(Press-News.org) REGENSBURG, Bavaria, Germany, 24 December 2024 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Professor Inga Neumann, Chair of the Department of Behavioural and Molecular Neurobiology at the University of Regensburg, reveals groundbreaking insights into how oxytocin shapes social behavior and emotional responses in the brain.
The interview, published in Brain Medicine (DOI: 10.61373/bm024k.0139), showcases Professor Neumann's pioneering research on neuropeptides, particularly oxytocin, which has evolved far beyond its popular characterization as simply the "love hormone."
"I am convinced that increasing our knowledge about the stimuli, dynamics, and consequences of their intracerebral release at the behavioural, physiological, cellular, and molecular levels will improve our understanding of general brain mechanisms," explains Professor Neumann, whose work spans from molecular mechanisms to behavioral outcomes.
Her research team has developed innovative approaches to studying social anxiety, including a breakthrough mouse model of social fear conditioning. This work has opened new avenues for understanding how chronic stress and early life experiences influence social behavior patterns.
"We started to focus on the potential role of the brain's oxytocin and AVP systems as therapeutic targets for psychiatric diseases such as depression and anxiety disorders or autism," Professor Neumann notes, highlighting the clinical implications of her research. "The hope is that one day it will be possible to apply oxytocin reliably to treat – for example – treatment-resistant patients suffering from anxiety disorders, especially social anxiety, but also autism and schizophrenia."
As the first woman appointed full professor at the Faculty of Biology and Preclinical Medicine at the University of Regensburg, Professor Neumann has not only advanced scientific understanding but also broken gender barriers in academia. Her leadership extends to directing the Elite Masters Programme in Experimental and Clinical Neuroscience and heading the Graduate School "Neurobiology of Socio-Emotional Dysfunctions."
The interview provides unique insights into the challenges and triumphs of conducting neuroscience research across different political eras, from her early work in East Germany to her current position as a leading international researcher. "My beginnings as a scientist behind the 'Iron Curtain' were bumpy," she recalls, describing how her team had to build their own research equipment using donated materials.
Her current research focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms of social fear, particularly investigating the role of oxytocin, CRF, and other neuroactive molecules. This work has significant implications for treating social anxiety disorders and understanding stress resilience.
Looking ahead, Professor Neumann's research raises intriguing questions about the future of psychiatric treatment: How can we optimize the delivery of oxytocin-based therapies to the brain? What role might epigenetic factors play in social behavior disorders? How can we better translate findings from animal models to human therapeutic applications?
Professor Inga Neumann's Genomic Press interview is part of a larger series that highlights the people behind today’s most influential scientific ideas. Each interview in the series offers a blend of cutting-edge research and personal reflections, providing readers with a comprehensive view of the scientists shaping the future. By combining a focus on professional achievements with personal insights, this interview style invites a richer narrative that both engages and educates readers. This format provides an ideal starting point for profiles that explores the scientist’s impact on the field, while also touching on broader human themes. More information on the research leaders and research rising stars featured by Genomic Press can be found in our publication website: https://genomicpress.kglmeridian.com/.
The complete interview, titled "Inga D. Neumann: Molecular underpinnings of the brain oxytocin system and its involvement in socio-emotional behaviour: More than a love story," is available on 24 December 2024 in Brain Medicine. The article is freely accessible online at https://doi.org/10.61373/bm024k.0139.
About Brain Medicine: Brain Medicine (ISSN: 2997-2639) is a peer-reviewed medical research journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Brain Medicine is a new home for the cross-disciplinary pathway from innovation in fundamental neuroscience to translational initiatives in brain medicine. The journal’s scope includes the underlying science, causes, outcomes, treatments, and societal impact of brain disorders, across all clinical disciplines and their interface.
END
Neuroscience leader reveals oxytocin's crucial role beyond the 'love hormone' label
Distinguished professor Inga Neumann discusses groundbreaking social behavior research in exclusive Genomic Press Interview
2024-12-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Twelve questions to ask your doctor for better brain health in the new year
2024-12-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE ON MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Improving your brain health in the new year can start with a simple step, talking with your neurologist or primary care physician about 12 factors to protect your brain. The factors are outlined in an Emerging Issues in Neurology article developed by the American Academy of Neurology and published in the December 16, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Neurologists are the experts in brain health, with the training and insight needed to help you ...
