(Press-News.org) Experiencing pain may increase the odds that cancer survivors will use cigarettes and cannabis, according to a recent study published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. The study also found that cigarette smoking and pain are linked to more treatment-related side effects and worse health among cancer survivors.
Pain and use of cigarettes, e-cigarettes, alcohol, and cannabis commonly occur together in the general population. To characterize pain in relation to such non-opioid substance use specifically among cancer survivors (who often experience pain), investigators analyzed data from two national samples of individuals with a past diagnosis of cancer in the United States: 1,252 adults from Wave 6 (2021) of the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study and 4,130 adults from the 2020 National Health Interview Survey.
PATH data indicated that higher past-week pain intensity was associated with a greater likelihood that cancer survivors would use cigarettes, e-cigarettes, and cannabis, and a lower likelihood that they would drink alcohol. National Health Interview Survey data indicated that chronic pain was associated with a greater likelihood of cigarette smoking and a lower likelihood of alcohol use. In both studies, cigarette smoking and pain were linked to fatigue, sleep difficulties, poorer mental/physical health, and lower quality of life.
“These findings show that because pain and substance use are interconnected among cancer survivors, it’s important to focus on treating both together in cancer care. Pain can drive substance use, and substance use can worsen pain, creating a cycle that’s hard to break,” said lead author Jessica M. Powers, PhD, of Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine. “While cancer survivors might smoke cigarettes or use substances to get immediate relief from their pain and cope with other symptoms, this can be incredibly harmful for their health by reducing the effectiveness of cancer treatments and increasing risk for cancer recurrence.”
Additional information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. A free abstract of this article will be available via the CANCER Newsroom upon online publication. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com
Full Citation:
“Relationship Between Pain and Non-Opioid Substance Use in Two National Samples of Cancer Survivors.” Jessica M. Powers, Lisa R. LaRowe, Dana Rubenstein, Judith A. Paice, Brian Hitsman, and Christine M. Rini. CANCER; Published Online: February 10, 2025 (DOI: 10.1002/cncr.35701).
URL Upon Publication: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/cncr.35701
Author Contact: Kristin Samuelson at ksamuelson@northwestern.edu
About the Journal
CANCER is a peer-reviewed publication of the American Cancer Society integrating scientific information from worldwide sources for all oncologic specialties. The objective of CANCER is to provide an interdisciplinary forum for the exchange of information among oncologic disciplines concerned with the etiology, course, and treatment of human cancer. CANCER is published on behalf of the American Cancer Society by Wiley and can be accessed online. Follow CANCER on X @JournalCancer and Instagram @ACSJournalCancer, and stay up to date with the American Cancer Society Journals on LinkedIn.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Does pain affect cancer survivors’ use of non-opioid substances?
U.S. data indicate that pain is linked with a greater likelihood of tobacco and cannabis use among cancer survivors.
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists find that a playful approach to life activates ‘lemonading’, which helps people cope with adversity
2025-02-10
Scientists have found that taking a playful approach to life doesn’t mean you don’t take your situation seriously, but it can mean you cope with it better. By surveying people about their experiences during a Covid-19 lockdown, they learned that more playful people were more positive about the future and coped more actively and creatively. Life gave them lemons, and they made lemonade.
“Our study revealed that playfulness and resilience are intimately connected through what we call ‘lemonading’ — the ability to imagine ...
Candidate genes in canine hepatocellular carcinoma for molecular targeted therapy
2025-02-10
Unresectable canine hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has limited nonsurgical treatment options. Sorafenib is a targeted therapy for unresectable canine HCC. However, there are limited reports on the expression of target genes. Therefore, the efficacy of the targeted therapies for canine HCC remains unclear.
In HCC, the prognosis is generally good when complete surgical resection is possible. Unresectable nodular and diffuse HCC have a poor prognosis and limited nonsurgical treatment options. In humans, systemic therapies including ...
Opioid prescriptions in the ED linked to small increases in future opioid use, hospitalizations
2025-02-10
Opioid prescriptions in the emergency department (ED) were associated with small increases in later opioid prescriptions and hospital admissions, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241542.
