
In reality, there was no opponent and the researchers randomly declared the participant the “winner” in half of the reaction time tasks. The purpose was simply to see if those who drank the alcoholic beverage would be willing to deliver stronger and longer shocks – and whether a higher pain threshold had an impact.
Results showed that for those drinking alcohol, the alcohol increased the level at which the shocks became painful to them. And the greater their tolerance for physical pain, the greater their level of aggression in terms of the intensity and length of shocks they were willing to deliver to the opponent.
Those who drank the placebo drinks weren’t as aggressive in their response, partly because their pain threshold was generally lower than those drinking alcohol, Bushman said.
“In other words, they were still able to feel their own pain – and didn’t want to inflict pain on others,” he said.
“There are many reasons that intoxicated people are more likely to intentionally hurt others, but this research suggests pain tolerance is one possible reason.”
Bushman noted that the people who drank alcohol in this study had blood alcohol concentrations averaging between 0.095% and 0.11%. That’s slightly above the legal limit in most states, which is 0.08%.
“The effects of alcohol on pain tolerance may be higher for those who drink more than what they did in these experiments,” Bushman said. “That may make them even more willing to be aggressive against others.”
Co-authors on the study were C. Nathan DeWall of the University of Kentucky, and Peter Giancola, a licensed clinical psychologist in Montreal.
The research was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and the National Center for Research Resources.
END
‘I don’t feel your pain’: How alcohol increases aggression
Study finds link to increase in pain threshold
2024-12-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Microprocessor inside you
2024-12-02
It’s a big year for microRNAs. The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine went to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun, who discovered the first microRNA in 1993. Today, we know that humans make more than 1,000 different microRNAS. These molecules are critical for building and maintaining healthy bodies, so it’s crucial that they’re made the right way. Errors in microRNA manufacture can put us at risk for developmental disorders, cancer, or neurodegenerative disease.
To learn how cells accurately generate a mind-boggling array of microRNAs, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Leemor ...
Landmark World Drought Atlas reveals systemic nature of hazard risks, underlines need for national plans, international cooperation
2024-12-02
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia — As record-breaking droughts are becoming a new normal around the globe, the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and the European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) launch the most comprehensive global publication on drought risks and solutions as an urgent wake-up call for world leaders and citizens.
The landmark new World Drought Atlas depicts the systemic nature of drought risks through dozens of maps, infographics, and case studies. It illustrates how drought risks are interconnected across sectors like energy, agriculture, river transport, and international trade and how they can trigger cascading effects, fueling inequalities and ...
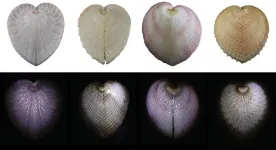
To build better fiber optic cables, ask a clam
2024-12-02
DURHAM, N.C. -- Since the first fiber optic cables rolled out in the 1970s, they’ve become a major part of everything from medical devices to high-speed internet and cable TV. But as it turns out, one group of marine mollusks was way ahead of us.
A new study reveals that clams called heart cockles -– so-named because of their heart-shaped shells -- have unique structures in their shells that act like fiber optic cables to convey specific wavelengths of light into the bivalves’ tissues.
Researchers from Duke University and Stanford University used electron and laser microscopy and computer simulations ...
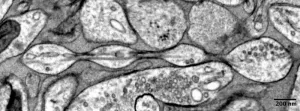
Study may reverse century-old understanding of the shape of ‘arms’ on mammals’ brain cells
2024-12-02
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL MONDAY, DEC. 2, AT 5 A.M.**
Biology textbooks may need a revision, say Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists, who present new evidence that an armlike structure of mammalian brain cells may be a different shape than scientists have assumed for more than a century.
Their study on mouse brain cells shows that the cells’ axons — the armlike structures that reach out and exchange information with other brain cells — are not the cylindrical tubes often pictured in books and on websites ...
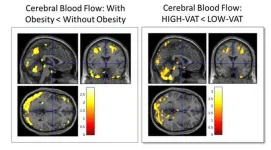
Hidden fat predicts Alzheimer’s 20 years ahead of symptoms
2024-12-02
CHICAGO – Researchers have linked a specific type of body fat to the abnormal proteins in the brain that are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease up to 20 years before the earliest symptoms of dementia appear, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The researchers emphasized that lifestyle modifications targeted at reducing this fat could influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This crucial result was discovered because we investigated Alzheimer’s disease pathology as ...
Countertop workers exposed to serious lung disease
2024-12-02
CHICAGO – Durable and attractive, engineered stone countertops are a popular feature in modern American kitchens, but the workers who build them are risking their health. A growing number of these countertop workers are developing silicosis, a serious and long-term lung disease, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“This is a new and emerging epidemic, and we must increase awareness of this disease process so we can avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment for our patients,” ...
Higher ratio of plant protein to animal protein may improve heart health
2024-12-02
Embargoed for release: Monday, December 2, 4:00 AM ET
Key points:
In a 30-year study of American adults’ diets, those who consumed the highest ratio of plant-based protein to animal-based protein had a 19% lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and a 27% lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) compared to those who consumed the lowest ratio.
According to the researchers, the findings suggest that a 1:2 ratio of plant to animal protein is effective in preventing CVD—and that an even higher ratio (1:1.3) may be needed to protect against CHD.
While global dietary guidelines recommend higher intake of plant ...
Lung cancer screening CTs find coronary artery disease in 83% of cases
2024-12-02
Lung cancer screening with low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) may detect more than just lung cancer. As new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231602 shows, these CTs can identify coronary artery calcium, a strong risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD), in patients without cardiac symptoms.
“Lung cancer screening, although primarily geared towards reducing deaths from lung cancer, also has an opportunity to help tackle the second ...
Consumers face barriers to embracing ethical fashion, psychologist warns
2024-12-02
Consumers are likely to continue making poor fashion choices unless eco-friendly choices become more accessible, according to a leading psychologist.
Carolyn Mair says brands must do more to promote sustainable clothing by making it more accessible to all, and by doing more to educate the public about mindful consumption.
Meaningful reforms to the current model of fashion production, in which garments are made from raw materials then discarded, have lagged, says Dr Mair who is also a fashion business consultant.
Making sustainable choices
In Dr Mair’s new book The Psychology of Fashion, she says eco-labels on garments are an important influence ...
Antiretroviral drugs for treatment and prevention of HIV in adults: 2024 recommendations of the International Antiviral Society–USA Panel
2024-12-01
About The Article: This narrative review from the International Antiviral Society–USA provides updated 2024 recommendations for HIV treatment and clinical management and HIV prevention. New approaches for treating and preventing HIV offer additional tools to help end the HIV epidemic, but achieving this goal depends on addressing disparities and inequities in access to care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rajesh T. Gandhi, MD email RGANDHI@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.24543)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] ‘I don’t feel your pain’: How alcohol increases aggressionStudy finds link to increase in pain threshold