(Press-News.org) Endocannabinoids in the brain play a key role in food intake and energy use. Modulating the action of these molecules could help fight obesity, say researchers at Université de Montréal’s affiliated hospital research centre (CRCHUM).
For years, Université de Montréal medical professor Stephanie Fulton and her team have been unravelling the mechanisms in the human nervous system that control people’s need to eat and to engage in physical activity, and how their metabolism affects their mood.
Their latest discovery, published in Nature Communications, takes that knowledge a step further.
In their study, first co-authors David Lau, an Université de Montréal doctoral student, and Stephanie Tobin, a former postdoctoral fellow, show that body-weight control in mice is strongly modulated by neurons in the nucleus accumbens, a region of the brain that’s rich in endocannabinoids and that helps regulate food reward and physical activity.
In the brain, the enzyme ABHD6 degrades a key endocannabinoid molecule known as 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
With the discovery in 2016 that whole-body inhibition of ABHD6 reduced body weight and protected against diabetes—a finding made by the team of Marc Prentki, a researcher at the CRCHUM—the question arose as to what this enzyme does in the brain to affect appetite and body weight.
“We expected that increasing 2-AG levels would stimulate food intake by increasing cannabinoid signalling, but paradoxically found that when we deleted the gene encoding ABHD6 in the nucleus accumbens in mice, there was less motivation for food and greater interest in physical activity,” said Fulton.
“The mice chose to spend more time on a running wheel as compared to the control group which became obese and lethargic.”
By injecting a targeted ABHD6 inhibitor into the brains of mice, her team was able to completely protect them from weight gain and obesity.
Can have opposite effects
The ability to target specific neuronal pathways in the brain to control weight is crucial for scientists today. Depending on the area of the brain targeted, inhibiting ABHD6 can have opposite effects.
In 2016, Fulton and her CRCHUM colleague Thierry Alquier showed that blocking ABHD6 in certain hypothalamic neurons made mice resistant to weight loss.
In the current study, however, the authors show that brain-wide inhibition of this molecule has a net effect of diminishing weight gain on a high-fat diet.
No signs of anxiety
“In our study, we also show that mice in which the gene encoding ABHD6 has been inhibited do not show signs of anxiety and depressive behaviour,” said Fulton.
This is important given that Rimonabant, a weight-loss drug that targeted cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system, was withdrawn from the market in the late 2000s after people taking the drug reported strong side effects: depression and suicidal tendencies.
Fulton’s team’s latest work helps pave the way for therapies to fight obesity and metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, the scientists believe.
While ABHD6 drug inhibitors are being screened, it remains to be seen whether the mechanisms targeted by the researchers in mice will be the same in humans.
Science writing: Bruno Geoffroy
###
About this study
“ABHD6 loss-of-function in mesoaccumbens postsynaptic but not presynaptic neurons prevents diet-induced obesity in male mice,” by David Lau and Stephanie Tobin under the supervision of Stephanie Fulton et al. was published Dec. 16, 2024 in Nature Communications. Funding was provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health, the Montreal Diabetes Research Center, Diabetes Québec and the Fonds de recherche du Québec. The research was supported by the CRCHUM’s small-animal phenotyping and imaging core platforms.
About the CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM)
Université de Montréal's affiliated hospital research centre, the CRCHUM, is one of North America’s leading hospital research centres. It strives to improve the health of adults through a continuum of research spanning disciplines such as basic science, clinical research and population health. About 2,130 people work at CRCHUM. These include more than 550 researchers and nearly 530 graduate students and postdoctoral fellows. crchum.com
About Université de Montréal
Deeply rooted in Montréal and dedicated to its international mission, Université de Montréal is one of the top universities in the French-speaking world. Founded in 1878, Université de Montréal today has 13 faculties and schools, and together with its two affiliated schools, HEC Montréal and Polytechnique Montréal, constitutes the largest centre of higher education and research in Québec and one of the major centres in North America. It brings together 2,300 professors and researchers and has close to 67,000 students. umontreal.ca
END
Trappist-1 b is one of seven rocky planets orbiting the star Trappist-1, located 40 light-years away. The planetary system is unique because it allows astronomers to study seven Earth-like planets from relatively close range, with three of them in the so-called habitable zone. This is the area in a planetary system where a planet could have liquid water on the surface. To date, ten research programmes have targeted this system with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) for 290 hours.
The current study, in which researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) ...
