(Press-News.org) DALLAS, January 27, 2025 — About 6.7 million American adults are living with heart failure (HF), and prevalence is expected to reach more than 8 million by 2030.[1]
While there is no cure for HF, many people with this condition can live full, enjoyable lives and disease progression can be slowed. While people with early-stage HF often can manage their condition with lifestyle modifications and medications, more advanced therapies may be needed as the disease progresses. Yet, a significant number of patients who may benefit from advanced HF specialty care don’t receive it — a gap that particularly affects populations with limited access to health care resources.[2],[3]
The American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, has launched a new $3 million initiative, supported financially by Abbott, that aligns with the rising need for advanced HF treatment pathways and education beyond traditional guideline-directed medical therapy. This effort will provide cardiovascular clinicians with information on care models that connect specialists and clinical teams to improve patient outcomes and support a growing HF population.
“Knowledge gaps among clinicians may contribute to variations and disparities in the types of patients who receive advanced HF therapies, and resultant delays or lack of referral can lead to adverse consequences for patients and their families,” said Mariell Jessup, M.D., FAHA, chief science and medical officer of the American Heart Association. “This initiative will create nationwide education on the full array of treatment options for eligible people living with advanced heart failure, helping to bridge these gaps.”
By engaging 15 carefully selected hospitals across the nation, the American Heart Association’s new three-year Heart Failure Education Initiative aims to improve understanding and amplify successful models of HF treatment pathways. Participating sites will:
collaborate to share challenges and develop solutions, and
have access to education sharing successful models of care through conferences, posters, webinars and more.
Multidisciplinary teams at each hospitals will engage in process mapping, expert collaboration and a national roundtable event. The 15 sites include:
Allina Health Minneapolis Heart Institute in Minneapolis
Avera McKennan Hospital and University Health Center in Sioux Falls, South Dakota
Baptist Memorial Hospital Memphis in Memphis, Tennessee
East Jefferson General Hospital in Metairie, Louisiana
Hackensack University Medical Center in Hackensack, New Jersey
JPS Health Network in Fort Worth, Texas
Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston, South Carolina
Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, Oregon
Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Center in Athens, Georgia
Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Missouri
The Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha, Nebraska
University of California San Diego in La Jolla, California
University of Chicago Medicine in Chicago
University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City
Yale New Haven Hospital in New Haven, Connecticut
“Across the United States, millions of people are living with heart failure, yet far too many of those people see their disease progress while never receiving access to new and innovative treatment approaches and therapy options,” said Keith Boettiger, vice president of Abbott’s heart failure business. “Fostering new connections between primary care physicians, cardiologists and advanced heart failure specialists is critical to ensuring more of these patients can access advanced therapy options that can improve and extend their life.”
Learn more about the initiative at heart.org/HFEducation.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link.
Health Lesson: Know Your Family Health History
Heart Failure | American Heart Association
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. Dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities, the organization has been a leading source of health information for more than one hundred years. Supported by more than 35 million volunteers globally, we fund groundbreaking research, advocate for the public’s health, and provide critical resources to save and improve lives affected by cardiovascular disease and stroke. By driving breakthroughs and implementing proven solutions in science, policy, and care, we work tirelessly to advance health and transform lives every day. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
[1] Chapter 22. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Circulation. February 20, 2024. 149(8):e347-e913. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209.
[2] Mwansa H, Lewsey S, Mazimba S, et al. Racial/Ethnic and Gender Disparities in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Curr Heart Fail Rep 2021(18):41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11897-021-00502-5.
[3] White-Williams C, Rossi LP, Bittner VA, Driscoll A, Durant RW, Granger BB, Graven LJ, Kitko L, Newlin K, Shirey M. American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Clinical Cardiology; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Addressing Social Determinants of Health in the Care of Patients With Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020 Jun 2;141(22):e841-e863. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000767.
END
Bridging critical gaps in advanced heart failure care
American Heart Association initiative, supported by Abbott, will create nationwide education to strengthen treatment pathways for people with advanced heart failure
2025-01-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover new way to store hydrogen using lignin jet fuel
2025-01-27
An international team of scientists has discovered a way to store and release volatile hydrogen using lignin-based jet fuel that could open new pathways for sustainable energy production.
In a new study in the International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Washington State University Professor Bin Yang and colleagues demonstrated that a type of lignin-based jet fuel they developed can chemically bind hydrogen in a stable liquid form. The research has many potential applications in fuels and transportation and could ultimately make it easier to harness ...
