(Press-News.org) Earth's tropical rain belt, responsible for monsoons that sustain billions of people and vibrant ecosystems, has long been a reliable feature of the planet's climate. But new research reveals this vital system wasn't always so dependable. A study published in Geophysical Research Letters shows that during the early Eocene—the hottest period in the last 65 million years—the rain belt's seasonal shifts weakened dramatically. These ancient changes could offer critical warnings about the impact of modern global warming.
A Greenhouse Climate 50 Million Years Ago
The early Eocene was a time of intense volcanic activity, releasing massive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide levels surged to over 1600 ppmv—approximately six times preindustrial levels—causing global temperatures to rise by 9–23°C.
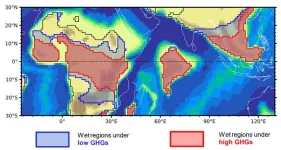
Researchers from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences used climate simulations and reconstructions of ancient climate conditions to uncover a striking pattern: extreme warming expanded subtropical dry zones and shrank tropical wet regions. Central to this disruption was a reduced seasonal movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)—a band of clouds and heavy rainfall that shifts north and south along with the seasons.
The mechanism underlying the muted swing
The ITCZ's seasonal movement is controlled by the tug-of-war between solar radiation and latent heat flux—the energy transported into atmosphere as water evaporates from ocean surfaces. In modern climates, cooler oceans moderate evaporation’s sensitivity to wind, allowing the ITCZ to shift largely into the summer hemisphere as the sun’s position changes.
“In the early Eocene, much warmer oceans made evaporation far more sensitive to wind speed,” said Dr. REN Zikun, the study's lead author. “This heightened sensitivity amplified wind-driven differences in surface evaporation between hemispheres, disrupting the balance with solar heating. The result was a reduced seasonal reach of the ITCZ and a contraction of tropical wet zones.”
Relevance to Today's Warming World
If current greenhouse gas emissions continue unchecked, carbon dioxide levels could rise to levels seen during the early Eocene. Prof. ZHOU Tianjun, the corresponding author, highlighted the study's broader implications: “The deep-time history of Earth provides critical evidence of how greenhouse gases reshape the global climate. While the Eocene's changes occurred over millennia, similar shifts could happen at an unprecedented pace due to human activities. This serves as a stark warning about the urgent need for mitigation efforts.”
END
Lessons from Earth's hottest epoch in the last 65 million years: How global warming could shrink the tropics' rain belt
2024-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Independent rice paddy methane model validated for global applications: Study highlights emission mitigation potential
2024-12-05
Rice paddies, responsible for approximately 10% of global anthropogenic methane (CH₄) emissions, are increasingly recognized as a key contributor to global warming. Reducing emissions from rice cultivation is essential to achieving international climate goals, especially in light of commitments to carbon neutrality and peak emissions targets.
A team led by Prof. LI Tingting from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has validated an independently developed methane emission model, CH4MOD, at the global scale. This research highlights the advantages of process-based models over the commonly ...
Infertility linked to onset of systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease after childbirth
2024-12-05
Women who experience infertility but do not use fertility treatments have a higher risk of developing a group of conditions called systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD) in the nine years after a naturally conceived birth compared to women without fertility problems.
The new research, published today (Thursday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, found that this was true even after accounting for higher rates of pre-eclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), preterm birth ...
Researchers use data from citizen scientists to uncover the mysteries of a blue low-latitude aurora
2024-12-05
Colorful auroras appeared around Japan's Honshu and Hokkaido islands on May 11, 2024, sparked by an intense magnetic storm. Usually, auroras observed at low latitudes appear red due to the emission of oxygen atoms. But on this day, a salmon pink aurora was observed throughout the night, while an unusually tall, blue-dominant aurora appeared shortly before midnight.
Smartphone videos and amateur photos captured the event, enabling scientists to combine public data with their own research and study the phenomenon.
In a ...
Possible colon cancer vaccine target uncovered in bacteria
2024-12-05
Higher rates of certain cancers in countries, such as the UK, may be linked to two particular strains of bacteria. Targeting these with treatments or vaccines could help reduce the risk of colorectal, bladder, and prostate cancers.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Helsinki, and collaborators investigated the differences in cancer incidence for colorectal, bladder and prostate cancers, and compared these to global data tracking Escherichia coli (E.coli) strains. Specifically, they looked at the dominant two E.coli strains that produce a substance that has been previously identified as a risk factor for colorectal cancer.
Their ...
Eating dark chocolate linked with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-12-05
Embargoed for release: Wednesday, Dec. 4, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
Study participants who consumed at least five servings of any chocolate per week showed a 10% lower risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared to those who rarely or never ate chocolate. Dark chocolate had an even bigger impact: Participants who consumed at least five servings of this chocolate per week showed a 21% lower risk of T2D.
Consumption of milk chocolate, but not dark chocolate, was not associated with T2D risk; it was associated ...
Eating dark but not milk chocolate linked to reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-12-05
Eating five servings of dark chocolate a week is associated with a reduction in the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a long-term US study published by The BMJ today.
Global rates of type 2 diabetes are set to rise to 700 million by 2045. Chocolate contains high levels of flavanols (a natural compound found in fruits and vegetables) which have been shown to promote heart health and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. But the link between chocolate consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes remains controversial due to inconsistent results.
In addition, most previous studies have not looked at whether eating dark and milk chocolate – which have different ...
End food and drink industry’s infiltration of UK children’s education, say experts
2024-12-05
An investigation published by The BMJ today reveals widespread influence of food and drink brands in schools and nurseries – through breakfast clubs, nutrition guidance, and healthy eating campaigns - while rates of obesity in the UK have worsened.
Experts say the tactics are “subtle but very problematic” and require much greater scrutiny and pushback.
Organisations influencing food provision and education in schools include Kellogg’s, Greggs, Nestle, and the British Nutrition Foundation, a “policy development” charity ...
Concerns over potential harms of tests advertised directly to consumers
2024-12-05
Better information and regulation are essential to protect consumers from potential harms of tests advertised directly to consumers, argue experts in The BMJ today.
Emma Gram at the University of Copenhagen and colleagues warn that consumers are at risk of buying products that do more harm than good and say the public needs high quality information and effective communication to protect consumers from unbalanced and misleading marketing.
Advances in diagnostic technology and digital health have increased the variety and volume of direct-to-consumer (DTC) tests, ...
War in Lebanon has turned a decade of education crisis into a catastrophe - report
2024-12-05
The recent conflict in Lebanon has deepened a national education crisis in which children have already lost up to 60% of school time over the past six years, new research warns.
The report, which will be launched on 5 December by the Centre for Lebanese Studies and the University of Cambridge’s REAL Centre, is the first to assess the state of education since Israel began its ground offensive in Lebanon in October. Using surveys and interviews with parents and teachers, it provides a snapshot of the situation a few weeks before the new ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah.
The study stresses that even ...
Spotted lanternflies in the US are living longer—and cities may be helping them spread
2024-12-05
Spotted lanternflies—invasive insects that first landed in the United States a decade ago—are emerging earlier and staying active later each year, according to an analysis of citizen-science data by researchers at New York University. This longer life cycle and shift in activity may be driven in part by cities and their warmer climates.
The spotted lanternfly, native to parts of Asia, was first found in the US in 2014 in eastern Pennsylvania. Since then, the population has spread across the Northeast and into the Midwest and Southeast, sparking concerns about its impact on local plants and agriculture.
The ...