New tool can detect fast-spreading SARS-COV-2 variants before they take off
Researchers have developed a powerful tool that can detect variants of SARS-CoV-2 with high transmission potential before they become widespread
2025-01-29
(Press-News.org)
By analysing millions of viral genome sequences from around the world, a team of scientists, led by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and the University of Pittsburgh, uncovered the specific mutations that give SARS-CoV-2 a ‘turbo boost’ in its ability to spread.
“Among thousands of SARS-CoV-2 mutations, we identified a small number that increase the virus’ ability to spread,” said Professor Matthew McKay, a Laboratory Head at the Doherty Institute and ARC Future Fellow in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at the University of Melbourne, and co-lead author of the study published in Nature Communications.
Many of these key mutations are in the spike protein, which helps the virus enter human cells and is the target of antibodies. But the team also found important mutations in other, less-studied parts of the virus that enhance its ability to bind to human cells, evade the immune system or alter protein structure.
"Our approach is mathematically simple yet highly effective,” added Professor McKay. “Unlike previous techniques, our model leverages genomic surveillance data to pinpoint the exact mutations driving the spread of certain variants, even when they appear in just a small fraction of cases.”
While this new model focuses exclusively on SARS-CoV-2, the researchers believe it can be adapted to study the transmission of other pathogens, such as influenza.
“This is one of the first practical tools to systematically quantify how individual mutations impact viral transmission on a global scale,” said Associate Professor John Barton from the University of Pittsburgh, co-lead author of the study.
“Our method is like a magnifying glass for viral evolution, helping public health systems spot and monitor highly transmissible variants before they become widespread.
“Not only can we track SARS-CoV-2 more effectively, but our method can also be adapted to study the evolution of other pathogens, helping us stay ahead of future outbreaks. It’s a powerful tool for global efforts to tackle emerging diseases.”
-- END
Additional information:
Peer-reviewed paper: Lee B, et al. Inferring effects of mutations on SARS-CoV-2 transmission from genomic surveillance data. Nature Communications (2024). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55593-0
Funding: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (USA), Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (China) and the Australian Research Council (Australia).
Collaboration: This study is the result of a collaborative effort between the Doherty Institute, the University of Pittsburgh, the University of California, Bahria University and the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-29
During the past year, there’s been an unusual set of samples at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab): material gathered from the 4.5-billion-year-old asteroid Bennu when it was roughly 200 million miles from Earth.
Berkeley Lab is one of more than 40 institutions investigating Bennu’s chemical makeup to better understand how our solar system and planets evolved. In a new study published today in the journal Nature, researchers found evidence that Bennu comes from an ancient wet world, with some material from the coldest regions of the solar system, likely beyond the orbit of ...
2025-01-29
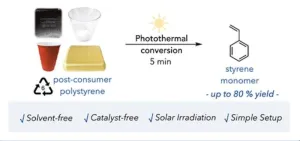
It turns out that the black plastic lid atop your coffee cup has a superpower. And the Stache Lab at Princeton Chemistry, which uncovered it, is exploiting that property to recycle at least two major types of plastic.
Their startling mechanism for promoting depolymerization relies on an additive that many plastics already contain: a pigment called carbon black that gives plastic its black color. Through a process called photothermal conversion, intense light is focused on plastic containing the pigment that jumpstarts the degradation.
So far, researchers have shown that carbon black can depolymerize polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), two of the least recycled plastics in the planet’s ...
2025-01-29
Researchers from Zhejiang University and HKUST (Guangzhou) have developed a cutting-edge AI model, ProtET, that leverages multi-modal learning to enable controllable protein editing through text-based instructions. This innovative approach, published in Health Data Science, bridges the gap between biological language and protein sequence manipulation, enhancing functional protein design across domains like enzyme activity, stability, and antibody binding.
Proteins are the cornerstone of biological functions, and their precise modification holds immense potential for medical therapies, synthetic biology, and biotechnology. While traditional protein editing methods ...
2025-01-29
A new analysis of samples from the asteroid Bennu, NASA’s first asteroid sample captured in space and delivered to Earth, reveals that evaporated water left a briny broth where salts and minerals allowed the elemental ingredients of life to intermingle and create more complex structures. The discovery suggests that extraterrestrial brines provided a crucial setting for the development of organic compounds.
In a paper published today, Jan. 29, in the journal Nature, scientists at the Smithsonian’s National Museum ...
2025-01-29
The launch of the nation’s 988 mental health hotline did not coincide with significant and equitable growth in the availability of most crisis services, except for a small increase in peer support services, according to a new RAND study.
Examining reports from thousands of mental health treatment facilities about the types of crisis services offered before and after the July 2022 rollout of the 988 hotline, researchers found that there was an increase in peer support services, a significant decrease in psychiatric walk-in services, and small declines in mobile crisis response and suicide prevention services.
Significant ...
2025-01-29
New research comparing different approaches to dementia care for people with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias found no significant differences in patient behavioral symptoms or caregiver strain, whether delivered through a health system, provided by a community-based organization, or as usual care over an 18-month period.
However, the Dementia Care Study, also known as D-CARE, also found that caregiver self-efficacy—a measurement of caregivers’ confidence in managing dementia-related challenges and accessing support — improved in both the health-system and community-based ...
2025-01-29
In the most comprehensive global analysis of genetic diversity ever undertaken, an international team of scientists has found that the genetic diversity is being lost across the globe but that conservation efforts are helping to safeguard species.
The landmark study, published in the pre-eminent scientific journal Nature, was led by Associate Professor Catherine Grueber from the School of Life and Environmental Sciences and a team of researchers from countries including the UK, Sweden, Poland, Spain, Greece and China.
The data spans more than three decades (from 1985-2019) and looks at 628 species of animals, plants and fungi across all terrestrial ...
2025-01-29
A pre-Columbian society in the Amazon developed a sophisticated agricultural engineering system that allowed them to produce maize throughout the year, according to a recent discovery by a team of researchers from the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology (ICTA-UAB) and the Department of Prehistory at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, (Spain); the Universities of Exeter, Nottingham, Oxford, Reading and Southampton (UK); the University of São Paulo (Brazil) and Bolivian collaborators. This finding contradicts previous theories that dismissed the possibility of intensive monoculture agriculture in the region.
The study, published today ...
2025-01-29
About The Study: This secondary analysis of the BP-CATCH trial found that among children with high blood pressure measurements, racial and ethnic disparities in receiving nutrition, lifestyle, and all 3 counseling topics were significant, although no significant disparities in receipt of weight counseling were noted. Racial disparities in receipt of counseling were not observed in participants with and without obesity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Moonseong Heo, PhD, email mheo@clemson.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.56238)
Editor’s ...
2025-01-29
About The Study: This repeated cross-sectional study including 69.2 million obesity management drug dispensed prescriptions revealed an increase from 0.76 million in July 2017 to 1.5 million in February 2024, with an upward trend in monthly phentermine and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist prescriptions. There was a robust positive correlation between public online search activity for semaglutide and tirzepatide and their prescription trends. The joint surge in prescriptions and online searches ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New tool can detect fast-spreading SARS-COV-2 variants before they take off
Researchers have developed a powerful tool that can detect variants of SARS-CoV-2 with high transmission potential before they become widespread