(Press-News.org) Computers also make mistakes. These are usually suppressed by technical measures or detected and corrected during the calculation. In quantum computers, this involves some effort, as no copy can be made of an unknown quantum state. This means that the state cannot be saved multiple times during the calculation and an error cannot be detected by comparing these copies. Inspired by classical computer science, quantum physics has developed a different method in which the quantum information is distributed across several entangled quantum bits and stored redundantly in this way. How this is done is defined in so-called correction codes. In 2022, a team led by Thomas Monz from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and Markus Müller from the Department of Quantum Information at RWTH Aachen and the Peter Grünberg Institute at Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany implemented a universal set of operations on fault-tolerant quantum bits, demonstrating how an algorithm can be programmed on a quantum computer so that errors can be corrected efficiently. However, different quantum error correction codes also come with different difficulties. A theorem states that no correction code can implement all the gate operations required for freely programmable computations with the logical quantum bits easily and protected against errors.
Quantum gates are realized with different correction codes
To circumvent this difficulty, Markus Müller's research group has established a method that allows the quantum computer to switch back and forth between two correction codes in an error-tolerant manner. “In this way, the quantum computer can switch to the second code whenever a logic gate that is difficult to realize appears in the first code. This makes it easier to implement all the gates required for computing,” explains Friederike Butt, a doctoral student in Markus Müller's research group. She developed the quantum circuits on which the experiment is based and implemented them in close collaboration with Thomas Monz's research group in Innsbruck. “Together, we have succeeded for the first time in realizing a universal set of quantum gates on an ion trap quantum computer using two combined quantum error correction codes,” says PhD student Ivan Pogorelov from the Innsbruck research group.
“This result is based on our many years of good collaboration with Markus Müller's team,” says Thomas Monz, who knows the theoretical physicist from his doctoral studies at the University of Innsbruck.
The findings of the current study were published in the journal Nature Physics. The research was financially supported among others by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG, the German DFG, the Bavarian State Government, the European Union and the Federation of Austrian Industries Tyrol.
Publication: Experimental fault-tolerant code switching. Ivan Pogorelov, Friederike Butt, Lukas Postler, Christian D. Marciniak, Philipp Schindler, Markus Müller, and Thomas Monz. Nature Physics 2025. DOI: 10.1038/s41567-024-02727-2 [arXiv: 2403.13732]
END
Calculating error-free more easily with two codes
Quantum computer efficiently suppresses errors with two different error correction codes
2025-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dissolving clusters of cancer cells to prevent metastases
2025-01-24
Certain tumour types do not remain at their point of origin but spread throughout the body and form metastases. This is because the primary tumour continuously releases cancer cells into the blood. These circulating tumour cells (CTCs) can join together into small clusters of up to a dozen cells and settle in other organs. There, the clusters grow into larger tumours, known as metastases. Metastatic tumours are still a major medical problem: every year, around seven million people worldwide die from them.
One example of such a spreading tumour is breast cancer. As soon ...
A therapeutic HPV vaccine could eliminate precancerous cervical lesions
2025-01-24
PHILADELPHIA – A therapeutic vaccine targeting human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) induced regression in high-grade precancerous cervical lesions, according to the results from a phase II clinical trial published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Nearly all premalignant cervical lesions and cervical cancers are caused by HPV infection, with HPV16 implicated in the majority of cases,” said Refika Yigit, MD, principal investigator and oncological gynecologist at University Medical Centre Groningen in the ...
Myth busted: Healthy habits take longer than 21 days to set in
2025-01-24
We’re nearly one month into 2025, but if you’re struggling to hold onto your New Year’s resolution, stay strong, as University of South Australia research shows that forming a healthy habit can take longer than you expect.
In the first systematic review of its kind, UniSA researchers found that new habits can begin forming within about two months (median of 59–66 days) but can take up to 335 days to establish.
It’s an important finding that could inform health interventions to ...
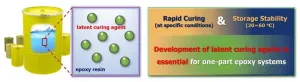
Development of next-generation one-component epoxy with high-temperature stability and flame retardancy
2025-01-24
Two-component epoxies, which require mixing resin and curing agent before use, often suffer from issues such as mixing ratio errors, limited working times, and inconsistent curing. Additionally, they must be used immediately after mixing, leading to wasted residue. To address these challenges, one-component epoxies have gained attention. One-component epoxies come pre-mixed, making them easy to use, reducing processing time, and ensuring consistent quality without mixing. In particular, using latent curing agents allows curing to be triggered only under specific conditions (e.g., heat or UV exposure), significantly improving storage stability. However, ...
Scaling up neuromorphic computing for more efficient and effective AI everywhere and anytime
2025-01-24
Neuromorphic computing—a field that applies principles of neuroscience to computing systems to mimic the brain’s function and structure—needs to scale up if it is to effectively compete with current computing methods. In a review published Jan. 22 in the journal Nature, 23 researchers, including two from the University of California San Diego, present a detailed roadmap of what needs to happen to reach that goal. The article offers a new and practical perspective toward approaching the cognitive capacity of the human brain with comparable form factor and power consumption.
“We ...
Make it worth Weyl: engineering the first semimetallic Weyl quantum crystal
2025-01-24
An international team of researchers led by the Strong Correlation Quantum Transport Laboratory of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) has demonstrated, in a world’s first, an ideal Weyl semimetal, marking a breakthrough in a decade-old problem of quantum materials.
Weyl fermions arise as collective quantum excitations of electrons in crystals. They are predicted to show exotic electromagnetic properties, attracting intense worldwide interest. However, despite the careful study of thousands of crystals, most ...
Exercise improves brain function, possibly reducing dementia risk
2025-01-24
A study led by scientists at Rutgers University-New Brunswick has shown that specialized cells involved in how the body responds to insulin are activated in the brain after exercise, suggesting that physical activity may directly improve brain function.
A study, published in Aging Cell, a journal focused on the biology of aging, indicates that therapies targeting this insulin action may be developed to offset or even prevent dementia progression.
“We believe this work is important because it suggests exercise may work to improve cognition and memory by improving the abilities of insulin to act on the brain,” ...
Diamonds are forever—But not in nanodevices
2025-01-24
Ultrawide-bandgap semiconductors—such as diamond—are promising for next-generation electronics due to a larger energy gap between the valence and conduction bands, allowing them to handle higher voltages, operate at higher frequencies, and provide greater efficiency compared to traditional materials like silicon. However, their unique properties make it challenging to probe and understand how charge and heat move on nanometer-to-micron scales. Visible light has a very limited ability to probe nanoscale properties, and moreover, it is not absorbed ...
School-based program for newcomer students boosts mental health, research shows
2025-01-24
The first randomized control trial of the school-based intervention called Supporting Transition Resilience of Newcomer Groups (STRONG) shows significant reductions in depression, anxiety and behavior problems among refugee and immigrant students. The study, funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, was co-led by Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Loyola University, in partnership with the Chicago Public Schools (CPS). Results were published in the American Journal of Community Psychology. Key findings are summarized ...
Adding bridges to stabilize quantum networks
2025-01-24
While entangled photons hold incredible promise for quantum computing and communications, they have a major inherent disadvantage. After one use, they simply disappear.
In a new study, Northwestern University physicists propose a new strategy to maintain communications in a constantly changing, unpredictable quantum network. By rebuilding these disappearing connections, the researchers found the network eventually settles into a stable — albeit different — state.
The key resides in adding a sufficient number of connections to ensure the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Calculating error-free more easily with two codesQuantum computer efficiently suppresses errors with two different error correction codes