(Press-News.org) Approximately 66 million years ago, the Chicxulub asteroid, estimated to be 10-15 kilometer in diameter, struck the Yucatán Peninsula (in current-day Mexico), creating a 200-kilometer-wide impact crater. This impact triggered a chain reaction of destructive events including a rapid climate change that eventually led to the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs and in total about 75% of species on Earth. The main culprit is most likely the “impact winter”, which was caused by massive release of dust, soot, and sulfur into the atmosphere, leading to extreme cold, darkness, and a collapse in global photosynthesis, with lasting effects on ecosystems for years to decades after impact.
Most previous studies considered sulfur as the most crucial factor in driving the cooling and extinction after the impact event. However, estimates of the volume of sulfate aerosols released from the vaporization of the impacted rocks in Mexico have varied widely over two orders of magnitude from one study to another. This is because such estimates are largely based on uncertain parameters, such as the proportion of sulfur-bearing rocks at the impact location, the size, velocity, and impact angle of the asteroid, and the resulting shock pressures of sulfur-bearing minerals.
In the new study, Katarina Rodiouchkina and colleagues used sulfur concentrations and isotopic compositions from new drill cores of impact rocks within the crater region, combined with detailed chemical profiles across K-Pg boundary sediments around the world. This way, the authors were able to empirically estimate, for the first time, the total amount of sulfur released into the atmosphere due to the Chicxulub asteroid impact event.
“Instead of focusing on the impact event itself, we focused on the aftermath of the impact “, explains chemist Katerina Rodiouchkina. “We first analyzed the sulfur fingerprint of the rocks within the crater region that were the source of sulfate aerosols released into the atmosphere. These sulfate aerosols distributed globally and were eventually deposited from the atmosphere back onto the Earth’s surface in the months to years after impact. The sulfur was deposited around the K-Pg boundary layer in sedimentary profiles all over the world. We used the corresponding change in the isotopic composition of sulfur to distinguish impact-related sulfur from natural sources and the total amount of sulfur released was calculated through mass balance.“
The scientists revealed that a total of 67 ± 39 billion tons of sulfur were released, approximately five times less than previously estimated in numerical models. This suggests a milder "impact winter" than previously believed, leading to a less severe temperature decline and faster climate recovery, which could have contributed to the survival of at least 25% of species on Earth following the event. While sulfur remains the primary driver of global cooling, it is important to note that a recent study by the Royal Observatory of Belgium and VUB suggests a massive plume of micrometer-sized fine dust may have played a crucial role in creating a two-year-long dark period, blocking photosynthesis and further compounding the environmental impacts.
The study was a collaboration between Luleå University of Technology, Ghent university (UGent), Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB), Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), Leibniz-Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW), University of Greifswald, University of Rostock, Australian Laboratory Services (ALS) Scandinavia AB, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KU Leuven), and the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences (RBINS). This research was supported by the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) through the EOS-Excellence of Science program (project ET-HoME) and Hercules funding for the acquisition of a multi-collector ICP-mass spectrometer at UGent, VUB Strategic Research Program, Chicxulub BRAIN-be (Belgian Research Action through Interdisciplinary Networks) and the FED-tWIN project MicroPAST both through the Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO).
Reference:
Katerina Rodiouchkina, Steven Goderis, Cem Berk Senel, Pim Kaskes, Özgür Karatekin, Michael Ernst Böttcher, Ilia Rodushkin, Johan Vellekoop, Philippe Claeys, Frank Vanhaecke. Reduced contribution of sulfur to the mass extinction associated with the Chicxulub impact event. Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55145-6
END
Asteroid impact sulfur release less lethal in dinosaur extinction
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows seed impact mills clobber waterhemp seed viability
2025-01-16
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 16 January 2025 – Recently published research in the journal Weed Science shows promise for controlling herbicide-resistant weeds in soybean fields by using a seed impact mill at harvest. When installed on a combine, this harvest weed-seed control system (HWSC) mechanically damages weed seeds as they move through the mill to render them non-viable.
Iowa State University Researchers Alexis Meadows and Ram (Ramawatar) Yadav conducted seed impact mill field experiments ...
Study links rising suicidality among teen girls to increase in identifying as LGBQ
2025-01-16
Amid an increase in suicidal behavior among teen girls, new research links this phenomenon to the significant increase in the number of female students identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or questioning (LGBQ).
