(Press-News.org) The concentration of the population in cities is accelerating, and difficulties in maintaining various infrastructures are arising due to extreme weather. Extensive infrastructures like waste landfill facilities face significant challenges due to the difficulty for managers to stay on-site or access them. These maintenance issues are resulting in various problems, including environmental pollution.
To solve these issues, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Sun Kyu, Park) has developed a cost-effective and high-efficiency maintenance technology using satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data.
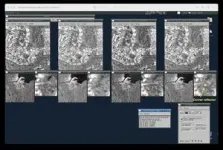
The satellite-based wide-area survey technology uses SAR to generate high-resolution images. It is an active remote sensing method that uses microwaves ranging from a few centimeters to several tens of centimeters, allowing observations under all weather conditions. Recently, satellite SAR data such as the European Space Agency's Sentinel satellites are being shared for free, making it possible to integrate this technology into cost-effective maintenance solutions.
Dr. Sungpil, Hwang and Dr. Wooseok, Kim of KICT has utilized satellite SAR data to study the impact of underground structures, including roads and subways. The research analyzed the effects of excavation, such as subsidence on the surface caused by blasting, and verified the applicability of the technology under various structural conditions in urban areas. With this technology, widespread monitoring of surface displacement is anticipated to become feasible.
The joint research team from KICT and the University of Tokyo conducted an analysis of an actual waste disposal facility to verify the applicability of the technology for landfill sites in 2024. In order to eliminate obstacles such as trees in wide-area sites like landfills, scatterers were applied. As a result of the scatterer application, data more than 15dB higher than the surrounding areas was obtained. This suggests that the maintenance of landfill facilities can be carried out more accurately. If this technology is implemented, maintenance costs will be reduced by more than 30% compared to existing methods, and blind spots in management will be eliminated.
Dr. Hwang, the lead researcher, highlighted the growing issue of aging infrastructure, stating, "The number of facilities requiring maintenance is increasing." He further emphasized the potential benefits of satellite SAR data, noting, "It is expected that using satellite SAR data will enable cost-effective and efficient maintenance."
KICT plans to develop and implement a maintenance system for landfill facilities that includes scatterers in the future. This innovative system will not only be applicable to landfills, offering maintenance solutions for infrastructures across wide-area regions.
###
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, a government-funded research institute with 42 years of extensive research experience, is at the forefront of solving national issues that are directly related to the quality of the people’s life.
Research for this work was carried out under the KICT Research Program (project no. 20240401-001, A Study on Monitoring Surface Displacement Using SAR Data from Satellite for Waste Landfill) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. An article explaining the results of this research was published in the latest issue of Sustainability, a renowned international journal in the Civil Engineering field (IF:3.3).
END
The new age of infrastructure maintenance using data from space
Development of low-cost and high-efficiency maintenance technology for difficult-to-maintain infrastructure
2025-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CNIO and CNIC research identifies a key protein for ‘burning’ fat
2025-01-13
This work reveals a new mechanism by which brown fat is converted into heat, and which protects from pathologies associated with obesity.
The MCJ protein is key to the fat burning mechanism now identified, making it a promising target for treating obesity, according to the authors in Nature Communications.
The research is led by Guadalupe Sabio, from Spain’s National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), and Cintia Folgueira, from both CNIO and the National Centre for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC).
Obesity, which affects 650 ...
‘True food’ research database offers rankings for 50,000 processed foods
2025-01-13
‘True Food’ Research Database Offers Rankings for 50,000 Processed Foods
The database, developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham and made available to the public, sheds light on the availability of processed foods at different grocery stores, highlighting the need for more understanding and regulation of the foods offered
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham provides information to empower consumers and policymakers about the degree of processing of the foods available at three large grocery retailers. Using an algorithm, the researchers analyzed ...
Mystery solved: how tumor cells die after radiotherapy
2025-01-13
Scientists at Children’s Medical Research Institute (CMRI) have solved a big mystery in cancer research – why cells die in different ways following radiotherapy. This surprising finding opens up new opportunities to improve treatment and increase cure rates.
