(Press-News.org) To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/About The Study: In hospitalized adults, daily procalcitonin -guided protocol reduced antibiotic duration safely compared with standard care, but daily C-reactive protein -guided protocol does not. All-cause mortality for C-reactive protein was inconclusive.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul Dark, MD, PhD, email adaptsepsistrial@warwick.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.26458)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the Critical Care Reviews Down Under meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.26458?guestAccessKey=bececbf0-6542-489f-88dd-1e444426bd6a&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=120924
END
Biomarker-guided antibiotic duration for hospitalized patients with suspected sepsis
JAMA
2024-12-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
American Meteorological Society announces Alan Sealls as 2025 President-Elect
2024-12-09
Members of the American Meteorological Society (AMS) have elected Alan Sealls to the position of AMS president-elect for 2025. Sealls is an AMS Fellow and Certified Broadcast Meteorologist who retired this year from a 37-year broadcast career, which included serving as chief meteorologist at WPMI-TV in Mobile, Alabama. He will be inducted as president-elect on Sunday, 12 January, 2025, during the 105th AMS Annual Meeting in New Orleans, Louisiana.
At the meeting, the AMS—the professional society for weather, water, and climate sciences ...
Dogs use two-word button combos to communicate
2024-12-09
A new study from UC San Diego’s Comparative Cognition Lab shows that dogs trained to use soundboards to “talk” are capable of making two-word button combinations that go beyond random behavior or simple imitation of their owners. Published in the journal Scientific Reports from Springer Nature, the study analyzed data from 152 dogs over 21 months, capturing more than 260,000 button presses – 195,000 of which were made by the dogs themselves.
“This is the first scientific study to analyze how dogs actually use soundboards,” said lead researcher Federico Rossano, associate professor of cognitive science at UC San Diego and director ...
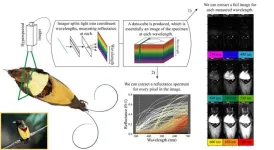
Researchers use a powerful imaging technique to illuminate the colorful plumage of birds
2024-12-09
Animals showcase a remarkable diversity of colors and patterns, from the shimmery appearance of a peacock’s tail to the distinctive rosettes on a jaguar’s fur. Quantifying animal color has been a longtime goal of evolutionary biologists, who aim to understand how color evolved over time—and the physical and genetic mechanisms involved. Ultimately, studying animal color is important because it can reveal how evolutionary forces, such as natural and sexual selection, favor certain traits over others. However, fully capturing animal color is challenging because researchers must choose between high spatial resolution (as in traditional ...
Jabuticaba peel improves nutritional characteristics of bread
2024-12-09
Researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil, have developed a sourdough bread formulation enriched with jabuticaba peel that could be an alternative for people with diabetes and others who need to control blood sugar. An article describing their research and test results is published in the journal Foods.
As noted in the article, the high carbohydrate content of bread can sharply raise blood sugar levels, risking hyperglycemia. Given the high demand for healthier bread, which is widely consumed, artisanal bakers seek to diversify their products with formulations that add nutritional value while involving fermentation ...
Department of Energy announces $36 million for student traineeships
2024-12-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced 29 projects totaling $36 million to 42 institutions in 16 states for traineeships for undergraduate students, graduate students, and postdoctoral researchers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). The funding, through the DOE Office of Science’s RENEW initiative, will support hands-on research experience, professional development activities to build or reinforce STEM identity, and mentorship to support personal and professional growth of trainees.
“The RENEW program provides new entry points to science for ...
Employee visits to adult or gambling sites doubles risk of infection by malware
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 9, 2024 – Malware (malicious software) is a worldwide threat to network security for organizations. Individual users within those networks may inadvertently download or interact with malware like viruses and ransomware by browsing unsafe websites, downloading software, or clicking on phishing links in emails.
Cybersecurity researchers from the University of Trento and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and the global cybersecurity firm Trend Micro wondered what behaviors bring the greatest risk of malware infection: working at night, browsing adult content, gambling, having a lot of software installed or just visiting strange places?
The ...
Biodiversity at risk in most rainforests
2024-12-09
New research has revealed less than a quarter of the remaining tropical rainforests around the globe can safeguard thousands of threatened species from extinction.
The research, co-authored by The University of Queensland’s Professor James Watson, evaluated the global availability of structurally intact, minimally disturbed tropical rainforests for more than 16,000 species of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
“Using remote sensing and forest integrity indicators, we analysed the quality of the rainforests across the ranges of the forest-dependent vertebrates,” Professor Watson said.
“Overall, up to 90 per cent of ...
Climate change impacting freshwater fish species, study finds
2024-12-09
Freshwater fish populations that dwell nearer the poles are outperforming their equatorial counterparts, researchers have found.
Large-bodied migratory species such as Atlantic salmon are thriving as warming temperatures opens up new habitats at the poleward edge of their ranges.
The study, published today in PNAS, was based on a dataset of over 10,000 time series and included over 600 species of fishes.
Climate change has emerged as a key threat to biodiversity, leading to broad-scale shifts in distributions of marine and terrestrial species as they attempt to track thermally suitable habitat. Despite ...
UVM research team unveils breakthrough mechanism in brain blood flow regulation
2024-12-09
Burlington, Vt.— A team of UVM scientists led by Mark Nelson, Ph.D., from the Larner College of Medicine at the University of Vermont, has uncovered a novel mechanism that reshapes our understanding of how blood flow is regulated in the brain. The study, published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a peer reviewed journal of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), introduces Electro-Calcium (E-Ca) Coupling, a process that integrates electrical and calcium signaling in brain capillaries to ensure precise blood flow delivery to active neurons.
In the human body, blood is delivered into the brain from surface arteries ...
How ‘Conan the Bacterium’ withstands extreme radiation
2024-12-09
Dubbed “Conan the Bacterium” for its extraordinary ability to tolerate the harshest of conditions, Deinococcus radiodurans can withstand radiation doses thousands of times higher than what would kill a human — and every other organism for that matter.
The secret behind this impressive resistance is the presence of a collection of simple metabolites, which combine with manganese to form a powerful antioxidant. Now, chemists at Northwestern University and the Uniformed Services University (USU) have discovered how this antioxidant works.
In ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] Biomarker-guided antibiotic duration for hospitalized patients with suspected sepsisJAMA