Tracking cfDNA release dynamics during colorectal cancer surgery
“Taken together, our results suggest that in addition to physiological age, comorbidities and unfavorable clinical traits, intense surgical manipulation from the tumor's extent, may result in greater tissue damage and elevated cfDNA release”
2025-01-27
(Press-News.org)
“Taken together, our results suggest that in addition to physiological age, comorbidities and unfavorable clinical traits, intense surgical manipulation from the tumor’s extent, may result in greater tissue damage and elevated cfDNA release.”
BUFFALO, NY – January 27, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 16 on January 21, 2025, titled “Assessment of cfDNA release dynamics during colorectal cancer surgery.”
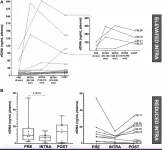
Researchers from the University of Brasília investigated how cell-free DNA (cfDNA) levels in the blood change before, during, and after colorectal cancer surgery. The study found that cfDNA levels increase significantly during and after surgery. The findings suggest that cfDNA could help clinicians evaluate surgery effectiveness and monitor patient outcomes.
cfDNA consists of small DNA fragments released into the bloodstream when cells die and break apart. In healthy individuals, cfDNA usually comes from normal cell turnover, while in cancer patients, some of it originates from tumor cells. Measuring cfDNA levels offers valuable insights into a patient’s condition and is already being used to track disease progression and treatment response in cancers such as lung, breast, and colorectal cancer.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Surgery is often the primary treatment, but up to 50% of patients experience cancer recurrence afterward. In this study, the research team, led by first author Mailson Alves Lopes and corresponding author Fabio Pittella-Silva, analyzed blood samples from 30 patients at three key time points: before, during, and after surgery.
It was found that cfDNA levels increased nearly threefold during surgery and doubled after surgery compared to pre-surgery levels. The increases were even higher in individuals over 60, those with preexisting conditions such as diabetes or heart disease, and patients with elevated levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a common cancer marker. Patients with the highest cfDNA levels were those with larger or more aggressive tumors, likely due to greater tissue damage during surgery. Additionally, longer surgeries were linked to higher cfDNA levels.
“[…]we observed that cfDNA concentration may rise in correlation with the duration of the surgery, highlighting its potential as a marker of surgical quality.”
These findings suggest that cfDNA could be a valuable, non-invasive biomarker for clinicians to monitor colorectal cancer patients. Tracking cfDNA levels may help better evaluate surgical outcomes and determine whether patients require closer follow-up care.
While these findings are promising, further research is needed to standardize cfDNA testing and validate its usefulness. Larger studies could help establish cfDNA testing as a reliable tool for cancer care and postoperative monitoring, with the potential to become a routine part of clinical practice in the future.
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28681
Correspondence to: Fabio Pittella-Silva – pittella@unb.br
Keywords: cancer, colorectal cancer, cfDNA, surgery
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-27
Climate change will likely result in a significant rise in deaths from heat across Europe, substantially surpassing any decrease in cold-related deaths. This trend persists across climate change scenarios and even under high adaptation to heat, reinforcing the need for aggressive mitigation policies.
A modelling study, led by researchers from the Environment & Health Modelling (EHM) Lab at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) and published in Nature Medicine, estimates that changes to the climate could directly result in over 2.3 million additional temperature-related deaths in 854 European cities by 2099 if urgent action ...
2025-01-27
RICHMOND, Va. (Jan. 27, 2025) — Infant mortality in the United States decreased by 24.2% between 1999 and 2022. Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU discovered this improvement in a study published Jan. 27 in the Journal of the American Medical Association Pediatrics. In the same study, however, they found mortality rates from Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID) rose significantly – by 11.8% – from 2020 to 2022.
“Although a prior CDC study – using data until 2020 – found that Sudden Unexpected Infant Death was increasing for Black infants, ...
2025-01-27
About The Study: This cohort study showed that, during the 2022 to 2023 season, infection with SARS-CoV-2 was associated with more severe disease outcomes than influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), whereas differences were less pronounced during the 2023 to 2024 season. During both seasons, RSV remained a milder illness, whereas COVID-19 was associated with higher long-term mortality. Vaccination attenuated differences in disease severity and long-term mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kristina L. Bajema, MD, email kristina.bajema@va.gov.
To access the ...
2025-01-27
About The Study: This cohort study evaluating hospitalizations for firearm-related injuries during the COVID-19 pandemic has 2 principal findings. From 2020 to 2021, there was a 34% increase in firearm-related hospitalizations, consistent with an additional 13,268 admissions. Second, the increase in firearm-related hospitalization disproportionately affected children, patients enrolled in Medicaid, and Black individuals. Taken together, these findings raise new concerns about the sustained increase in firearm-related injury that disproportionately ...
2025-01-27
About The Study: This study found that infant mortality from sudden unexpected infant death (SUID) has increased significantly. Previous data through 2020 showed that SUID increased among Black infants. The current analysis, which included 2021 and 2022 data, showed a more generalized increase. Possible explanations include COVID-19 or other respiratory illnesses, maternal opioid use, and social media’s influence on infant sleeping practices.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Elizabeth R. Wolf, MD, ...
2025-01-27
About The Study: This study provides evidence for a sensorimotor cortical biomarker signature for pain sensitivity. The combination of accuracy, reproducibility, and reliability suggests the peak alpha frequency/corticomotor excitability biomarker signature has substantial potential for clinical translation, including predicting the transition from acute to chronic pain.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, David A. Seminowicz, PhD, email dseminow@uwo.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
2025-01-27
Firearm injuries that sent victims to the hospital had gone down steadily over the five years before the COVID-19 pandemic began, but reversed course sharply over the next two years, a new University of Michigan study finds.
In all, 34% more people were hospitalized for a firearm-related injury in 2020 and 2021 than would have been predicted based on pre-pandemic trends.
The gap between expected and actual hospitalizations was even bigger for patients under the age of 18, those covered by Medicaid insurance for people with low incomes or disabilities, and those who are Black. The study is published in JAMA Network Open.
These ...
2025-01-27
New York, NY – January 27, 2025 – ProCure On-Demand’s 500th transplanted organ, being announced today, is emblematic of the gaps and inefficiencies in the current transplant system that the organ recovery, technology and logistics company is regularly solving.
The case involving the transplant of the 500th organ underscores ProCure's reputation for quality work, efficient logistics and swift turnaround times, which have become integral to their success. With less than five hours to recover bilateral lungs, ProCure tapped into its unique Recovery Team Network, to deploy a surgeon within seven miles ...
2025-01-27
Monday 27 January, 2025: A new international study has unveiled critical insights in understanding post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE), a condition that can develop following traumatic brain injury. Led by researchers at FutureNeuro, the Research Ireland Centre for Translational Brain Science and RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and published in Theranostics, the study highlights the important role played by a receptor in the brain called P2X7. It suggests how we could both reduce epilepsy ...
2025-01-27
Researchers have pioneered an innovative method using helioseismology to measure the solar radiative opacity under extreme conditions. This groundbreaking work, published in Nature Communications, not only reveals gaps in our understanding of atomic physics but also confirms recent experimental results, thereby opening new perspectives in astrophysics and nuclear physics.
Helioseismology is a discipline dedicated to studying the Sun's acoustic oscillations, enabling us to probe the interior of our star with remarkable precision. By analysing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tracking cfDNA release dynamics during colorectal cancer surgery
“Taken together, our results suggest that in addition to physiological age, comorbidities and unfavorable clinical traits, intense surgical manipulation from the tumor's extent, may result in greater tissue damage and elevated cfDNA release”