The findings were published in Nature Cell Biology by first author Dr Radoslaw Szmyd of CMRI’s Genome Integrity Unit, which is led by Professor Tony Cesare.
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is a critically important type of cancer treatment. Scientists have struggled for decades to understand why radiation therapy kills cells from the ...
Bacterial survival genes uncovered using evolutionary map
2025-01-13
The most detailed study to date on the mechanisms by which a common type of bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus, adapts to living on the human body could help improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of certain infections.
The study, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, the Institute of Biomedicine of Valencia (IBV) at the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and their collaborators, involved using the genomes of thousands of S. aureus isolates cultured from the human nose and on the skin to investigate which genes are important for the bacteria to adapt and persist.
Published today (13 January) in Nature Communications, ...
Sodium-ion batteries need breakthroughs to compete
2025-01-13
Legions of battery engineers and their supporters have sought for years to build batteries cheaper than the dominant lithium-ion technology, hoping to capture some of lithium-ion’s $50 billion-a-year and growing market. The latest darling contender among researchers, startups, and venture capitalists – sodium-ion batteries – has received much attention after COVID-induced mineral supply chain challenges sent lithium prices on a wild ride. Still, achieving a low-cost contender may be several years away for sodium-ion batteries and will require a set of technology advances and favorable ...
Tumor DNA in the blood can predict lung cancer outcome
2025-01-13
Scientists from the Francis Crick Institute, UCL, UCLH and Personalis have found that a test to detect circulating tumour DNA can predict lung cancer outcome in a Cancer Research UK-funded study.
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) is fragments of DNA released into the blood by tumours. It’s known to be important for disease prognosis but can be difficult to measure precisely.
In research published today in Nature Medicine, Crick and UCL scientists worked with Personalis to test a platform called NeXT Personal, which can detect very small amounts – 1 part per million – ...
New study unveils breakthrough in understanding cosmic particle accelerators
2025-01-13
Scientists have come a step closer to understanding how collisionless shock waves – found throughout the universe – are able to accelerate particles to extreme speeds.
These shock waves are one of nature's most powerful particle accelerators and have long intrigued scientists for the role they play in producing cosmic rays – high-energy particles that travel across vast distances in space.
The research, published today in Nature Communications, combines satellite observations from NASA’s MMS (Magnetospheric Multiscale) and THEMIS/ARTEMIS missions with recent theoretical advancements, offering a comprehensive new model ...
Previous experience affects family planning decisions of people with hereditary dementia
2025-01-13
Living in a family where there is genetic risk for dementia significantly affects choices about having children and how to parent, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in the Journal of Genetic Counselling, interviewed 13 people – both parents and non-parents – who are at risk of developing familial frontotemporal dementia (fFTD).
This form of dementia often begins in mid-life and is characterised by behavioural and personality changes. Children of an affected parent are at 50% risk of inheriting the gene that causes the disease.
People in affected families fall into three groups: people who don’t choose to find out whether ...
Does obesity affect children’s likelihood of survival after being diagnosed with cancer?
2025-01-13
A recent population-based study indicates that among children with cancer, those with obesity at the time of diagnosis may face an elevated risk of dying. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The retrospective study was based on information from the Cancer in Young People in Canada (CYP-C) database, including all children with newly diagnosed cancer aged 2 to 18 years across Canada from 2001 to 2020. Obesity was defined as age and sex-adjusted body mass index at or above the 95th percentile.
Among ...
Understanding bias and discrimination in AI: Why sociolinguistics holds the key to better Large Language Models and a fairer world
2025-01-13
The language ‘engines’ that power generative artificial intelligence (AI) are plagued by a wide range of issues that can hurt society, most notably through the spread of misinformation and discriminatory content, including racist and sexist stereotypes.
In large part these failings of popular AI systems, such as ChatGPT, are due to shortcomings with the language databases upon which they are trained.
To address these issues, researchers from the University of Birmingham have developed a novel framework for better understanding large language ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] The new age of infrastructure maintenance using data from spaceDevelopment of low-cost and high-efficiency maintenance technology for difficult-to-maintain infrastructure