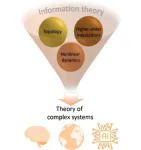
(Press-News.org) (Embargo: 19 Feb, 10am GMT) A groundbreaking study led by Professor Ginestra Bianconi from Queen Mary University of London, in collaboration with international researchers, has unveiled a transformative framework for understanding complex systems. Published in Nature Physics, this pioneering study establishes the new field of higher-order topological dynamics, revealing how the hidden geometry of networks shapes everything from brain activity to artificial intelligence.
“Complex systems like the brain, climate, and next-generation artificial intelligence rely on interactions that extend beyond simple pairwise relationships. Our study reveals the critical role of higher-order networks, structures that capture multi-body interactions, in shaping the dynamics of such systems,” said Professor Bianconi.
By integrating discrete topology with non-linear dynamics, the research highlights how topological signals, dynamical variables defined on nodes, edges, triangles, and other higher-order structures, drive phenomena such as topological synchronization, pattern formation, and triadic percolation. These findings not only advance the understanding of the underlying mechanisms in neuroscience and climate science but also pave the way for revolutionary machine learning algorithms inspired by theoretical physics.
“The surprising result that emerges from this research” Professor Bianconi added, is that topological operators including the Topological Dirac operator, offer a common language for treating complexity, AI algorithms, and quantum physics. “
From the synchronised rhythms of brain activity to the dynamic patterns of the climate system, the study establishes a connection between topological structures and emergent behaviour. For instance, researchers demonstrate how higher-order holes in networks can localise dynamical states, offering potential applications in information storage and neural control. In artificial intelligence, this approach may lead to the development of algorithms that mimic the adaptability and efficiency of natural systems.
“The ability of topology to both structure and drive dynamics is a game-changer,” Professor Bianconi added. This research sets the stage for further exploration of dynamic topological systems and their applications, from understanding brain research to formulate new AI algorithms. “
This study brings together leading minds from institutions across Europe, the United States, and Japan, showcasing the power of interdisciplinary research. “Our work demonstrates that the fusion of topology, higher-order networks, and non-linear dynamics can provide answers to some of the most pressing questions in science today,” Professor Bianconi remarked.
ENDS
This press release is based on an article 'Topology shapes dynamics of higher-order networks', scheduled for publication in Nature Physics on 19 February 2025 at 10:00 (London time)
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-024-02757-w
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-024-02757-w
About Queen Mary University of London
At Queen Mary University of London, we believe that a diversity of ideas helps us achieve the previously unthinkable. Throughout our history, we’ve fostered social justice and improved lives through academic excellence. And we continue to live and breathe this spirit today, not because it’s simply ‘the right thing to do’ but for what it helps us achieve and the intellectual brilliance it delivers.
Our reformer heritage informs our conviction that great ideas can and should come from anywhere. It’s an approach that has brought results across the globe, from the communities of east London to the favelas of Rio de Janeiro. We continue to embrace diversity of thought and opinion in everything we do, in the belief that when views collide, disciplines interact, and perspectives intersect, truly original thought takes form.
Visit qmul.ac.uk to find out more.
END
Groundbreaking study reveals how topology drives complexity in brain, climate, and AI
Study introduces higher-order topological dynamics, unlocking new frontiers in science and technology
2025-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lifestyle and environmental factors affect health and ageing more than our genes
2025-02-19
A new study led by researchers from Oxford Population Health has shown that a range of environmental factors, including lifestyle (smoking and physical activity), and living conditions, have a greater impact on health and premature death than our genes.
The researchers used data from nearly half a million UK Biobank participants to assess the influence of 164 environmental factors and genetic risk scores for 22 major diseases on ageing, age-related diseases, and premature death. The study is published today in Nature Medicine.
Key findings
Environmental factors explained 17% of the variation in risk of death, compared to less than 2% explained by genetic predisposition (as ...
New mRNA produces 200 times more protein: Hope for treatment of cancer and protein disorders
2025-02-19
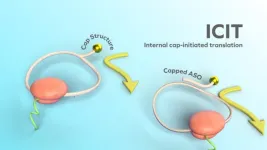
Imagine a breakthrough in cancer treatment where only malignant cells are targeted, sparing healthy host cells; or patients with abnormal protein synthesis are treated to produce a healthy protein. Hiroshi Abe and his colleagues at Nagoya University have identified two applications, among others, in a new study. Their innovative approach, reported in Nature Biotechnology, called the Internal Cap-Initiated Translation (ICIT) mechanism, introduces a novel way to 'switch on' protein synthesis ...
