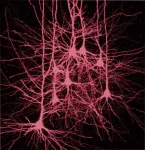
New insights into brain mechanisms underlying empathy
A research team from the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia has uncovered a key brain mechanism that modulates how animals react to others’ emotions
2024-12-12
(Press-News.org)
Genova (Italy), 12th December 2024 – A specific brain mechanism modulates how animals respond empathetically to others’ emotions. This is the latest finding from the research unit Genetics of Cognition, led by Francesco Papaleo, Principal Investigator at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT - Italian Institute of Technology) and affiliated with IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino in Genova. The study, recently published in Nature Neuroscience, provides new insights into psychiatric conditions where this socio-cognitive skill is impaired, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), autism, and schizophrenia.
Psychological studies have shown that the way humans respond to others’ emotions is strongly influenced by their own past emotional experiences. When a similar emotional situation—such as a past stressful event—is observed in another person, we can react in two different ways. On one hand, it may generate empathy, enhancing the ability to understand others’ problems and increasing sensitivity to others altered emotions. On the other hand, it may induce self-distress resulting into an avoidance towards others.
The research group at IIT has demonstrated that a similar phenomenon also occurs in animals: recalling a negative experience strongly influences how an individual responds to another who is experiencing that same altered emotional state. More specifically, animals exhibit different reactions only if the negative event they experienced in the past is identical to the one they observe in others. This indicates that even animals can specifically recognize an emotional state and react accordingly even without directly seeing the triggering stimuli.
Although the ability to respond to others’ emotions has profound impact in our everyday life and this is evolutionary conserved between humans and animals, the brain mechanisms that modulate its expression remain unclear.
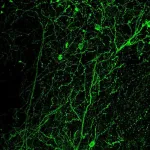
Papaleo’s group has identified the crucial role of the prefrontal cortex in these socio-cognitive processes. They conducted preclinical tests and employed advanced techniques to study the brain mechanisms underlying emphatic-related behaviors. Their findings reveal that a specific group of cells is a key modulator of emotional reactions to others based on emotional self-experience. These neurons produce corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), a molecule involved in the stress-response mechanism, and according to IIT researchers, they function as a sort of emotional memory, influencing reactions to socio-emotional stimuli.
“Understanding these brain mechanisms with such precision could help clarify many aspects of human reactions to others' emotions," said Francesco Papaleo, coordinator of the Genetics of Cognition unit at IIT. "For example, why, based on past emotional experience, some people tend to avoid others in stress, while others are more prone to help."
"Moreover, identifying the specific brain mechanisms involved in modulating empathetic responses," added Federica Maltese, first author of the study and currently a researcher at National Research Center (CNR) in Milan, "could aid clinical research in developing new targeted therapies aimed at improving the altered emotional responses observed in various psychiatric conditions.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-12
The Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) announced that Dr. Yong-Hun Kim from the Energy & Environment Materials Research Division and Dr. Kyung Song from the Material Characterization Center, in collaboration with Professor Hyun-Sang Hwang's team from POSTECH, have successfully developed a groundbreaking heterojunction technology. This technology integrates tungsten disulfide (WS₂), a two-dimensional (2D) material, with hafnium zirconium oxide (HZO), a ferroelectric material, achieving both interfacial stability and superior crystallinity. The results have been accepted by the International Electron Devices Meeting 2024 (IEDM 2024), ...
2024-12-12
“Rich” and “full-bodied” are terms that people often use to describe the taste of wine. They are also the properties that kokumi compounds bring to foods like mature Gouda cheese, though scientists haven’t widely explored them in wines. In ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers now connect the dots and report 11 probable kokumi compounds in sparkling wines.
Kokumi is often confused with the better-known term umami. Umami is a savory, meaty flavor and is one of the basic five tastes, along with sweet, ...