When one tectonic plate sinks beneath another, it generates magmas rich in volatiles such as water, sulphur and chlorine. As these magmas ascend, they release magmatic fluids, in which sulphur and chlorine bind to metals such as gold and copper, and transport these metals towards the surface of the Earth. As the extreme conditions relevant to natural magmas are very difficult to reproduce in the laboratory, the precise role of the different forms of sulphur in metal transport remains highly debated. However, an innovative approach ...
New TRAPPIST-1 observations with JWST underscore the complexities of confirming a planet's atmosphere using only broadband thermal emission data. This insight takes on added significance with the newly approved "Rocky Worlds" observation program by Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) which plans to apply this very method to study numerous rocky exoplanets orbiting cool stars.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is revolutionizing the study of exoplanets (planets orbiting stars other than the Sun), notably by enabling detailed spectroscopic studies of small rocky planets, but only if ...
Statement Highlights:
About 800,000 people experience a stroke each year in the U.S., and due to recent advances in acute treatment, more people survive. Many stroke survivors experience long-term physical, mental and emotional health challenges.
Palliative care is both a specialty and an approach to care that focuses on helping stroke survivors and their caregivers cope with these challenges by offering symptom management and improving communication about goals of care and quality of life.
For a variety of reasons, palliative care is often underused, especially among Black, Hispanic and Asian patients.
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association outlining palliative ...
Philadelphia, December 16, 2024 – Law enforcement provides critical community services, yet Black autistic youth often face elevated risk of negative outcomes during police interactions. In an effort to learn more about these encounters within the autistic community, researchers at the Center for Autism Research at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) conducted a study to examine perceptions and concerns of Black caregivers of Black autistic children regarding police interactions. The findings, published online today by the journal Autism, revealed important changes that could be made to improve the quality of interactions between police and Black autistic youth.
Autistic ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – When young children’s behavior becomes challenging, many parents resort to threats – from taking away toys to threatening that Santa will skip their house, a national poll suggests.
Parents of children ages three to five were most likely to say they use threats to address misbehavior – with a fourth threatening their child with no Santa or gifts – according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
Many parents have also threatened to leave an activity or place, take away toys or not get dessert while nearly half of parents polled ...
The order Primates consists of not only our closest relatives on earth, the seven great apes, but also over 450 species of monkeys, lemurs, lorises, and galagos. Primates are fantastically diverse, from 400-pound gorillas to mouse lemurs (Microcebus) weighing just a single ounce. They exhibit some of the most remarkable behaviors observed in nature; chimpanzees ‘fish’ for termites in hollow logs using specially selected sticks, while orangutans use leaves as gloves to handle spiky durian fruit.
They are some of the most intensely studied species on Earth, and yet there is no comprehensive molecular phylogenetic hypothesis of primate evolutionary history that summarizes the pattern ...
Hamilton, ON, Dec. 16, 2024 – Researchers at McMaster University have uncovered unexpected diversity in the genetic processes that determine the sex of the African clawed frog, a significant discovery in what was already one of the most widely studied amphibians in the world.
A genomic analysis has uncovered a total of eight different sex chromosomes in just 11 species of the frog, many or all of which may contain unique and newly evolved genes that trigger male or female sexual differentiation.
Previously, researchers had known of only three different sex chromosomes ...
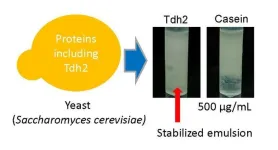
Mention emulsifiers and many people might be unaware what they are used for, but they are present in many daily products, from food to cosmetics. They keep substances that don’t usually mix, like water and oil, from separating and are either synthetically made or derived from milk, eggs, and soybeans, which are known as major food allergens. Thus, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers are looking at yeast proteins as emulsifiers.
A research group led by Graduate School of Engineering Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima previously showed that three yeast cell wall proteins ...
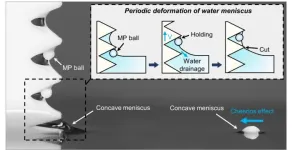
In recent years, microplastics have garnered significant attention due to their detection in tap and bottled water, as well as in rivers, lakes, and oceans. Conventional filtering technologies for water treatment have difficulty effectively filtering out microplastics of various sizes and shapes and are prone to clogging. Additionally, recovering small particles requires extremely fine filter meshes, which increases pressure and drastically reduces filter efficiency. Furthermore, they are not effective in open spaces such as lakes, rivers, or oceans, where microplastic pollution is increasing.
Dr. Seong Jin Kim ...