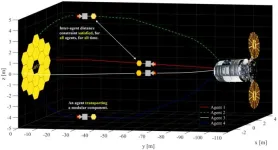
(Press-News.org) As more satellites, telescopes, and other spacecraft are built to be repairable, it will take reliable trajectories for service spacecraft to reach them safely. Researchers in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in The Grainger College of Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign are developing a methodology that will allow multiple CubeSats to act as servicing agents to assemble or repair a space telescope. Their method minimizes fuel consumption, guarantees that servicing agents never come closer to each other than 5 meters, and can be used to solve pathway guidance problems that aren’t space related.
“We developed a scheme that allows the CubeSats to operate efficiently without colliding,” said aerospace Ph.D. student Ruthvik Bommena. “These small spacecrafts have limited onboard computation capabilities, so these trajectories are precomputed by mission design engineers.”
Bommena and his faculty adviser Robyn Woollands demonstrated the performance of the algorithm by simulating two, three or four vehicle swarms simultaneously transporting modular components between a service vehicle and a space telescope undergoing in-space servicing.
“These are difficult trajectories to compute and calculate, but we came up with a novel technique that guarantees its optimality,” Bommena said.
Bommena said the most difficult aspect is the scale of the distances. The James Webb Space Telescope’s orbit is about 1.5 million kilometers away, at the Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 2. It’s where the gravitational force of the Sun and Earth balance each other, making it the perfect place in space for deep-space observation satellites to maintain orbit while facing away from the Sun.
“Without getting too technical, we used indirect optimization methods to guarantee that the output solution is fuel optimal. Direct methods do not guarantee that."
“We also incorporated the anti-collision path inequality constraints into the optimal control formulation as a hard constraint, so the spacecraft do not violate the constraint at any point during the trajectory.”
Bommena explained that traditional direct or indirect methods with constraints, such as collision-avoidance, break the trajectory into multiple arcs, increasing the complexity exponentially.
“Our methodology allows the trajectories to be solved as single arcs. We are just going from the starting point directly to the destination point. It’s more fuel optimal and more computationally efficient.”
Another major outcome from the research is the development of a novel target-relative circular restricted three-body problem dynamical model.
“We needed to mitigate the numerical challenges that come from the large distance between the Sun and the Earth,” Bommena said. “To do that, we first shifted the center of the frame along the x-axis from the Sun-Earth barycenter to the location of Lagrange point L2 and then derived the equations of motion relative to the target spacecraft. We also introduced a new distance unit by applying a scaling factor that proportionally adjusts in relation to the original distance measurement.”
Bommena said he and Woollands worked on this project for about a year and a half. His breakthrough came on a long-distance flight.
“The math was working on paper. The major problem we had was wrestling with numerics. I was coding during a long flight. I tried a couple of things and suddenly the solution converged. At first, I didn't believe it. That was a very exciting moment and the next few days felt awesome.”
Bommena said although the application for this work is to make in-space servicing and assembly safer and more efficient, the methodology they developed is very versatile and can be used in other trajectory optimization scenarios with different constraints.
This work was partially supported by Ten One Aerospace through a NASA STTR Phase I research grant.
The study, “Indirect Trajectory Optimization with Path Constraints for Multi-Agent Proximity Operations,” was written by Ruthvik Bommena and Robyn Woollands. It is published in The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences. DOI: 10.1007/s40295-024-00470-7
END
New research sheds light on using multiple CubeSats for in-space servicing and repair missions
2025-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research suggests comprehensive CT scans may help identify atherosclerosis among lung cancer patients
2025-02-14
Several cardiovascular risk factors, such as advanced age and smoking history, are prevalent among lung cancer patients at the time of the diagnosis and increase their risk of future heart disease, according to a new study being presented at ACC’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient course. Comprehensive assessments are needed in this vulnerable group to improve survival outcomes and quality of care for cancer patients.
Heart disease and cancer are the leading causes of death in the United States. Smoking is a shared risk factor for lung cancer and cardiovascular disease, and lung cancer patients have an amplified mortality rate with the presence of ...
Adults don’t trust health care to use AI responsibly and without harm
2025-02-14
A study finds that 65.8% of adults surveyed had low trust in their health care system to use artificial intelligence responsibly and 57.7% had low trust in their health care systems to make sure an AI tool would not harm them.