2024-12-12
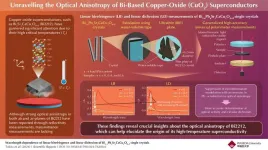
Superconductors are materials which conduct electricity without any resistance when cooled down below a critical temperature. These materials have transformative applications in various fields, including electric motors, generators, high-speed maglev trains, and magnetic resonance imaging. Among these materials, CuO2 superconductors like Bi2212 stand out due to their high critical temperatures that surpass the Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer limit, a theoretical maximum temperature limit for superconductivity. However, ...
2024-12-12
Artificial molecular machines, nanoscale machines consisting of a few molecules, offer the potential to transform fields involving catalysts, molecular electronics, medicines, and quantum materials. These machines operate by converting external stimuli, like electrical signals, into mechanical motion at the molecular level. Ferrocene, a special drum-shaped molecule composed of an iron (Fe) atom sandwiched between two five-membered carbon rings, is a promising foundational molecule for molecular machinery. Its discovery earned the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973, and it has since ...
2024-12-12
Plastic pollution is an ever-growing problem in today’s world, as most societies have become overly dependent on plastics for packaging, medical supplies, and general goods. Plastic litter accumulation in the ocean, either through deliberate dumping or by being transported from a river, poses significant environmental challenges. Additionally, this plastic eventually degrades into small fragments called microplastics, which then impact diverse marine and land ecosystems by working their way up the food chain and into most living organisms. Though their negative effects on cell health are still under study, many nations have taken a cautionary stance, ...
2024-12-12
EUGENE, Ore. — Dec. 12, 2024 — Tiny implantable sensors are helping University of Oregon researchers optimize the process of recovery from severe bone injuries.
Scientists at the UO’s Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact have developed miniature implantable sensors that transmit real-time data about what’s happening at an injury site. In a new study, they use the technology to show that a resistance-training rehabilitation program can significantly improve femur injuries in rats ...
2024-12-12
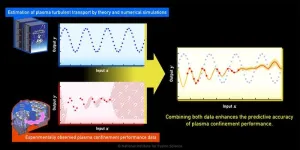
Fusion energy research is being pursued around the world as a means of solving energy problems. Magnetic confinement fusion reactors aim to extract fusion energy by confining extremely hot plasma in strong magnetic fields. Its development is a comprehensive engineering project involving many advanced technologies, such as superconducting magnets, reduced-activation materials, and beam and wave heating devices. In addition, predicting and controlling the confined plasma, in which numerous charged particles and electromagnetic fields interact in complex ...
2024-12-12
A new study led by investigators from Mass General Brigham has identified a unique brain network that links varied patterns of brain atrophy, or shrinkage, associated with schizophrenia. By combining neuroimaging data from multiple studies involving more than 8,000 participants, the research team found a specific connectivity pattern of atrophy that was present across different stages and symptoms of schizophrenia — and distinct from brain networks associated with other psychiatric disorders. The findings will help to guide a clinical trial that will start recruiting patients soon and will ...
2024-12-12
Research has long shown that humans are susceptible to “social identity bias”—favoring their group, whether that be a political party, a religion, or an ethnicity, and disparaging “outgroups.” A new study by a team of scientists finds that AI systems are also prone to the same type of biases, revealing fundamental group prejudices that reach beyond those tied to gender, race, or religion.
“Artificial Intelligence systems like ChatGPT can develop ‘us versus them’ biases similar to humans—showing favoritism toward their perceived ‘ingroup’ while expressing ...
2024-12-12
It has been known for nearly 20 years that slow, synchronous electrical waves in the brain during deep sleep support the formation of memories. Why that is was previously unknown. Now, writing in the journal Nature Communications, a team of researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin posits an explanation. According to the study, the slow waves make the neocortex, the location of long-term memory, especially receptive to information. The findings could help to optimize the treatment approaches that are intended to support memory formation from outside.
How do permanent memories form? Experts believe that while we sleep, our brains replay the events of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New insights into brain mechanisms underlying empathy
A research team from the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia has uncovered a key brain mechanism that modulates how animals react to others’ emotions