To understand the relationship between opioid prescribing in the ED and subsequent harm, researchers looked at opioid prescribing at all Alberta EDs from 2010 to 2020. Of the more than 13 million visits, 689 074 patients (5.3%) filled an opioid prescription. The researchers found that opioid prescriptions did not increase the risk of ...
During pandemic, playful people were remarkably resilient, OSU research shows
2025-02-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Adults with high levels of playfulness showed strong resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to less playful individuals, new research shows.
The study led by Xiangyou “Sharon” Shen of Oregon State University is important because playfulness is a vital but underappreciated resource for building resilience and maintaining well-being during difficult periods such as the pandemic, Shen said. And it’s a resource that individuals can cultivate.
“Understanding how playful people navigate adversity can inform interventions and strategies to help people cope with stress and uncertainty,” said Shen, an assistant professor ...
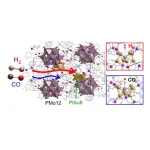
Tracing gas adsorption on “crowns” of platinum and gold connected by nanotunnels
2025-02-08
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have elucidated how hydrogen and carbon monoxide is adsorbed into solids containing a crown-motif structure of platinum and gold. Using quick-scan X-ray absorption measurements and theoretical calculations, they studied a solid of [PtAu8(PPh3)8]-H[PMo12O40] called PtAu8-PMo12 and found that gas adsorption is affected strongly by the dimension of nanoscale voids in the structure. This highlights the importance of engineering voids in materials for next generation sensors and gas separation.
Ligand-protected metal clusters have been a source of ...
Rare bird skull from the age of dinosaurs helps illuminate avian evolution
2025-02-08
A new study in Nature describing a fossil of a nearly complete and intact bird skull from Antarctica is shedding light on the early evolution of today’s birds and avian diversity at the end of the Age of Dinosaurs.
The skull is from Vegavis iaai, an extinct duck-like bird that lived during the Late Cretaceous, just before non-avian dinosaurs went extinct. It’s one of very few 3D bird skulls known to science from the Cretaceous — a 79-million-year geological period and the last era when ...
Researchers find high levels of the industrial chemical BTMPS in fentanyl
2025-02-08
A UCLA research team has found that drugs being sold as fentanyl contain high amounts of the industrial chemical bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate, or BTMPS. This new substance of concern emerged in the illicit drug supply nearly simultaneously in multiple U.S. locations from coast-to-coast.
From June through October 2024, the team quantitatively tested samples of drugs sold as fentanyl that had high levels of the chemical, which belongs to a class of compounds called hindered amine light stabilizers ...
Decoding fat tissue
2025-02-08
As many as 40% of Americans are obese, putting them at an increased risk for high blood pressure, diabetes, stroke, heart disease and certain cancers, according to the CDC. New research from the University of Delaware aims to tackle the issue by investigating obesity at the gene level.
Principal investigator Ibra Fancher, assistant professor of kinesiology and applied physiology in UD’s College of Health Sciences, discovered significant differences in gene expression in adipose tissue, more commonly known as fat. Formerly considered fat storage, adipose tissue is now recognized as a vital ...
Solar and electric-powered homes feel the effects of blackouts differently, according to new research from Stevens
2025-02-08
Hoboken, N.J., February 7, 2025 — As winter storms and summer heat waves increasingly stress the nation’s power grids, Stevens researchers have developed a new way to identify the homes most vulnerable to blackouts — without even visiting them.
The timing couldn't be more critical. With more than a quarter of U.S. homes already fully electric, and solar installations set to triple during the next five years, understanding vulnerabilities has become critical for emergency planning and public safety.
"We're ...
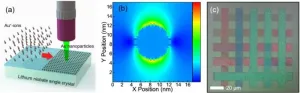
Metal ion implantation and laser direct writing dance together: constructing never-fading physical colors on lithium niobate crystals
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240193 , discusses a novel approach towards robust construction of physical colors on lithium niobate crystal.
Color has a profound impact on the way humans observe, perceive and understand the world. It is like a silent language, subtly shaping our perception and response to the surrounding environment. From the first ray of sunshine in the morning to the twinkling stars in the night sky, colors are everywhere. They are not only a visual ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Does pain affect cancer survivors’ use of non-opioid substances?U.S. data indicate that pain is linked with a greater likelihood of tobacco and cannabis use among cancer survivors.