Robot rehabilitation can offer optimal post-stroke treatment
Use of automated system in upper extremity paralysis care proves beneficial for patients and medical staff
2024-12-18
(Press-News.org)
The increasing number of strokes and subsequent rehabilitation has highlighted the growing need for effective care strategies. Serious side effects, such as motor paralysis, can be challenging to mend, but the recent incorporation of robots into treatment has shown promise.
Automated robots repeatedly provide the proper movements necessary to recover motor function. However, to ensure appropriate care tailored to the degree of motor paralysis, knowledge of robots and rehabilitation is needed.
Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Takashi Takebayashi of the Graduate School of Rehabilitation Science led a team in collecting data from the actual use of Teijin Pharma Ltd.’s rehabilitation robot ReoGo-J.
The team looked into the rehabilitation programs that were selected by medical staff to match the degree of motor paralysis. By analyzing the data, the group developed the world’s first system that automatically recommends the optimal rehabilitation program. Based on a simple test to check the degree of motor paralysis in a patient’s hands, an appropriate treatment can be determined.
“By using this system, as long as medical professionals can carry out the test, even staff without experience with robots can provide appropriate robotic rehabilitation for motor paralysis,” stated Professor Takebayashi. “We hope this will lead to the further promotion of robot rehabilitation and a reduction in the burden on medical staff.”
The findings are published in Scientific Reports.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-18
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Dec 18, 2024)–A woman’s sex drive may diminish with age—partially because of problems with genitourinary symptoms during the menopause transition. Yet, some older women maintain very active sex lives. Why? A new study suggests that one difference could be sexual identity, with nonheterosexual women more likely to report better sexual functioning, despite menopause. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
An estimated 25% to 85% of postmenopausal women report challenges ...
2024-12-18
Researchers at the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa recently discovered that a virus, FloV-SA2, encodes one of the proteins needed to make ribosomes, the central engines in all cells that translate genetic information into proteins, the building blocks of life. This is the first eukaryotic virus (a virus that infects eukaryotes, such as plants, animals, fungi) found to encode such a protein.
Viruses are packets of genetic material surrounded by a protein coating. They replicate by getting inside of a cell where they take over the cell’s replication machinery and direct it to make more viruses. ...
2024-12-18
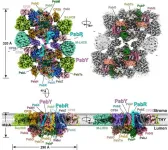
In higher plants and green algae, Photosystem II (PSII) usually combines with Light Harvesting Complex II (LHCII) to form the PSII-LHCII supercomplex. Under low-light conditions, the PSII-LHCII supercomplexes are organized laterally into higher-order PSII-LHCII megacomplexes and semi-crystalline arrays to optimize photosynthetic efficiency.
A recent collaborative study has deciphered the cryo-EM structure of the spinach type I PSII-LHCII megacomplex, providing insights into the principles of higher-order ...
2024-12-18
The Keck School of Medicine of USC has joined the Ryght Research Network, a global network of academic institutions, community practices and health care systems that uses generative artificial intelligence to make clinical trials more efficient. As the network’s first academic site in the United States, the Keck School of Medicine will leverage the collaboration to offer more clinical trials to more patients and to build new AI tools that safely speed up the process of developing medical treatments.
Ryght AI’s ...
2024-12-18
A team of University of Melbourne researchers from the Caruso Nanoengineering Group has created an innovative drug delivery system with outstanding potential to improve drug development.
The team has pioneered a drug delivery system that is a coordination network composed of only metal ions and biomolecules, known as metal–biomolecule network (MBN). This system eliminates the need for complicated drug ‘carriers’, making it potentially more useful in a range of applications.
The research has been published in Science Advances and was led by Melbourne Laureate Professor and NHMRC Leadership Fellow Frank Caruso, from the Department of ...
2024-12-18
Drinking a small or moderate amount of wine may lower the risk of serious cardiovascular disease in people at a higher risk who are following a Mediterranean diet, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday).
Previous studies on the effects of wine on cardiovascular health have produced inconsistent results. This may be in part because research often relies on people reporting how much wine they drink. Instead, in the new study, researchers measured the amount of a chemical, called tartaric acid, in participants’ urine. Researchers say this is an “objective and reliable measure” of wine consumption.
The ...
2024-12-18
Apes orphaned by the illegal trade in bushmeat and pets can overcome trauma and develop social abilities like those of their mother-reared peers.
A new study led by Durham University, UK, looked at the effects of rehabilitation by the world’s only bonobo sanctuary on the social and emotional development of orphaned bonobo apes across a 10-year period.
Bonobos are our closest living relatives, along with chimpanzees, and are only found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The early life trauma of maternal loss and the deprivation from being captured by humans can have long lasting negative effects on bonobos’ social abilities.
Researchers wanted to see what impact rehabilitation ...
2024-12-18
Researchers at Tohoku University's Institute for Materials Research and New Industry Creation Hatchery Center have made a breakthrough in a multi-material 3D printing technique, demonstrating the process for creating a lightweight yet durable automobile part.
The process of metal 3D printing involves building objects by depositing metals layer by layer, using heat to bind them together. The precision of 3D printing allows for the production of unique, highly customizable shapes that often create less wasteful byproducts than traditional manufacturing ...
2024-12-18
Reston, VA (December 17, 2024)—A new molecular imaging agent can accurately identify a crucial biomarker found among many different types of cancer. Precise visualization of the trophoblast cell surface antigen 2 (Trop2) biomarker can provide physicians with valuable insights for diagnosis, development of a personalized treatment plan, and response assessment. This research was published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Trop2 has garnered interest among cancer researchers recently due to the significant role it plays in cell self-renewal, proliferation, ...
2024-12-18
A new material for high density data storage can be erased and recycled in a more efficient and sustainable way, providing a potential alternative to hard disk drives, solid-state drives and flash memory in future.
The low-cost polymer stores data as ‘dents’, making a miniscule code in patterns, with the indents just nanometers in size – promising to store more data than typical hard disk drives.
The new Flinders University Chalker Lab polymer, which can have the information in it wiped in seconds by short bursts of heat and be reused several times, is described in a major new ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Robot rehabilitation can offer optimal post-stroke treatment
Use of automated system in upper extremity paralysis care proves beneficial for patients and medical staff