(Press-News.org) VANCOUVER, Wash. – While many studies have looked at possible evolutionary links between men’s strength and sexual behavior, a Washington State University study included data on women with a surprising result. Women, as well as men, who had greater upper body strength tended to have more lifetime sexual partners compared to their peers.
The study, published in the journal Evolution and Human Behavior, was designed to test evolutionary theories for human sexual dimorphism—namely that in early human history there was likely a reproductive advantage selecting for men’s greater upper body strength.
Another finding in this study did hint at a reason for that physical difference: men with greater upper body strength were also more likely to to be in long-term relationships.
“People have assumptions about men’s sexual behavior and how that’s related to evolution. Besides acquiring more sexual partners, establishing long-term relationships was likely also important for men in evolutionary history,” said lead author Caroline Smith, a recent WSU Ph.D. graduate in anthropology.
For this study, Smith and her advising professor, WSU evolutionary anthropologist Ed Hagen, analyzed data on 4,316 U.S. adults from 2013-2014 from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They primarily used grip strength, a common measure to approximate upper body strength, and compared it to participants’ survey responses about their sexual behavior.
The findings present a mixed picture, the authors said.
There are several hypotheses around why men have greater upper body strength. One popular theory, known as the sexual selection hypothesis, is based on competition: that like other primates, human males competed against each other for access to mates so needed to be physically formidable to pass their genes on. This theory predicts little relationship between women’s strength and their mating success.
“Men are stronger than women, on average, and men report more lifetime partners than women, but men and women are on the same regression line,” said Hagen. “Regardless of whether they’re males or females, stronger individuals have more lifetime sexual partners. That was a surprising finding and somewhat contrary to the sexual selection hypothesis.”
On the other hand, this study’s finding about long-term partners seems to support another theory based on “provisioning.” Since human babies require a lot of care and resources, particularly from women during pregnancy and lactation, men were more desirable as partners when they could provide meat through hunting, which for hundreds of thousands of years before the modern era required upper body strength. The stronger human males, who also stuck around and helped provide more food resources to those children as they grew, also would better ensure their survival.
While there are theories for men’s strength in relation to reproductive success, there are not so many for women’s strength, in part because women are not often included in these types of studies.
There was not an obvious explanation in this study’s data why women with greater upper body strength also had greater number of lifetime partners. The researchers controlled for many variables, including general health and testosterone levels, but the connection still held. They did cite a few potential theories, including that it is due to “assortative mating,” meaning physically stronger people tend to partner with each other more frequently. It could also be that women who are physically stronger require less male investment or feel like they can take more risks.
Ultimately, more studies involving women would be needed to uncover more evidence for the reasons behind this connection as well as a better understanding of human evolution in general.
“I believe it’s important to continually test our theories, especially by expanding our research questions to include women,” said Smith.
END
Strength connected to sexual behavior of women as well as men
2025-01-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Eating pork linked with better handgrip strength, vegetable intake in Korean older adults
2025-01-14
New research1 underscores the potential role of pork consumption in supporting dietary and muscle health in Korean older adults. Older adults are a nutritionally vulnerable population who often face unique challenges, including meeting daily protein and micronutrient requirements.
The study,* conducted through a collaborative partnership between researchers from Gachon University in South Korea, Tufts University, Think Healthy Group, LLC, and other leading institutions, suggests that pork consumption may be positively linked to nutrient intake, diet quality and handgrip strength—an indicator of overall muscle strength in older adults.
Using data from more than 2,000 ...
Direct discharge electrical pulses for carbon fiber recycling
2025-01-14
The world is hurtling rapidly towards a developed future, and carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) play a key role in enabling technological and industrial progress. These composite materials are lightweight and highly strong, making them desirable for applications in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, automotive, wind power generation, and sports equipment.
However, recycling CFRPs presents a significant challenge, with waste management being a pressing issue. Conventional recycling methods ...
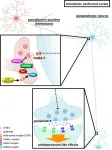
Scientists uncover rapid-acting, low-side-effect antidepressant target
2025-01-14
The global burden of anxiety- and depression-related disorders is on the rise. While multiple drugs have been developed to treat these conditions, current medications have several limitations, including slow action and adverse effects with long-term use. This underscores the urgent need for novel, rapidly-acting therapeutic agents with minimal side effects.
