(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Basel are able to test in parallel the effects of over 1500 active substances on cell metabolism. Their analysis also led to the discovery of previously unknown mechanisms for known medications. This approach might help scientists to better predict side effects and find additional uses for commercially available pharmaceuticals.
How do active substances alter metabolic processes in cells? Answering that question would provide valuable clues for the development of new medications. However, investigating such modes of action for a whole compound library would have been very resource-intensive in the past.
Researchers at the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel have just presented a method of testing the metabolic effects of thousands of active substances at the same time. They have published the results of this method, known as high-throughput metabolomics, in the scientific journal Nature Biotechnology.
Predicting side effects and interactions
“When we have a better understanding of exactly how active substances intervene in cell metabolism, the development of medication can be accelerated,” explains Professor Mattia Zampieri. “Our method provides additional characterization of the substances, from which we can infer possible side effects or interactions with other medications.”
The researchers, led by Dr. Laurentz Schuhknecht, lead author of the study, grew cells in thousands of little wells in cell culture plates. They then treated the cells in each well with one of over 1500 substances from a compound library, and used a method called mass spectrometry to measure how thousands of small biomolecules inside the cells (known as metabolites) change upon treatment.
This allowed the research team to gather data on the changes of over 2000 metabolic products in the cells for each active compound. They then compared these changes with those obtained from untreated cells via computer-aided analysis. This resulted in an overview of the effects on cell metabolism of each active substance, which gave them a very accurate picture of its respective mode of action.
New applications for tried and tested medications
“Commercially available drugs can influence cell metabolism much more than we had imagined,” says Zampieri, summing up the results of the experiments. Particularly of note were the previously unknown modes of action of common medications. For example, the team discovered that tiratricol, a drug for treating a rare condition involving the thyroid gland function, aside its primary mode of action also influences the production of certain nucleotides, the building blocks for DNA synthesis.
“This medication would therefore potentially be a good candidate for a new field of application: modulating nucleotide biosynthesis and hence being used for instance in cancer therapy to inhibit tumor growth,” says Schuhknecht.
Comprehensive data from high-throughput methods such as this, can help train artificial intelligence for designing new medications. “Our long-term vision is to match patient specific metabolic profiles of a disease with the mode of metabolic interference of thousands of compound candidates to unravel the best medication able to revert the molecular changes induced by the disease,” says Zampieri.
In order to get closer to this vision, it is not only important to understand the action of the substances on metabolism, the pharmacologist emphasizes. It is equally important how the human body processes the active substances and thus how it changes their effect. The scientists are therefore conducting further research to examine the interaction between the body and active substances more closely.
END
Testing the effect of thousands of compounds on cellular metabolism
How high-throughput metabolomics reveals unknown modes of action of known drugs, potential side-effects and additional uses
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Follow the water: Searching for a lunar oasis
2025-01-28
As humankind imagines living off-planet — on the moon, Mars and beyond — the question of how to sustain life revolves around the physical necessities of oxygen, food and water. We know there is water on the moon, but how do we find it? Is it in the craters? The shadowed regions? The poles? Knowing where to look gives astronauts the best chance at successfully living on the moon, something that has, heretofore, remained the stuff of science fiction.
Researchers from the University of California ...
Ocean-surface warming four times faster now than late-1980s
2025-01-28
The rate of ocean warming has more than quadrupled over the past four decades, a new study has shown.
Ocean temperatures were rising at about 0.06 degrees Celsius per decade in the late 1980s, but are now increasing at 0.27 degrees Celsius per decade.
Published today (Tuesday, 28 January 2025) in Environmental Research Letters, the study helps explain why 2023 and early 2024 saw unprecedented ocean temperatures.
Professor Chris Merchant, lead author at the University of Reading, said: “If the oceans were a bathtub of water, then in the 1980s, the hot tap was running slowly, warming up ...
Study explores whether dietary supplement could provide first effective treatment for cirrhosis
2025-01-28
A dietary supplement used to build muscle – or prevent muscle loss as a result of ageing or illness – is to be trialled as a potential treatment for chronic liver disease.
Β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate, otherwise known as HMB, is used predominantly to build muscle bulk and function but previous studies have demonstrated it can have clinical applications.
In a new study, scientists and clinicians will test its potential to benefit some of the 60,000 people in the UK who have been diagnosed with cirrhosis, a condition that results from scarring to the liver.