Magnetic semiconductor preserves 2D quantum properties in 3D material
2025-02-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — There is a big problem with quantum technology — it’s tiny. The distinctive properties that exist at the subatomic scale usually disappear at macroscopic scales, making it difficult to harness their superior sensing and communication capabilities for real-world applications, like optical systems and advanced computing. Now, however, an international team led by physicists at Penn State and Columbia University has developed a novel approach to maintain special quantum characteristics, even in three-dimensional (3D) materials.
The researchers published ...
Magnetic switch traps quantum information carriers in one dimension
2025-02-19
Illustration
A quantum "miracle material" could support magnetic switching, a team of researchers at the University of Regensburg and University of Michigan has shown.
This recently discovered capability could help enable applications in quantum computing, sensing and more. While earlier studies identified that quantum entities called excitons are sometimes effectively confined to a single line within the material chromium sulfide bromide, the new research provides a ...
Using light to activate treatments in the right place
2025-02-19
Acting in the right place at the right time is the key to effective medical treatment with minimal side effects. However, this feat remains difficult to achieve. Biologists and chemists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have succeeded in developing a tool that controls the location at which a molecule is activated by a simple pulse of light lasting only a few seconds. Tested on a protein essential for cell division, this system could be applied to other molecules. The potential applications are vast, both in basic research and in improving ...
Democracy in crisis: Trust in democratic institutions declining around the world
2025-02-19
New research from the University of Southampton has found that trust in representative institutions, such as parliaments, governments and political parties, has been declining in democratic countries around the world.
The study, published in The British Journal of Political Science, presents the largest and most comprehensive analysis of trends in political trust worldwide to date. It brings together results from 3,377 surveys covering 143 countries between 1958 and 2019, representing over five million survey respondents.
Whereas trust in representative institutions is generally in decline, trust in non-representative institutions ...
Finalists announced for the 2025 UK Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists
2025-02-19
19 February 2025 – London – The Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences today announced the Finalists for the eighth Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists in the United Kingdom. The Awards recognise scientific advances by UK researchers across Life Sciences, Chemical Sciences, and Physical Sciences & Engineering.
On Wednesday, 4 March, Professor Shitij Kapur, FMedSci, Vice-Chancellor & President, King’s College London, will announce the three 2025 Laureates at a gala dinner and awards ceremony. The three Laureates will each receive an unrestricted award of £100,000 (US$126,000). ...
Bio-hybrid drone uses silkworm moth antennae to navigate using smell
2025-02-19
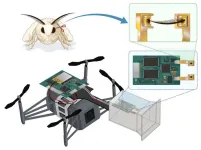
Conventional drones use visual sensors for navigation. However, environmental conditions like dampness, low light, and dust can hinder their effectiveness, limiting their use in disaster-stricken areas. Researchers from Japan have developed a novel bio-hybrid drone by combining robotic elements with odor-sensing antennae from silkworm moths. Their innovation, which integrates the agility and precision of robots with biological sensory mechanisms, can enhance the applicability of drones in navigation, gas sensing, and disaster response.
Technological advances have led to the development of drones with diverse applications, ...
Do seizures in newborns increase children’s risk of developing epilepsy?
2025-02-19
Seizures in newborns are one of the most frequent acute neurological conditions among infants admitted to neonatal care units. A study published in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology indicates that newborns experiencing such neonatal seizures face an elevated risk of developing epilepsy.
For the study, investigators analyzed data on all children born in Denmark between 1997 and 2018, with the goal of comparing the risk of epilepsy in children with and without neonatal seizures.
Among 1,294,377 children, the researchers identified 1,998 who experienced neonatal seizures. The cumulative risk of epilepsy was 20.4% among children with neonatal seizures compared with 1.15% among children ...
Does the brain produce estrogen to control appetite?
2025-02-19
Although a woman’s ovaries produce the most estrogen, various types of estrogen are also synthesized throughout different tissues in the body, including the brain’s neurons. New research in The FEBS Journal indicates that such neuroestrogens help suppress appetite.
Knowing that the enzyme aromatase is important for the production of estrogens, investigators depleted or knocked out the gene encoding aromatase in mice, so that the animals were unable to synthesize estrogens in a systemic or body-wide manner. These mice demonstrated increased food intake and body weight compared with their aromatase-expressing counterparts. Restoring aromatase expression specifically ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] Groundbreaking study reveals how topology drives complexity in brain, climate, and AIStudy introduces higher-order topological dynamics, unlocking new frontiers in science and technology