The delta opioid receptor (DOP) plays a key role in mood regulation, making it a promising target for therapeutic intervention. Studies have shown that selective DOP agonists (compounds that activate DOP), such as SNC80 ...
Diamond continues to shine: new properties discovered in diamond semiconductors
2025-01-14
CLEVELAND and CHAMPAIGN-URBANA, ILL.—Diamond, often celebrated for its unmatched hardness and transparency, has emerged as an exceptional material for high-power electronics and next-generation quantum optics. Diamond can be engineered to be as electrically conductive as a metal, by introducing impurities such as the element boron.
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have now discovered another interesting property in diamonds with added boron, known as boron-doped diamonds. Their findings could pave the way for new types ...
Researchers find the key to Artificial Intelligence’s learning power – an inbuilt, special kind of Occam’s razor
2025-01-14
A new study from Oxford University has uncovered why the deep neural networks (DNNs) that power modern artificial intelligence are so effective at learning from data. The new findings demonstrate that DNNs have an inbuilt ‘Occam's razor,’ meaning that when presented with multiple solutions that fit training data, they tend to favour those that are simpler. What is special about this version of Occam’s razor is that the bias exactly cancels the exponential growth of the number of possible solutions with complexity. The study has been published ...
Genetic tweak optimizes drug-making cells by blocking buildup of toxic byproduct
2025-01-14
An international team of researchers led by the University of California San Diego has developed a new strategy to enhance pharmaceutical production in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, which are commonly used to manufacture protein-based drugs for treating cancer, autoimmune diseases and much more. By knocking out a gene circuit responsible for producing lactic acid—a metabolite that makes the cells’ environment toxic—researchers eliminate a primary hurdle in developing cells that can produce higher amounts of pharmaceuticals like Herceptin and Rituximab, without compromising their growth or energy production.
The research, published on Jan. 14 in Nature Metabolism, ...
University of Birmingham researchers awarded grant to tackle early-stage heart disease in chronic kidney disease
2025-01-14
New research funding will investigate the early stages of heart disease associated with chronic kidney disease led by the University of Birmingham.
Dr Davor Pavlovic will lead an international research team after receiving almost £300,000 from the British Heart Foundation to understand the mechanisms driving the early stages of CKD-associated cardiomyopathy.
The research approach will allow detailed investigation of cellular and electrophysiological changes before irreversible damage to the heart occurs. Researchers will also test whether in the setting of CKD, early treatment can reverse or prevent heart disease.
The research will be ...
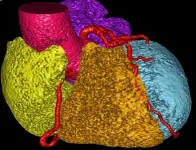
Researchers harness AI to predict cardiovascular risk from CT scans
2025-01-14
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University, University Hospitals and Houston Methodist will harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to more accurately predict risk of heart failure and other cardiovascular events, including estimating when an adverse event might occur, by developing an AI model that “learns” from patient scans.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, claiming over 17 million lives every year, according to the American Heart Association. Accurately ...
Samsung takes top spot in U.S. patents for third year running while TSMC rises into second place; after four-year falloff, grants increase nearly 4%
2025-01-14
New Haven, Conn., Jan. 14, 2025—After four years of decline, U.S. patent grants headed upward, rising 3.8 percent from calendar year 2023 to 324,043 and Samsung retained the top spot for the third year in a row, according to IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, the world’s most trusted patent data source.
IFI CLAIMS Patent Services is a Digital Science company that compiles and tracks data from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and other patent-issuing agencies around the globe. IFI translates its world-leading data into an annual U.S. Top 50 and ...
HKU ecologist highlights critical gaps in global wildlife trade monitoring
2025-01-14
Wildlife trade poses one of the greatest threats to the survival of numerous species. According to the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) at least 50,000 species are involved in trade. However, while this figure already seems huge, it risks overlooking less traditional sectors of wildlife trade, such as the pet or fashion trade. For instance, recent data shows that the number of butterflies traded exceeds the total number of terrestrial arthropods in the IPBES assessment. This raises a critical question: How many ...