Statistical and engineering approaches to federated learning: Comprehensive benchmarking for healthcare applications
2024-12-11
(Press-News.org)
Statistical and Engineering Approaches to Federated Learning: Comprehensive Benchmarking for Healthcare Applications
A groundbreaking study conducted by Duke-NUS Medical School evaluates federated learning (FL) methods to guide healthcare researchers in choosing privacy-preserving algorithms tailored to their clinical goals. This comprehensive benchmark compared statistical and engineering FL frameworks, offering actionable insights to balance predictive accuracy and interpretability in medical research.
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a powerful tool in healthcare, enabling collaboration across institutions without compromising patient privacy. With stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR, FL frameworks have gained traction. However, their varying methodologies—statistical and engineering-based—pose challenges in selecting the right approach for specific research needs.
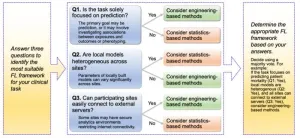
In the first comprehensive comparison of its kind, Duke-NUS researchers evaluated seven FL frameworks—three statistical and four engineering-based—using both simulated data and real-world emergency department datasets. Statistical FL methods were found to be more reliable for interpreting relationships between factors and clinical outcomes, making them ideal for non-predictive tasks. Engineering-based FL algorithms, on the other hand, demonstrated superior predictive performance, excelling in outcome prediction tasks.
"Our study bridges the gap between federated learning approaches and their practical application in healthcare," said lead author Siqi Li, a PhD candidate at Duke-NUS Medical School. "By providing clear guidelines, we empower researchers to choose FL frameworks that align with their specific priorities, whether it’s interpretability or predictive power."
Senior Research Assistant Di Miao added, "These findings highlight the unique strengths of each method, paving the way for more effective and ethical collaborations in clinical research."
This research not only underscores the potential of federated learning in advancing privacy-preserving AI but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in clinical decision-making and patient care.
The team aims to further refine FL algorithms for broader applications, fostering privacy-preserving collaborations across institutions and enhancing healthcare outcomes through innovative AI solutions.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-11
Drug addiction has been one of America’s growing public health concerns for decades. Despite the development of effective treatments and support resources, few people who are suffering from a substance use disorder seek help. Reluctance to seek help has been attributed to the stigma often attached to the condition. So, in an effort to address this problem, researchers at Drexel University are raising awareness of the stigmatizing language present in online forums and they have created an artificial intelligence tool to help educate users and offer alternative language.
Presented at the recent ...
2024-12-11
Religious believers are no more generous than atheists – at least as long as they don’t know what the recipient believes in. Finding this out increases generosity significantly, mainly because people give more to those who share their religion. This is the conclusion of a study carried out at Linköping University, Sweden.
Nathalie Hallin is an atheist. Her colleague Hajdi Moche is a Christian. They both have a postdoc position at the Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning at Linköping. Together they wanted to find out if a religious belief makes a person more generous, which research has so far disagreed on and they themselves have ...
2024-12-11
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with high-risk, BRCA-positive breast cancer who received olaparib (Lynparza) after standard treatment continued to have better survival outcomes than those who received placebo after a median follow-up of 6.1 years, according to the latest results from the phase III OlympiA clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“The OlympiA trial examines adding one year of the oral PARP inhibitor olaparib after completion of standard treatment ...
2024-12-11
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with germline BRCA mutations who were diagnosed with breast cancer at or before age 40 and who underwent a bilateral risk-reducing mastectomy (RRM) and/or a risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) had lower rates of recurrence, secondary breast and/or ovarian malignancies, and death than those who did not undergo these surgeries, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“The benefits of RRM and RRSO have been shown for BRCA-mutation carriers without a prior history of cancer, but their impact for BRCA-mutation carriers with a history of early-onset breast cancer is less clear,” ...
2024-12-11
SAN ANTONIO – Imlunestrant, an investigational next-generation selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), improved progression-free survival in patients with endocrine therapy-pretreated, ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer—as monotherapy in patients with ESR1 mutations and as combination therapy with abemaciclib (Verzenio) in all patients, regardless of ESR1 mutation status—according to results from the phase III EMBER-3 clinical trial presented at the San Antonio ...
2024-12-11
Carnegie Mellon University Africa and Challenger Center Collaborate to Deliver STEM Programs
Partnership Will Promote STEM Education and Careers to Secondary School Students in Africa
Carnegie Mellon University Africa, CMU’s College of Engineering location in Kigali, Rwanda, and Challenger Center, will partner to deliver Challenger Center’s Virtual Missions to hundreds of secondary school students on the continent. This project will help grow the population of African students who are motivated to pursue higher education and careers in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields.
Challenger Center’s Virtual Missions are space-themed experiences for students ...
2024-12-11
Identifying novel therapeutic strategies and making fundamental discoveries related to small cell lung cancer. Creating environmental and sustainable solutions for lithium-ion battery technology. Improving the safety and efficacy of gene editing and understanding the mechanisms of DNA repair to potentially cure diseases. Discovering the most distant and massive galaxies that have reshaped our understanding of early Universe star formation and supermassive black holes. Pioneering geochemical fingerprinting technology to optimize energy production processes.
These are the breakthroughs ...
2024-12-11
DNA stores the instructions for life and, along with enzymes and other molecules, computes everything from hair color to risk of developing diseases. Harnessing that prowess and immense storage capacity could lead to DNA-based computers that are faster and smaller than today’s silicon-based versions. As a step toward that goal, researchers report in ACS Central Science a fast, sequential DNA computing method that is also rewritable — just like current computers.
“DNA computing as a liquid computing paradigm has unique application ...
2024-12-11
Street art takes many forms, and the vibrant murals on the Berlin Wall both before and after its fall are expressions of people’s opinions. But there was often secrecy around the processes for creating the paintings, which makes them hard to preserve. Now, researchers reporting in the Journal of the American Chemical Society have uncovered information about this historic site from paint chips by combining a handheld detector and artificial intelligence (AI) data analysis.
“The research highlights the powerful impact of the synergy between chemistry and deep learning in quantifying matter, exemplified in this case by pigments that make street ...
2024-12-11
HOUSTON ― Lauren Averett Byers, M.D., professor of Thoracic/Head & Neck Medical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, has received the
2025 Edith and Peter O’Donnell Award in Medicine from the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST). The award recognizes her fundamental discoveries and contributions to identifying novel therapeutic strategies for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which have paved the way for personalized treatments, even in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Statistical and engineering approaches to federated learning: Comprehensive benchmarking for healthcare applications