Microelectronics Science Research Centers to lead charge on next-generation designs and prototypes
2024-12-23
RICHLAND, Wash.—Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that doesn’t just keep pace but sets new standards for the next generation of technological advances. Today, the Department of Energy announced the creation of three Microelectronics Science Research Centers to address the nation’s specific needs for microelectronics designed to operate in extreme environments such as high radiation, extreme cold, and high magnetic field—situations where robust and reliable operating environments are crucial. The new MSRCs not only focus on the next generation ...
Study identifies genetic cause for yellow nail syndrome
2024-12-23
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 23 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
New drug to prevent migraine may start working right away
2024-12-23
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug recently approved to prevent migraine may start working right away, according to a study published in the December 23, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study looked at the drug atogepant, which is a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist taken by mouth.
“With many current drugs to prevent migraine, it takes time to find the right dosage for the individual ...
Good news for people with MS: COVID-19 infection not tied to worsening symptoms
2024-12-23
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with multiple sclerosis (MS), having a COVID-19 infection is not associated with worsening MS symptoms or disability, according to a study published in the December 23, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Infections may be associated with more disability among people with MS,” said study author Amber Salter, PhD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, ...
Department of Energy announces $179 million for Microelectronics Science Research Centers
2024-12-23
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $179 million in funding for three Microelectronics Science Research Centers (MSRCs). These three MSRCs will perform basic research in microelectronics materials, device and system design, and manufacturing science to transform future microelectronics technologies. The MSRCs were authorized by the Micro Act, passed in the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, and complement the activities appropriated under the CHIPS and Science Act at the Department of Commerce, the Department of Defense, and other agencies.
For decades, DOE has been at ...
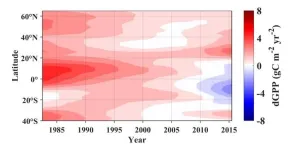
Human-related activities continue to threaten global climate and productivity
2024-12-23
The pace at which anthropogenic climate change has altered the terrestrial carbon stores is making our current climate-change mitigation efforts seem fruitless, unless behaviors are quickly changed.
Climate change induced by human behaviors, or anthropogenic climate change, has been a hot topic for decades and is not going away. As with any problem, reviewing datasets from the past to analyze trends and garner information is one of the first steps towards a solution. Gross primary productivity, or GPP, is a key indicator of the overall health of an ecosystem and is the amount of CO2 fixed by plants per unit of time and area. Researchers ...
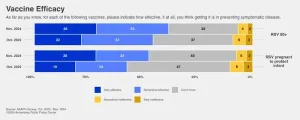
Public shows greater acceptance of RSV vaccine as vaccine hesitancy appears to have plateaued
2024-12-23
PHILADELPHIA – A year after becoming available, vaccines to protect against RSV in newborns and older adults are being more widely accepted by the American public, according to a new Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) health survey conducted in November 2024.
Over half of U.S. adults (52%) think the vaccine given to pregnant individuals to protect their infants from RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) is effective, up from 42% in October 2023, soon after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended the vaccine. And 61% say the RSV vaccine for adults age 60 and older is effective, up from 54% ...
Unraveling the power and influence of language
2024-12-23
A choice was made to include each word in this sentence. Every message, even the most mundane, is crafted with a specific frame in mind that impacts how the message is perceived.
The study of framing effects is a multidisciplinary line of research that investigates when, how, and why language influences those who receive a message and how it impacts their response.
This multifaceted science is in the spotlight in the latest issue of Psychological Science in the Public Interest. Stephen Flusberg of Vassar College and his team provide a comprehensive review of ...
Gene editing tool reduces Alzheimer’s plaque precursor in mice
2024-12-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new gene editing tool that helps cellular machinery skip parts of genes responsible for diseases has been applied to reduce the formation of amyloid-beta plaque precursors in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign report.
The application in live mice shows the improved efficiency of the tool, called SPLICER, over the current standard in gene editing technology, as well as the potential for application in other diseases, the researchers said. Led by Pablo Perez-Pinera, a professor of bioengineering at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Neuroscience leader reveals oxytocin's crucial role beyond the 'love hormone' labelDistinguished professor Inga Neumann discusses groundbreaking social behavior research in exclusive Genomic Press Interview