“This finding suggests that the overall increase in female suicidality is not due to all female students becoming more suicidal, but rather to a larger proportion of students being part of a group that has historically experienced higher rates of suicidal thoughts and behaviors due to social and structural pressures,” says lead author Joseph Cimpian, ...
Mind’s eye: Pineal gland photoreceptor’s 2 genes help fish detect color
2025-01-16
We see color because photoreceptor cones in our eyes detect light waves corresponding to red, green, and blue, while dimness or brightness is detected by photoreceptor rods. Many non-mammalian vertebrates like fish, however, are known to detect color and brightness with the pineal gland, which is part of the brain. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group has further elucidated on how the pineal organ of fish do so.
Previously, the research group led by Professor Akihisa Terakita and Professor Mitsumasa Koyanagi of the Graduate School of Science revealed that ...
Nipah virus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention
2025-01-16
Nipah virus (NiV), a zoonotic paramyxovirus with significant human health implications, has garnered considerable attention due to its high fatality rates and potential for human-to-human transmission, posing a global public health threat. Emerging in South and Southeast Asia, NiV is known for its recurrent outbreaks, with a particular focus on its genetic lineages, NiV-MY and NiV-BD, which differ in pathogenicity and transmissibility. The virus, initially isolated in Malaysia in 1998, has since caused outbreaks linked to contact with infected ...
FDA ban on Red Dye 3 and more are highlighted in Sylvester Cancer's January tip sheet
2025-01-16
FDA BANS RED DYE 3 IN FOOD AND INGESTED DRUGS
Citing two studies linking Red Dye 3 to cancer in laboratory male rats, the FDA today revoked authorization for the use of the dye in food and ingested drugs. The move came in response to a 2022 color additive petition. “This is long overdue,” said Tracy Crane, Ph.D., RDN., director of Lifestyle Medicine and Prevention at Sylvester. “Red Dye 3 has been banned for use in cosmetics and topical drugs for more than three decades,” she said. “Yet it gives more than 9,000 foods in the United States their red coloring. These colorful foods and drinks are particularly appealing to young children,” ...
Mapping gene regulation
2025-01-16
KYOTO – An international team of researchers has taken an important step toward understanding how gene expression is controlled across the human genome. A new study has comprehensively analyzed “cis-regulatory elements” (CREs), which are the DNA sequences that regulate gene transcription. This work sheds light on how these elements contribute to cell-specific gene expression and how mutations within them may influence health and disease.
CREs, including enhancers and promoters, are essential for controlling when and where genes are ...
Exposure to air pollution before pregnancy linked to higher child body mass index, study finds
2025-01-16
In a study of more than 5,000 mothers and their children, exposure to air pollution during the three months before pregnancy predicted higher child body mass index (BMI) and related obesity risk factors up to two years of age. Findings from the study, which was supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, were published in the journal Environmental Research.
Past research has linked air pollution exposure during pregnancy to a broad range of health problems in children, including respiratory ...
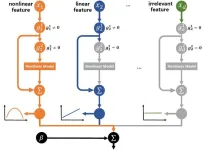
Neural partially linear additive model
2025-01-16
Interpretability has drawn increasing attention in machine learning. Partially linear additive models provide an attractive middle ground between the simplicity of generalized linear model and the flexibility of generalized additive model, and are important models for addressing the two interpretability problems of feature selection and structure discovery. The existing partially linear additive models still have various imperfect performances in terms of fitting ability.
To solve the problems, a research team lad by Han LI published their new research on 15 December 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The ...
Dung data: manure can help to improve global maps of herbivore distribution
2025-01-16
Researchers have used dung records to create high-resolution maps of herbivore distribution around the world. Their new study, recently published in Nature Food, reveals a strong positive relationship between dung presence and grazing pressure, meaning the amount of dung found in a particular location could help us understand approximately how many herbivores live there.
Many people consider dung simply as the manure left behind by horses and cows at country shows, or something to be avoided when you visit the cousins’ farm. But dung is actually an important resource for millions of people worldwide.
Dung ...
Concerns over maternity provision for pregnant women in UK prisons
2025-01-16
Senior midwives and researchers with experience in criminal and social justice are among those calling for improved maternity provision for pregnant women in UK prisons.
In an article published by The BMJ today, Laura Abbott and colleagues highlight gaps in clinical care for pregnant women and say the systemic problems need tackling urgently to protect the health of pregnant women, new mothers, and babies while in criminal justice settings.
Figures from April 2023 to March 2024 show that 229 pregnant women ...