Utilizing a nanomedicine to achieve tumor catalysis-enhanced differentiation therapy
2025-02-14
(Press-News.org)
Tumor metastasis, recurrence, and therapeutic resistance are the main reasons for the failure of clinical cancer treatment. Studies have found that the presence of cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) with stemness characteristics in malignant tumors is a key factor leading to the above undesirable results. However, there are significant limitations to current strategies with traditional molecular drugs for combating CSCs, such as the unsatisfactory in vivo stemness-suppressing efficiency, and the lack of powerful tumor-specific lethal action, resulting in remaining massive bulk tumor cells that can convert to CSCs via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Although some combination methods using different drugs/therapeutics have been reported to simultaneously combat CSCs and inhibit tumor cells, the complicated procedures and inevitable side effects will pose significant challenges for practical therapeutic applications. Therefore, developing new efficacious strategies that can differentiate CSCs and simultaneously kill tumor cells is expected to achieve efficient tumor treatment and address the issues of tumor recurrence and metastasis.
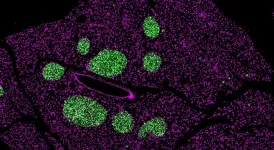
For solving these challenges, Dr. Yufang Zhu, Dr Chengtie Wu, and Dr Jianlin Shi (Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) developed a coordination nanomedicine (ZnDHT NM) featuring cascade specific Fe3+ capturing and in situ catalysis mainly by 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (DHT) complexing Zn2+ in this study.
The results of performance testing and theoretical calculations exhibited that due to the stronger binding force of DHT molecules to Fe3+ compared to other metal ions, ZnDHT NM can specifically capture Fe3+ in the environment, promote the catalytic generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by in situ forming a hexacoordinated Fe-DHT conformation with enhanced reducibility, and release Zn2+ from the skeleton. On the one hand, ZnDHT NM can deplete Fe in the tumor microenvironment and promote intracellular ROS production, resulting in synergistically promoting CSC differentiation and inhibiting EMT by separately blocking the Wnt signaling pathway and inducing the FoxO3 activation. On the other hand, ZnDHT NM can release Zn2+, which inactivates glutathione reductase (GR) and downregulates glutathione (GSH) in tumor cells, and combine with the selective ROS production to intervene in the redox homeostasis of tumor cells, activating their apoptosis/ferroptosis pathways.
Further, in the in vivo experiments, the researchers found that this ZnDHT NM, which can simultaneously treat CSCs and tumor cells, effectively inhibited the growth of orthotopic triple-negative breast tumors, and possessed the effect of inhibiting tumor postoperative recurrence and metastasis.
“This study presents an innovative perspective of establishing biosafe nanomedicines to evoke effective therapeutic mechanisms against CSCs and bulk tumor cells concurrently by modulating endogenous substances, which is highly encouraging for cancer nanomedicine design and future tumor therapeutics,” Yufang Zhu says.
###
See the article:
Cascade specific endogenous Fe3+ interference and in situ catalysis for tumor therapy with stemness suppression
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwae434
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-14
Palmyra is one of the most famous sites in Syria for its extraordinary heritage and archaeological remains. Inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1980, the city saw much of its heritage destroyed during the war. Following the liberation of Syria from the Assad regime on 8 December, a multidisciplinary team has carried out a field study in Palmyra to assess the current state of the archaeological monuments and the surrounding residential areas, comparing them with their condition before the start of the Syrian uprising in 2011. The report is an initiative of Palmyrene Voices of the NGO Heritage for Peace in collaboration with the CSIC's Milà i Fontanals Institution.
‘We ...
2025-02-14
University of Virginia Brain Institute and School of Medicine researchers have received an initial $9.3 million award from the National Institutes of Health for a $30 million clinical trial to determine if the powerful anesthetic ketamine can save patients from prolonged, life-threatening grand mal seizures that won’t respond to other treatments.
“Status epilepticus,” as the seizures are known, are seizures that last more than five minutes or that strike repeatedly without the ...
2025-02-14
Digital@INSEAD is hosting a free TECH TALK X webinar, “The Future of Agentic AI & Autonomous Organizations” on Thursday, 27 February 2025 at 9.00 am ET / 3.00 pm CET (60 min).
AI is evolving beyond tools and assistants – it is becoming autonomous. But what is holding enterprises back from fully leveraging Agentic AI?
Join in the free webinar for a deep dive with Rotem Alaluf, CEO of Wand – a pioneering platform for enterprise-grade AI systems – and Peter Zemsky, ...
2025-02-14
Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) is a vital cash-crop for four to six million small-holder farmers across the tropics, and supports a global chocolate industry valued at over USD 100 billion annually. The combination of millions of farmers relying on cocoa for their livelihoods, and increasing global demand for the crop, has driven cocoa plantation expansion and intensification of farming practices, often at the expense of biodiversity and long-term sustainability.
A new research study led by the University ...
2025-02-14
A recent study reveals that age plays a significant role in the outcomes of intermittent fasting. Researchers from Technical University of Munich (TUM), LMU Hospital Munich, and Helmholtz Munich discovered that chronic intermittent fasting disrupted the development of insulin-producing beta cells in young mice. The findings raise concerns about potential risks for humans, especially teenagers.
“Intermittent fasting is known to have benefits, including boosting metabolism and helping with ...
2025-02-14
Astrophysicists have unearthed a surprising diversity in the ways in which white dwarf stars explode in deep space after assessing almost 4,000 such events captured in detail by a next-gen astronomical sky survey. Their findings may help us more accurately measure distances in the Universe and further our knowledge of “dark energy”.
The dramatic explosions of white dwarf stars at the ends of their lives have for decades played a pivotal role in the study of dark energy – the mysterious force responsible for the accelerating expansion of the Universe. They also provide the origin of many elements in our ...
2025-02-14
Pangolins are unique as they are the only mammal to be covered in scales. Even though they are scaly, photos of them are typically met with “awwws” from the viewers who find them adorable. Importantly, though, pangolins play an essential role in maintaining their ecosystem. Their other “unique trait” is that they are the most trafficked wild animal in the world, with more than 900,000 poached in the past two decades. Much of this is due to their high value for use in traditional medicine that ...
2025-02-14
We hope to be cured when we stay in hospital. But too often, we acquire new infections there. Such ‘healthcare-associated infections’ (HAI) are a growing problem worldwide, taking up an estimated 6% of global hospital budgets. In the EU alone, HAIs add up to more than 3.5 million cases per year, resulting in 2.5 million disability-adjusted life years, a cost of up to €24 billion, and 90,000 deaths. They are likewise the sixth leading cause of death in the US.
Patients with lowered immune defenses, and in some hospitals, ...
2025-02-14
RICHLAND, Wash.—Sometimes, in order to go big, you first have to go small. That’s what researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have done with their latest innovation in energy storage.
With a goal to speed the time to discovery of new grid energy storage technology, the team designed a compact, high-efficiency flow battery test system that requires an order of magnitude less starting material while delivering results equal to the standard lab-scale ...
2025-02-14
Collaboration efforts between the Texas A&M University Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering and the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) have led to innovative research on how petroleum coke is processed.
This almost $3 million three-year research project will convert petroleum coke to graphite for energy storage. The newer process uses a lower temperature and shorter time to produce graphite from petroleum coke.
This new catalytic graphitization technology will ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Utilizing a nanomedicine to achieve tumor catalysis-enhanced differentiation therapy