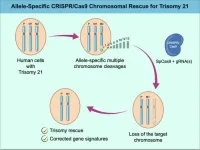
(Press-News.org) Gene editing techniques may eventually allow trisomy to be treated at the cellular level, according to an in vitro proof-of-concept study. Down syndrome is caused by the presence of a third copy of the 21st chromosome. The condition occurs in approximately 1 in 700 live births and is relatively easy to diagnose at early stages of development. However, there are no treatments. Ryotaro Hashizume and colleagues use the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system to cleave the third chromosome in previously generated trisomy 21 cell lines derived from both pluripotent cells and skin fibroblasts. The technique is able to identify which chromosome has been duplicated, which is necessary to ensure the cell does not end up with two identical copies after removal, but instead has one from each parent. The authors were able to remove duplicate chromosomes from both induced pluripotent stem cells and fibroblasts. Suppressing chromosomal DNA repair ability increased the rate of duplicate chromosome elimination. The authors show that the chromosomal rescue reversibly restores both gene expression and cellular phenotypes. The approach is not yet ready for in vivo application, however, in part because the current technique can also change the retained chromosomes. According to the authors, similar approaches could eventually be used in neurons and glial cells and form the basis of novel medical interventions for people with Down syndrome.
END
Using CRISPR to remove extra chromosomes in Down syndrome
2025-02-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
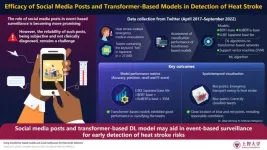
Social media posts and transformer-based models for early detection of heat stroke
2025-02-18
Heat stroke poses a significant health risk, especially during extreme temperature conditions. As global temperatures rise due to climate change, the frequency and severity of heatwaves have increased, putting vulnerable populations at greater risk. This shift underscores the need for effective, real-time methods for early detection and response to heat stroke risks, ensuring timely intervention and reduced impact of these rising threats. While previous studies have highlighted the potential of social media posts, such as tweets, to offer real-time insights into various events, its application in detecting heat stroke risks ...
Restoring grasslands led to fewer human-wildlife conflicts in Kenya, research finds
2025-02-18
ARLINGTON, Va. (Feb. 18 2025) – A new study led by Conservation International scientists and published today has found that grassland restoration can reduce human-wildlife conflict and social conflicts in communities facing resource scarcity.
Grasslands, vital ecosystems for livelihoods and biodiversity, are under increasing pressure from climate change and human activity. The Chyulu Hills region of Kenya exemplifies these challenges, as it is home to iconic wildlife such as African elephants and black rhinos, which share the land with pastoral Maasai communities. This coexistence often leads to competition over limited water, land and pasture, sparking ...
What makes us remember our dreams?
2025-02-18
Some people wake up vividly recalling their dreams from the night, and can tell precise stories experienced during the night, while others struggle to remember even a single detail. Why does this happen? A new study, conducted by researchers at the IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, and published on Communications Psychology explores the factors that influence so called "dream recall"— the ability to remember dreams upon awakening—and uncovers which individual traits and sleep patterns shape this phenomenon.
The reason why there is such a difference in recalling dreams remains a mystery. Some studies found that women, young persons, ...
New tool reveals disruption of immune cells in blood is linked to cancer outcomes
2025-02-18
The immune systems of cancer patients are highly disrupted, with those who have a higher number of immune cells in their blood having a better survival rate, finds a new study that uses a pioneering technique developed by researchers at UCL and the Francis Crick Institute.
The tool, described in Nature Genetics, is called Immune Lymphocyte Estimation from Nucleotide Sequencing (ImmuneLENS). It enables researchers to calculate the proportion of T cells and B cells (types of immune cell) from whole genome sequencing (WGS) data for the first time.
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) uses a blood sample to create a complete ...
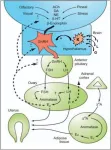
Newfound circuit better explains how the brain recognizes what is familiar and important
2025-02-18
*** Embargoed for release until Tuesday, Feb. 18, 2025, at 5 a.m. EST ***
A newly identified part of a brain circuit mixes sensory information, memories, and emotions to tell whether things are familiar or new, and important or just “background noise.”
Led by researchers from NYU Langone Health, the work found that a circuit known to carry messages from a brain region that processes sensory information, the entorhinal cortex (EC), to the memory processing center in the hippocampus (HC) has a previously unrecognized pathway that carries messages directly back to the EC.
Publishing online Feb. 18 in Nature Neuroscience, the study results show that this direct feedback ...
A single protein may have helped shape the emergence of spoken language
2025-02-18
The origins of human language remain mysterious. Are we the only animals truly capable of complex speech? Are Homo sapiens the only hominids who could give detailed directions to a far-off freshwater source or describe the nuanced purples and reds of a dramatic sunset?
Close relatives of ours such as the Neanderthals likely had anatomical features in the throat and ears that could have enabled the speaking and hearing of spoken language, and they share with us a variant of a gene linked to the ability to speak. And yet it is only in modern humans that we find expanded brain regions that are critical for language production and comprehension.
Now researchers from The Rockefeller University ...
Scientists decode diet from stool DNA – no questions asked
2025-02-18
SEATTLE – Scientists have developed a breakthrough method to track diet using stool metagenomic data.
Developed by researchers at the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB), the new method, called MEDI (Metagenomic Estimation of Dietary Intake), detects food-derived DNA in stool samples to estimate dietary intake. MEDI leverages stool metagenomics, which refers to sequencing all the DNA present in fecal samples (including microbial, human, and food-derived DNA). This non-invasive, data-driven approach offers an objective alternative to traditional food diaries and questionnaires, ...
Biologists transform gut bacteria into tiny protein pharmacies
2025-02-18
Hundreds of different species of microbes live, laugh, and love in your gut. In the future, one of these might serve a new function: microscopic in-house pharmacist.
A new study published Feb. 18 in Nature Biotechnology shows how gut bacteria can be directed to produce and release proteins within the lower gastrointestinal tract — eliminating a major roadblock to delivering drugs to that part of the body.
Oral medication is the most common and practical means of drug administration, but the stomach doesn’t let much pass through unscathed. This is good when it comes to things like foodborne ...
Study sheds light on the genetics of stopping smoking
2025-02-18
The effectiveness of a common drug to quit smoking could be down to people’s genes, according to a study from the University of Leicester (United Kingdom).
Varenicline is widely recognised as the most effective medication for helping people stop smoking, but unfortunately it does not work for everyone.
Researchers from Leicester have uncovered important insights into how people’s DNA affects their response to the drug, which will soon be available to smokers through the UK’s National Health Service (NHS).
Varenicline ...
Landmark review maps complex interactions between sex hormones and neurological health
2025-02-18
MONTREAL, Québec, Canada, 18 February 2025 - A comprehensive review published today in Brain Medicine by leading neuroendocrinologist Professor Hyman M. Schipper from McGill University’s Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery maps out the extensive influence of reproductive hormones on neurological health and disease. This landmark review, appearing in a special Festschrift issue honoring Dr. Seymour Reichlin’s centennial, systematically examines how sex hormones affect a broad ...