The extreme teeth of sabre-toothed predators were ‘optimal’ for biting into prey, new study reveals
2025-01-09
(Press-News.org)
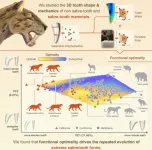
Sabre-toothed predators – best know from the infamous Smilodon – evolved multiple times across different mammal groups. A new study, published today in Current Biology reveals why: these teeth were ‘functionally optimal’ and highly effective at puncturing prey.
The study, led by scientists at the University of Bristol in collaboration with Monash University shows that long, sharp blade-like teeth gave sabre-tooth’s a real advantage as specialised weapons for capturing prey.
The findings help explain why sabre-teeth evolved so many times (at least five independent times in mammals) and also provides a possible explanation for their eventual demise. Their increasing specialisation may have acted as an ‘evolutionary ratchet’, making them highly effective hunters – but also more vulnerable to extinction when ecosystems changed and their prey became scarce.
The team, set out to test whether sabre-tooth shape was an optimal balance between the two competing needs: sharp and slender enough to effectively puncture prey and blunt and robust enough to resist breaking. Using 3D-printed steel tooth replicas in a series of biting experiments and advanced computer simulations, they analysed the shape and performance of 95 different carnivorous mammal teeth, including 25 sabre-toothed species.
Lead author Dr Tahlia Pollock, part of the Palaeobiology Research Group in Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, explained: “Our study helps us better understand how extreme adaptations evolve – not just in sabre-toothed predators but across nature.
“By combining biomechanics and evolutionary theory, we can uncover how natural selection shapes animals to perform specific tasks.”
Another key finding challenges the traditional idea that sabre-toothed predators fell into just two categories: ‘dirk-toothed' and 'scimitar-toothed’. Instead, the research uncovered a spectrum of sabre-tooth shapes, from the long, curved teeth of Barbourofelis fricki to the straighter, more robust teeth of Dinofelis barlowi. This supports a growing body of research suggesting a greater diversity of hunting strategies among these predators than previously thought.
Looking ahead, the team plans to expand their analysis to include all tooth types, aiming to uncover the biomechanical trade-offs that shaped the evolution of diverse dental structures across the animal kingdom.
“The findings not only deepen our understanding of sabre-toothed predators but also have broader implications for evolutionary biology and biomechanics,” added Professor Alistair Evans, from the School of Biological Sciences at Monash University. “Insights from this research could even help inform bioinspired designs in engineering.”
Paper:
‘Functional optimality underpins the repeated evolution of the extreme ‘sabre-tooth’ morphology’ by Tahlia Pollock et al in Current Biology.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-09
Russell W. Jenkins, MD, PhD, a physician investigator in the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center and an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, is senior author of a new study in Cancer Immunology Research, “TBK1 is Identified as a Therapeutic Strategy to Enhance CAR T-Cell Efficacy Using Patient-Derived Organotypic Tumor Spheroids”.
The study was a collaboration with the late Soldano Ferrone, MD, PhD, and was carried across the finish line by his daughter Cristina Ferrone, MD, Moshe Sade-Feldman, PhD, and several other collaborators ...
2025-01-09
Which medicine is best when you are affected by cancer? This can vary from person to person. A new method can help people with a specific type of blood cancer get the best medicine for them.
“The new method can help those affected by chronic myelogenous leukemia,” says Jennifer Sheehan, a PhD research fellow from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Production at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Sheehan was first author of a new publication in PLOS Computational Biology that describes ...
2025-01-09
Miami (January 9, 2025) – Additional research addressing the connection between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and metabolic syndrome is needed to improve holistic patient care, according to a new editorial. The editorial is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke ...
2025-01-09
A Mount Sinai-led team of researchers has enhanced an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered algorithm to analyze video recordings of clinical sleep tests, ultimately improving accurate diagnosis of a common sleep disorder affecting more than 80 million people worldwide. The study findings were published in the journal Annals of Neurology on January 9.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep condition that causes abnormal movements, or the physical acting out of dreams, during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep. RBD that occurs in otherwise healthy adults ...
2025-01-09
The Kinsey Institute at Indiana University has acquired remarkable archives from three pioneering figures in the study of human sexuality, relationships, and wellbeing: the legendary sex therapist Dr. Ruth Westheimer, renowned anthropologist Dr. Helen Fisher, and respected feminist historian Dr. Judith Allen. These invaluable collections represent decades of groundbreaking research, education, and cultural contributions that will advance future scholarship and research.
“For almost 80 ...
2025-01-09
An innovative project jointly funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) brings together a team of scientists from Florida Atlantic University and Lehigh University, along with a team from Japan that includes researchers from Kyoto University, University of Tokyo and Kumamoto University.
The project, titled “NSF-JST: An Inclusive Human-Centered Risk Management Modeling Framework for Flood Resilience,” is supported by a three-year, $1 million award split evenly between the U.S. and Japanese teams, with the U.S. team receiving $499,271. ...
2025-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Tracking coyote movement in metropolitan areas shows the animals spend lots of time in natural settings, but a new study suggests the human element of city life has a bigger impact than the environment on urban coyote survival.
Researchers monitoring coyotes in Chicago found that habitat – areas with relatively high levels of vegetation cover and low levels of human infrastructure – did not influence coyote survival in positive or negative ways. Instead, areas densely populated with humans were ...
2025-01-09
Given that today’s children will inherit the consequences of climate change, schools are instrumental in mobilizing a global response to the climate crisis, a science educator argues.
Climate literacy advocate Kelley T. Lê argues that climate change is the defining issue of our time, and in her new book, Teaching Climate Change for Grades 6–12: Activating Science Teachers to Take on the Climate Crisis Through NGSS, Lê provides teachers, administrators, and global leaders with practical tools to empower ...
2025-01-09
The emissions scandal in the automotive industry that came to light in 2015 has set many things in motion. Last but not least, the discussion about the need for realistic tests for vehicles in order to correctly determine their pollutant emissions instead of just testing on test rigs. Such tests and the applicable emission limits are now required by law for cars, but not for so-called category-L vehicles (mopeds, motorbikes, tricycles and quads). As part of the “LENS” project (L-vehicles Emissions and Noise mitigation Solutions) funded by the European ...
2025-01-09
Research Highlights:
More than one-third of Asian, Black and Hispanic women in the study group reported experiencing at least one microaggression related to race and gender during or after their pregnancy.
The link between racial microaggressions and postpartum blood pressure was strongest 10 or more days after delivery, when the blood pressure may be monitored less often, the researchers noted.
The researchers also noted that these types of gendered racial microaggressions can raise blood pressure postpartum and suggest blood pressure monitoring and/or treatment for high blood pressure may need to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The extreme teeth of sabre-toothed predators were ‘optimal’ for biting into prey, new study reveals