In the UK, cirrhosis is most commonly caused by harmful alcohol use or fatty liver disease. In severe cases, those ...
Individual cells can be connected to plastic electrodes
2025-01-28
Researchers at Linköping University have succeeded in creating a close connection between individual cells and organic electronics. The study, published in Science Advances, lays the foundation for future treatment of neurological and other diseases with very high precision.
“We could target individual cells and explore how this affected their ability to stay healthy and functional,” says Chiara Musumeci, researcher at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics, LOE, at Linköping University.
The brain is controlled by electrical signals that are converted into chemical substances in the communication between the brain ...
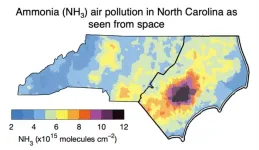
University of Virginia study reveals air pollution inequities linked to industrial swine facilities are detectable from space
2025-01-28
A groundbreaking study led by researchers from the University of Virginia has used satellite measurements to show the long-term persistence of air pollution inequalities tied to industrialized swine facilities in Eastern North Carolina. Using satellite data spanning a 15-year period from 2008–2023, the study quantifies disparities in ammonia (NH₃) — an air pollutant emitted by swine operations — for Black, Hispanic and Indigenous communities. These inequalities, exacerbated by hot and calm weather ...
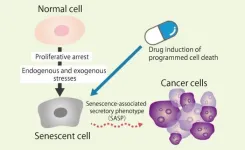
Cell death and aging in cancer research review
2025-01-28
Aging cells secrete substances known to promote the growth of cancer cells. The development of drugs that can selectively kill these cells or inhibit the secretion of substances is ongoing. The latest findings on the interaction between cell death and cellular senescence in cancer and their pathophysiological significance have been reviewed by a team from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine and Harvard Medical School.
Lecturer Kouhei Shimizu and Professor Fuminori Tokunaga of OMU and Dr. Hiroyuki Inuzuka of Harvard Medical School outlined ...
Flame retardants in battery enclosures may do more harm than good
2025-01-28
As dangerous lithium-ion battery fires are on the rise, regulators and manufacturers are scrambling for solutions. Unfortunately, one common strategy may cause serious health harm and not work to slow or stop the fires. A new Viewpoint in Environmental Science & Technology explains that adding flame retardants to the plastic cases surrounding these batteries has no proven fire-safety benefit. The scientists further warn that the types of flame retardants widely used in electronics enclosures are linked to cancer and other health harms and can end up in children’s toys, food containers, and other products made from recycled plastic.
“The use of flame ...
Kenya study highlights complexity of tree-planting schemes
2025-01-28
Research with smallholder farmers in Kenya shows that tree-planting schemes must account for complex local issues and preferences.
Tree planting is central to many countries’ climate mitigation and biodiversity conservation goals, and Kenya alone plans to plant 15 billion trees by 2032.
Adding trees and shrubs to farmland (called agroforestry) can boost biodiversity, carbon storage, soil health, food production and income. But many tree-planting schemes overlook diversity and promote a narrow range of species.
The new study – led by the University of Exeter – examined the factors that enable or prevent Kenyan smallholders from increasing the diversity of ...
Transforming longevity research: AI paves the way for personalised treatments in ageing science
2025-01-28
A collaborative study between researchers from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), and the Institute for Biostatistics and Informatics in Medicine and Ageing Research, Rostock University Medical Center, Germany, investigated how advanced AI tools, like Large Language Models (LLMs), can make it easier to evaluate interventions for ageing and provide personalised recommendations. The findings were published in the leading review journal Ageing Research Reviews.
Research into ...
Humanoid robots join human musicians for synchronized musical performances
2025-01-28
In a fascinating blend of technology and artistry, researchers present a study in PeerJ Computer Science, showcasing how humanoid robots can collaborate seamlessly with human musicians during live musical performances. This innovative work highlights the evolving role of robotics in entertainment and creativity.
The study introduces a human-robot musical band featuring Polaris, a mid-sized humanoid robot as a drummer, and Oscar, a Robotis-OP3 humanoid robot as a keyboardist. These robots performed alongside human musicians, achieving natural synchronization and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Testing the effect of thousands of compounds on cellular metabolismHow high-throughput metabolomics reveals unknown modes of action of known drugs, potential side-effects and additional uses