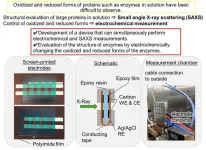
Electrochemical x-ray scattering unlocks secrets of redox enzymes
2025-01-27
Redox enzymes are proteins that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between molecules. Redox enzymes are crucial in bioelectrochemical devices, such as biosensors or biofuel cells. For instance, biosensors catalyze reactions that convert biochemical signals into measurable electrical signals, enabling the detection of substances like glucose. In biofuel cells, redox enzymes convert biological energy into electricity, powering small devices like medical implants. Their ability to facilitate the efficient transfer of electrons between molecules makes them indispensable ...
Unveiling Japan's geological history through volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits
2025-01-27
The Earth’s surface is constantly reshaped by the movement of tectonic plates, which make up the continental crust on which we are living. These tectonic plates are in continuous motion, and when one plate is pushed under another, it is called “subduction.” These processes play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s landmasses, including the islands of Japan, over several hundred million years. Studying ancient mineral deposits offers a valuable way to uncover the timing of these events. However, determining the precise timing of these tectonic events has ...
Unraveling the connection between Canadian wildfires and arctic ice clouds
2025-01-27
Clouds, composed of tiny water droplets or ice crystals, play a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by influencing the amount of solar radiation that reaches the surface. The cloud phase significantly impacts the surface energy balance as liquid water clouds reflect more radiation than ice clouds. Ice clouds typically form at temperatures below −38°C, but recent observations indicate their formation at higher temperatures in the Arctic. This phenomenon is facilitated by ice-nucleating particles (INPs), including mineral dust, organic aerosols and bioaerosols, which promote ice cloud formation above the usual freezing ...
Delayed REM sleep could be an early sign of Alzheimer’s
2025-01-27
Scientists have recently shown that both the quality and the amount of sleep we get may influence our risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Now, a study suggests that people who take significantly longer to start the dream phase of sleep, known as rapid eye movement (REM), may be experiencing an early symptom of the disease.
REM follows three phases of non-REM sleep, each deeper than the last. The four phases take 90 minutes or more to complete, depending on age, and a person may cycle through them four or five times in a typical night. Older people take longer to reach REM.
During REM sleep the brain processes memories, ...
Weight-loss surgery lowers risk of developing complications of liver disease in patients with cirrhosis and obesity
2025-01-27
Weight-Loss Surgery Lowers Risk of Developing Complications of Liver Disease in Patients with Cirrhosis and Obesity
SPECCIAL study suggests bariatric surgery favorably influences progression of cirrhosis
UNDER EMBARGO Monday, January 27, 2025, at 05:00 AM (US Eastern Time) CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that patients with obesity and fatty liver-related cirrhosis who had bariatric (weight-loss) surgery significantly lowered their future risk of developing serious ...
Heart disease remains leading cause of death as key health risk factors continue to rise
2025-01-27
Highlights:
According to the American Heart Association’s 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics Update, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S.
While medical advances have helped more people live longer with cardiovascular diseases, many of the risk factors which lead to these diseases, including high blood pressure and obesity, continue to grow at alarming rates.
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, claim more lives in the U.S. than all forms of cancer and accidental deaths – the #2 and #3 causes of death – combined.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET Monday, Jan. 27, 2025
DALLAS, Jan. 27, 2025 — Heart ...
Preterm babies receive insufficient pain management
2025-01-27
A large proportion of babies born very early need intensive care, which can be painful. But the healthcare system fails to provide pain relief to the full extent. This is shown by the largest survey to date of pain in neonatal care, now published in the journal Pain.
Every day for 4.5 years, neonatal care staff have recorded the occurrence of pain, the causes of pain, and how pain is assessed and treated in premature babies in Sweden. The study covers 3,686 babies born between 22 and 31 weeks of gestation from 2020 to 2024. The total observation time was just over 185,000 days of care. Data were collected in the Swedish ...
Does historic redlining—a form of structural racism—affect survival in young people with cancer?
2025-01-27
A recent study indicates that children and young adults with cancer face an elevated risk of dying if they live in previously redlined neighborhoods—residential areas marked in the 1920s–1930s by lenders as undesirable for mortgage loans due to their racial demographics. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Historic redlining prevented Black households and other communities of color from accessing home mortgages for many years, leading to economic disadvantage and racial ...
How animal poop helps ecosystems adapt to climate change
2025-01-27
Climate change is melting away glaciers around the world, but in the Andes Mountains, a wild relative of the llama is helping local ecosystems adapt to these changes by dropping big piles of dung.
This finding, published Dec 30 in Scientific Reports, revealed that the activity of this animal could accelerate the time plants usually take to establish on new land by over a century, highlighting a surprising way organisms are adapting to climate change.
“It’s interesting to see how a social behavior of these animals ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Bridging critical gaps in advanced heart failure careAmerican Heart Association initiative, supported by Abbott, will create nationwide education to strengthen treatment pathways for people with advanced heart failure