The research letter was published in JAMA Network Open.
Adults who had higher levels of overall trust in their health care systems were more likely to believe their providers would protect them from AI-related harm.
The letter, authored by Jodyn Platt, Ph.D., of the Department of Learning Health Sciences at University of Michigan Medical School and Paige Nong, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota School of Public Health comes from survey of a nationally ...
INSEAD webinar on the dual race to AI & global leadership
2025-02-14
Digital@INSEAD is hosting a free TECH TALK X webinar “The Dual Race to AI & Global Leadership” on Wednesday, 19 February 2025 7.00 am ET / 1.00 pm CET (Duration: 60 min).
The TECH TALK will be featuring a discussion between Tim Gordon (MBA’00D), Partner, Best Practice AI and Theos Evgeniou, INSEAD Professor of Technology & Business and Director of Executive Programs in AI.
Tim, an INSEAD alumnus with over 20 years of international experience in digital transformation, global strategy and innovation, will join Theos to explore the two critical AI races reshaping our world: ...
Ketamine: From club drug to antidepressant?
2025-02-14
Ketamine has received a Hollywood makeover. It used to be known as a rave drug (street name special K) and cat anesthetic. However, in recent years, some doctors have prescribed ketamine to treat conditions from post-traumatic stress disorder to depression. “The practice is not without controversy,” notes Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Hiro Furukawa.
‘Should we give a hallucinogen to patients in compromised mental states?’ wonder ketamine’s skeptics. The controversy came to ...
Multilevel stressors and systemic and tumor immunity in Black and White women with breast cancer
2025-02-14
About The Study: The findings of this cross-sectional study of Black and white women with breast cancer suggest that perceived stress, perceived inadequate social support, perceived racial and ethnic discrimination, and neighborhood deprivation were associated with deleterious alterations to the systemic and tumor immune environment, particularly for Black women. Understanding biology as a possible mediator of cancer health disparities may inform prevention and public health interventions.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
Childhood lifestyle behaviors and mental health symptoms in adolescence
2025-02-14
About The Study: This cohort study of Finnish children and adolescents found that higher physical activity and lower screen time from childhood were associated with perceived stress and depressive symptoms in adolescence. These findings emphasize reducing screen time and increasing physical activity to promote mental health in youth.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Eero A. Haapala, PhD, email eero.a.haapala@jyu.fi.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.60012)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Most comprehensive study on U.S. health care spending by county reveals wide variation
2025-02-14
At $144 billion, type 2 diabetes was the most expensive single health condition.
Emergency department care had the fastest growth.
SEATTLE, Wash., Feb. 14, 2025 – Researchers present the most comprehensive study on U.S. health care spending and variations across 3,110 counties by four payers, 148 health conditions, 38 age/sex groups, and seven types of care. That’s according to the newest and most extensive studies published in JAMA and JAMA Health Forum today.
As part of this study, researchers ...
Tracking U.S. health care spending by health condition and county
2025-02-14
About The Study: Broad variation in health care spending was observed across U.S. counties. Understanding this variation by health condition, sex, age, type of care, and payer is valuable for identifying outliers, highlighting inequalities, and assessing health care gaps.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joseph L. Dieleman, PhD, email dieleman@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.26790)
Editor’s ...
Drivers of variation in health care spending across U.S. counties
2025-02-14
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, variation in health care spending among U.S. counties was largely related to variation in service utilization. Understanding the drivers of spending variation in the U.S. may help policymakers assess the allocation of health care resources.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joseph L. Dieleman, PhD, email dieleman@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.5220)
Editor’s ...
INSEAD webinar on scaling affordable healthcare: balancing purpose, innovation & growth
2025-02-14
Digital@INSEAD is hosting a free INTHECASE webinar, “Scaling Affordable Healthcare: Balancing Purpose, Innovation & Growth” on Thursday, 20 February 2025 at 9.00 am ET / 3.00 pm CET (60 min).
Register and join the webinar for an engaging discussion on Access Afya’s journey to scale its affordable healthcare model while staying true to its mission of serving underserved communities.
Explore how the company:
Balances mission and growth
Navigates the complexities of scaling up
Leverages technology and data to improve care delivery
With a proven business model in Kenya, ...